2 i/o ports, Toshiba, H<---------- h-i------------^l-f------------^1 – Toshiba TMP87CP24AF User Manual
Page 53
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
TOSHIBA
TMP87CM24A/P24A
2.2
I/O Ports
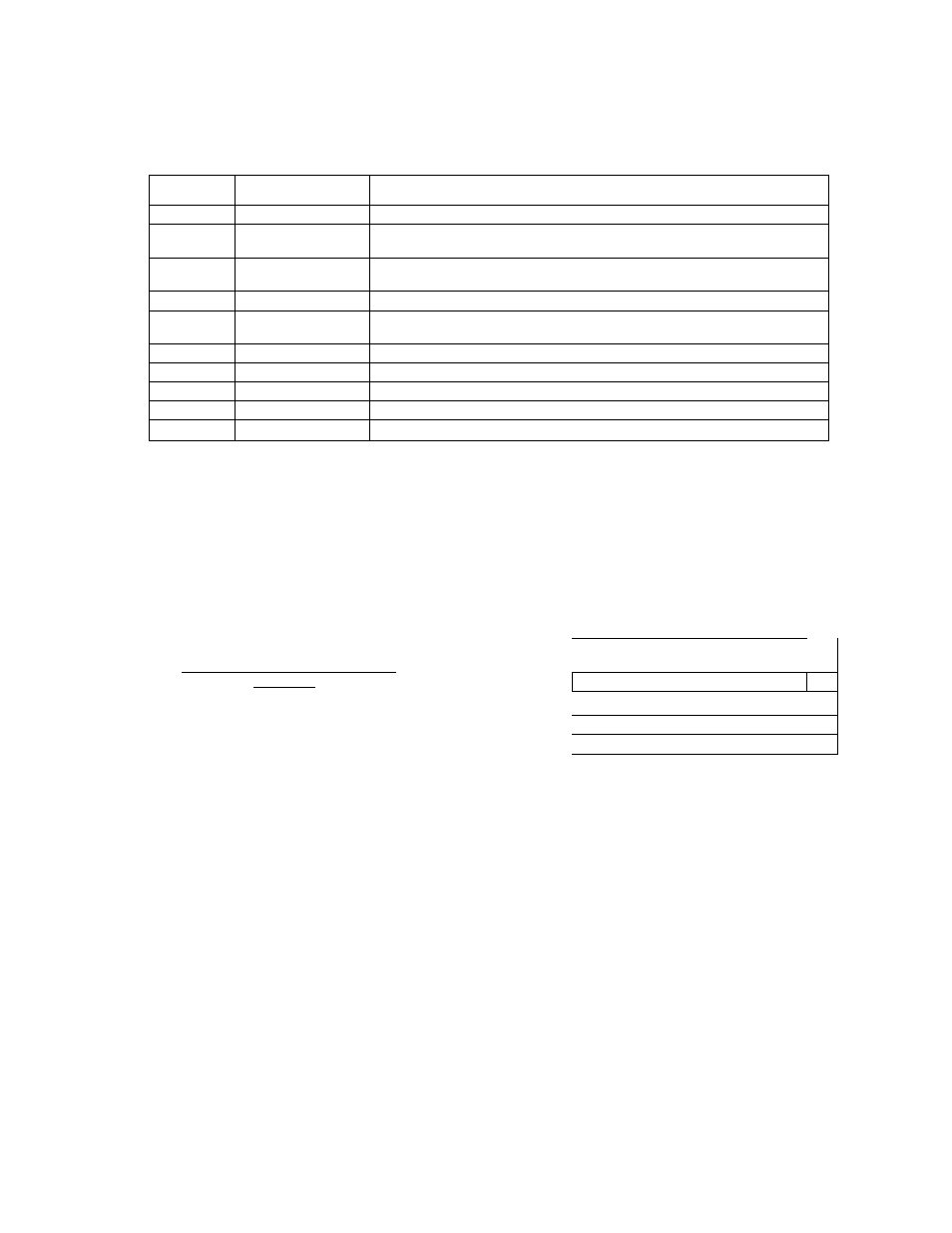
The TMP87CM24A/P24A have 10 parallel input/output ports (69 pins) each as follows:
Primary Function
Secondary Functions
Port PO
8
-bit I/O port
Port PI
8
-bit I/O port
External interrupt input, timer/counter input/output, and divider
output
Port P2
3-bit I/O port
Low-frequency resonator connections, external interrupt input, and
STOP mode release signal input
Port P3
6
-bit I/O port
Port P4
8
-bit I/O port
Serial interface, external interrupt input, timer/counter
input/output
Port P5
8
-bit I/O port
Analog input
Port P
6
8
-bit I/O port
Segment Output
Port P7
8
-bit I/O port
Segment Output
Port P
8
8
-bit I/O port
Segment Output
Port P9
4-bit I/O port
Segment Output
Each
output
port
contains
a
latch,
which
holds
the
output
data.
All
input
ports
do
not
have
latches,
so
the
external
input
data
should
either
be
held
externally
until
read
or
reading
should
be
performed
several times before processing. Figure 2-2 shows input/output timing examples.
External
data
is
read
from
an
I/O
port
in
the
SI
state
of
the
read
cycle
during
execution
of
the
read
instruction.
This
timing
can
not
be
recognized
from
outside,
so
that
transient
input
such
as
chattering
must be processed by the program.
Output
data
output
changes
in
the
S2
state
of
the
write
cycle
during
execution
of
the
instruction
which
writes to an I/O port.
Fetch cycle Fetch cycle Read cycle
h<---------- H-i------------^l-f------------^1
Instruction SO S1 S2 S3 SO S1 S2 S3 SO S1 S2 S3
execution
cycle —
Input strobe—
Data input
Fetch cycle Fetch cycle Write cycle
E)jc.: L,D
jx)
J____ I___ I___ I___ L
n.
execution
cycle"
Output latch__.
pulse
Data output
^ ^^
so SI S2 S3 SO SI S2 S3 SO SI S2 S3
___ 1 1 ...................................................
n
Old
X
New
(a) Input Timing
(b) Output Timing
Note: The positions of the read and write cycles may vary, depending on the instruction.
Figure 2-2. Input/Output Timing (Example)
When
reading
an
I/O
port
except
programmable
I/O
ports,
whether
the
pin
input
data
or
the
output
latch
contents are read depends on the instructions, as shown below:
(1)
Instructions that read the output latch contents
© XCH r, (src)
(D LD
(pp). b, CF
@ CLR/SET/CPL (src).b
© ADD/ADDC/SUB/SUBB/AND/OR/XOR (src), n
© CLR/SET/CPL (pp).g
© (src) side of ADD/ADDC/SUB/SUBB/AND/OR/XOR (src), (HL)
@ LD
(src).b,CF
(2)
Instructions that read the pin input data
® Instructions other than the above (1)
© (HL) side of ADD/ADDC/SUB/SUBB/AND/OR/XOR (src),(HL)
3
-
24-53
2002
-
10-03
