3 stand-by controller, Toshiba – Toshiba TMP87CP24AF User Manual
Page 18
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
TOSHIBA
TMP87CM24A/P24A
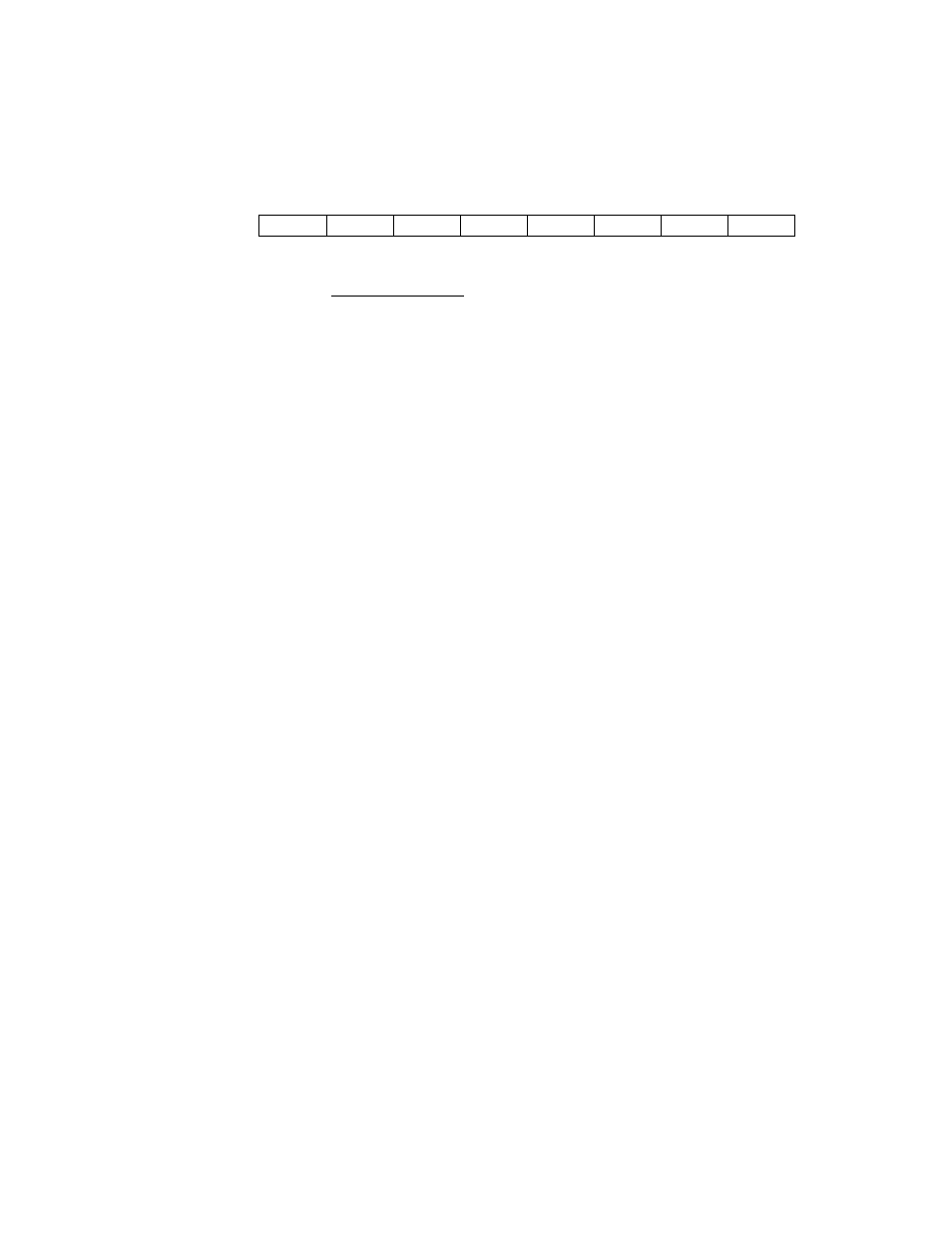
1/fc or 1/fs [s]
Main System Clock
1
_
State
SO
SI
S2
S3
SO
SI
S2
S3
-------Machine cycle-------------
0.5//S
atfc=8MHz
122 //s at fs = 32.768 kHz
Figure 1-13. Machine Cycle
1.8.3 Stand-by Controller
The
stand-by
controller
starts
and
stops
the
oscillation
circuits
for
the
high-frequency
and
low-frequency
clocks,
and
switches
the
main
system
clock.
There
are
two
operating
modes:
single-clock
and
dual-clock.
These modes are controlled by the system control registers (SYSCR1, SYSCR2).
Figure 1-14 shows the operating mode transition diagram and Figure 1-15 shows the system control
registers. Either the single-clock or the dual-clock mode can be selected by an option during reset.
TMP87PP24 is only fixed on the single-clock after reset release. When using the dual-clock mode, turn on
the oscillation circuits for low-frequency clocks at the beginning of program.
(1) Single-dock mode
Only
the
oscillation
circuit
for
the
high-frequency
clock
is
used,
and
P21
(XTIN)
and
P22
(XTOUT)
pins
are
used
as
input/output
ports.
As
main
system
clock
is
mode
from
high
frequency
clock,
in
the
single-clock mode, the machine cycle time is4/fc [s] (0.5
jjs
at fc = 8 MHz).
© NORMAL1 mode
In
this
mode,
both
the
CPU
core
and
on-chip
peripherals
operate
using
the
high-frequency
clock.
In
the
case
where
the
single-clock
mode
has
been
selected
as
an
option,
the
TMP87CM24A/P24A are placed in this mode after reset.
® IDLE1 mode
In
this
mode,
the
internal
oscillation
circuit
remains
active,
and
the
CPU
and
the
watchdog
timer
are
halted;
however,
on-chip
peripherals
remain
active
(operate
using
the
high-
frequency
clock).
IDLE1
mode
is
started
by
setting
IDLE
bit
in
the
system
control
register
2
(SYSCR2),
and
IDLE1
mode
is
released
to
NORMAL1
mode
by
an
interrupt
request
from
on-
chip
peripherals
or
external
interrupt
inputs.
When
IMF
(interrupt
master
enable
flag)
is
"1"
(interrupt
enable),
the
execution
will
resume
upon
acceptance
of
the
interrupt,
and
the
operation
will
return
to
normal
after
the
interrupt
service
is
completed.
When
IMF
is
"0"
(interrupt
disable),
the
execution
will
resume
with
the
instruction
which
follows
IDLE
mode
start instruction.
(3)
STOP1 mode
In
this
mode,
the
internal
oscillation
circuit
is
turned
off,
causing
all
system
operations
to
be
halted.
The
internal
status
immediately
prior
to
the
halt
is
held
with
the
lowest
power
consumption
during
this
mode.
The
output
status
of
all
output
ports
can
be
set
to
either
output hold or high-impedance under software control.
STOP1
mode
is
started
by
setting
STOP
bit
in
the
system
control
register
1
(SYSCR1),
and
STOP1
mode
is
released
by
an
input
(either
level-sensitive
or
edge-sensitive
can
be
programmably
selected)
to
the
STOP
pin.
After
the
warming-up
period
is
completed,
the
execution resumes with the next instruction which follows the STOP mode start instruction.
3
-
24-18
2002
-
10-03
