9 interrupt controller, Toshiba, Imf<-0 – Toshiba TMP87CP24AF User Manual
Page 30
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
TOSHIBA
TMP87CM24A/P24A
1.9
Interrupt Controller
The
TMP87CM24A/P24A
each
have
a
total
of
14
interrupt
sources:
5
externals
and
9
internals.
Nested
interrupt
control
with
priorities
is
also
possible.
Two
of
the
internal
sources
are
pseudo
non-maskable
interrupts; the remainder are all maskable interrupts.
Interrupt
latches
(IL)
that
hold
the
interrupt
requests
are
provided
for
interrupt
sources.
Each
interrupt
vector is independent.
The
interrupt
latch
is
set
to
"1"
when
an
interrupt
request
is
generated
and
requests
the
CPU
to
accept
the
interrupt.
The
acceptance
of
maskable
interrupts
can
be
selectively
enabled
and
disabled
by
the
program
using
the
interrupt
master
enable
flag
(IMF)
and
the
individual
interrupt
enable
flags
(EF).
When
two
or
more
interrupts
are
generated
simultaneously,
the
interrupt
is
accepted
in
the
highest
priority order as determined by the hardware. Figure 1-22 shows the interrupt controller.
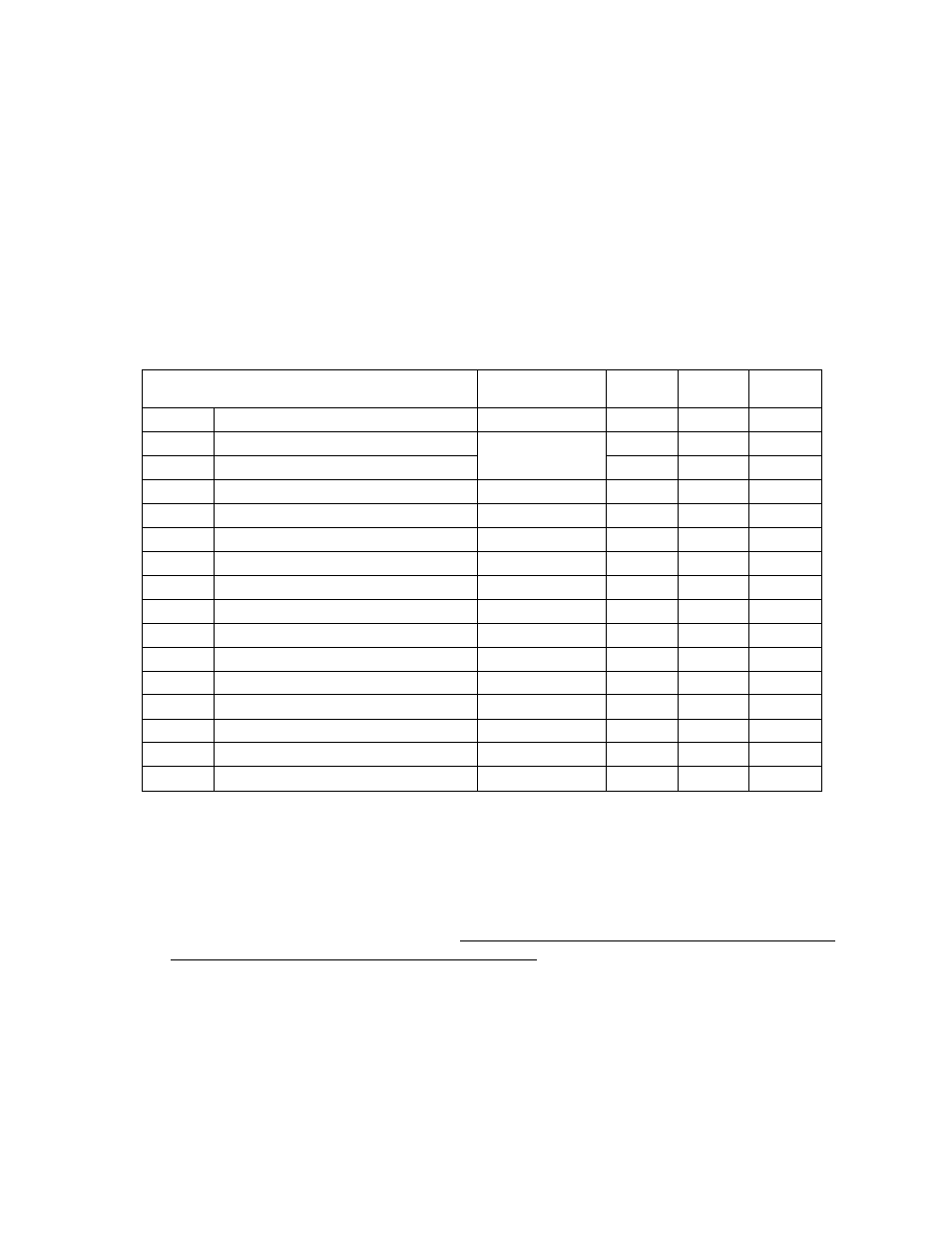
Table 1-2. Interrupt Sources
Interrupt Source
Enable Condition
Interrupt
Latch
Vector Table
Address
Priority
Internal/
External
(Reset)
Non-Maskable
—
FFFE
h
High 0
Internal
INTSW
(Software interrupt)
Pseudo
—
FFFC
h
1
Internal
INTWDT
(Watchdog Timer interrupt)
non-maskable
IL
2
FFFA
h
2
External
INTO
(External interrupt 0)
IMF= 1, INT0EN = 1
IL
3
FFF
8
h
3
Internal
INTTC1
(16-bitTCI interrupt)
IMF- EF
4
= 1
IL
4
FFF
6
h
4
External
INTI
(External interrupt 2)
IMF- EFs= 1
IL
5
FFF4
h
5
Internal
INTTBT
(Time Base Timer interrupt)
IMF- EFe= 1
iLe
FFF2
h
6
External
INT2
(External interrupt 2)
IMF- EFy= 1
IL
7
FFFO
h
7
Internal
INTTC3
(
8
-bit TC3 interrupt)
IMF- EFs= 1
ILs
FFEE
h
8
Internal
INTSI01
(Serial Interface 1 interrupt)
IMF- EFg= 1
IL
9
FFEC
h
9
Internal
INTTC5
(
8
-bit TC5 interrupt)
IMF- EFio= 1
IL
10
FFEA
h
10
External
INT3
(External interrupts)
IMF- EF
11
= 1
IL
11
FFE
8
h
11
Reserved
IMF- EF
i
2
= 1
IL
12
FFE
6
h
12
Internal
INTSI02
(Serial Interface 2 interrupt)
IMF- EFi
3
= 1
IL
13
FFE4
h
13
Internal
INTTC2
(16-bit TC2 interrupt)
IMF- EF
i
4
= 1
I L
i
4
FFE2
h
14
External
INT5
(External interrupt 5)
IMF- EF
i
5
= 1
I L
i
5
FFEO
h
Low 15
(
1
)
Interrupt Latches
(IL 15to
2
)
Interrupt
latches
are
provided
for
each
source,
except
for
a
software
interrupt.
The
latch
is
set
to
"1"
when
an
interrupt
request
is
generated,
and
requests
the
CPU
to
accept
the
interrupt.
The
latch
is
cleared
to
"0"
just
after
the
interrupt
is
accepted.
All
interrupt
latches
are
initialized
to
"0"
during
reset.
The
interrupt
latches
are
assigned
to
addresses
OOBC
h
and
OOBD
h
in
the
SFR.
Each
latch
can
be
cleared
to
"
0
"
individually
by
an
instruction;
however,
the
read-mod
ify-write
instruction
such
as
bit
manipulation
or
operation
instructions
cannot
be
used
(Do
not
clear
the
IL2
for
a
watchdog
timer
interrupt
to
"0").
Thus,
interrupt
requests
can
be
cancelled
and
initialized
by
the
program.
Note
that interrupt latches cannot be set to "
1
" by any instruction.
The
contents
of
interrupt
latches
can
be
read
out
by
an
instruction.
Therefore,
testing
interrupt
requests by software is possible.
Example 1 : Clears interrupt latches
Dl
LDW
El
(IL), 1110100000111111B
IMF<-0
IL
i
2# ILiotolL5<—0
IMF<-1
3
-
24-30
2002
-
10-03
