6 program status word (psw), 1 register bank selector (rbs), 2 flags – Toshiba TMP87CP24AF User Manual
Page 13: Toshiba
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
TOSHIBA
TMP87CM24A/P24A
1.6
Program Status Word (PSW)
The
program
status
word
(PSW)
consists
of
a
register
bank
selector
(RBS)
and
four
flags,
and the
PSW is
assigned to address OOBF
h
in the SFR.
The
RBS
can
be
read
and
written
using
the
memory
access instruction
(e.g.
[LD
A,
(003FH)],
[LD
(OOBFH),
A],
however
the
flags
can
only
be
read.
When
writing
to
the
PSW,
the
change
specified
by
the
instruction
is
made
without
writing
data
to
the
flags.
For
example,
when
the
instruction
[LD
(OOBFH),
OSH]
is
executed, "5" is written to the RBS and the JF is set to "1", but the other flags are not affected.
[PUSH PSW] and [POP PSW] are the PSW access instructions.
1.6.1 Register Bank Selector (RBS)
The register bank selector (RBS) is a 4-bit register used to
select
general-purpose
register
banks.
For
example,
when
RBS = 2, bank 2 is currently selected. During reset, the RBS
is initialized to "0".
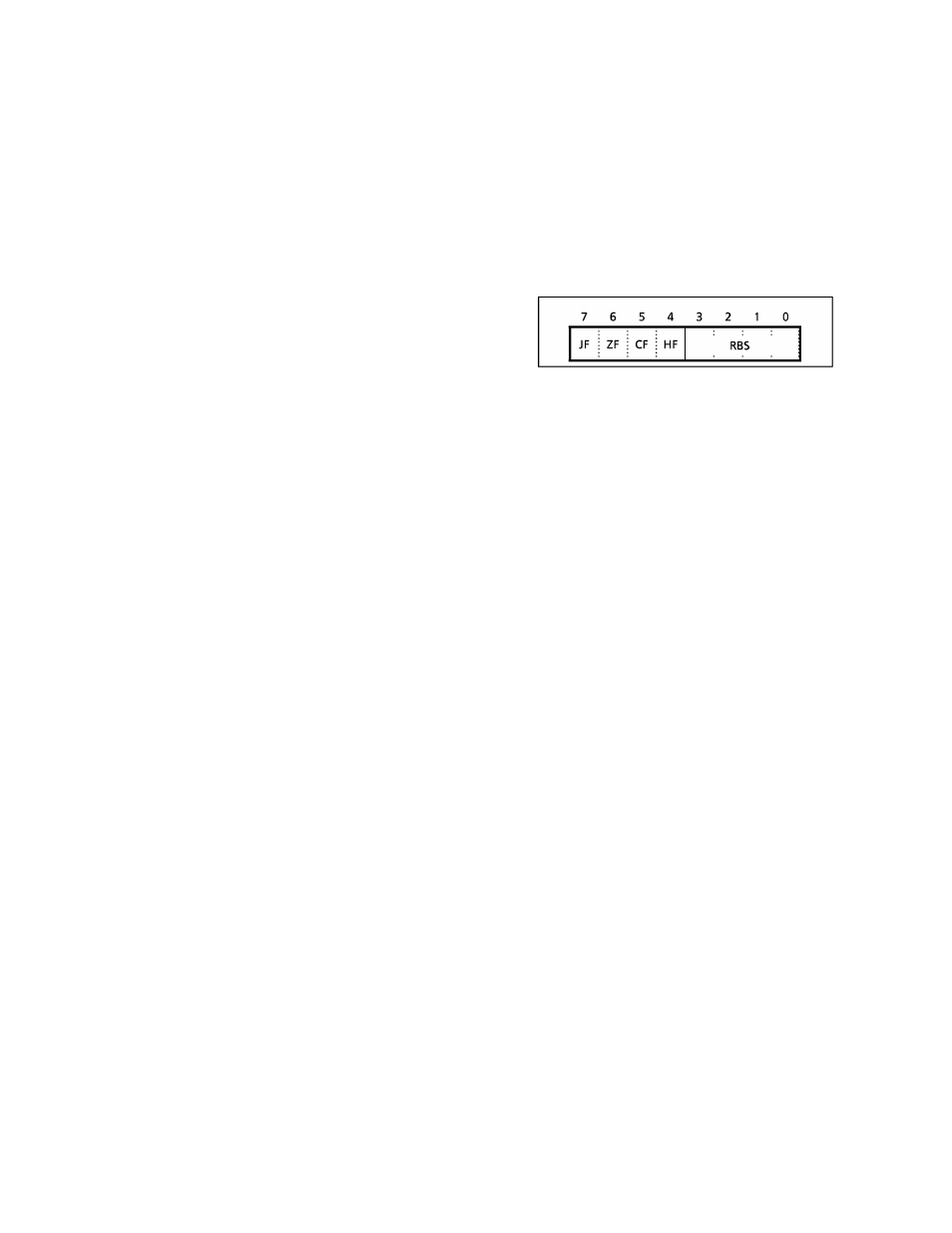
Figure 1-6. PSW (Flags, RBS) Configuration
1.6.2 Flags
The flags are configured with the upper 4 bits : a zero flag, a carry flag, a half carry flag and a jump status
flag.
The
flags
are
set
or
cleared
under
conditions
specified
by
the
instruction.
These
flags
except
the
half carry flag are used as jump condition "cc" for conditional jump instructions [JR cc, $ + 2 + d]/[JRS cc,
$ + 2 + d]. After reset, the jump status flag is initialized to "1", other flags are not affected.
(1) Zero flag (ZF)
The ZF is set to "1" if the operation result or the transfer data is OO
h
(for 8-bit operations and data
transfers)/0000H
(for 16-bit operations); otherwise the ZF is cleared to
"0".
During the bit manipulation instructions [SET, CLR, and CPL], the ZF is set to "1" if the contents of the
specified bit is "0"; otherwise the ZF is cleared to "0".
This
flag
is
set
to
"1"
when
the
upper
8
bits
of
the
product
are
OO
h
during
the
multiplication
instruction
[MUL],
and
when
OO
h
for
the
remainder
during
the
division
instruction
[DIV];
otherwise
it
is cleared to "0".
(2)
Carry flag (CF)
The CF is set to "1" when a carry out of the MSB (most significant bit) of the result occurred during
addition
or
when
a
borrow
into
the
MSB
of
the
result
occurred
during
subtraction;
otherwise
the
CF
is cleared to "0". During division, this flag is set to "1" when the divisor is
OO
h
(divided by zero error),
or
when
the
quotient
is
IOO
h
or
higher
(overflow
error);
otherwise
it
is
cleared.
The
CF
is
also
affected
during
the
shift/rotate
instructions
[SHLC,
SHRC,
ROLC,
and
RORC].
The
data
shifted
out
from a register is set to the CF.
This flag isalsoa 1-bit register(a boolean accumulator) for the bit manipulation instructions.
Set/clear/complement are possible with the CF manipulation instructions.
Examplel : Bit manipulation (The result of exclusive-OR between bit 5 content of address
0?
h
and
bit 0 content of address
9A
h
is written to bit 2 of address 01 h
)
LD
CF, (0007H).5
; (0001
h
)2 {0007
h
)
s
V
(009A
h
)
o
XOR
CF, (009AH). 0
LD
(0001H).2, CF
(3)
Half carry flag (HF)
The HF is set to "1" when a carry occurred between bits 3 and 4 of the operation result during an 8-
bit
addition,
or
when
a
borrow
occurred
from
bit
4
into
bit
3
of
the
result
during
an
8-bit
subtraction;
otherwise
the
HF
is
cleared
to
"0".
This
flag
is
useful
in
the
decimal
adjustment
for
BCD
operations (adjustments using the [DAA r], or [DAS r] instructions).
3
-
24-13
2002
-
10-03
