3 basic principles, 1 wireless technology – JUMO 902931 Wtrans Receiver with Wireless Data Transmission Operating Manual User Manual
Page 13
13
3 Basic principles
3.1
Wireless technology
The characteristic framework conditions for each transmission system include the available
band width in the electro-magnetic spectrum and the maximum admissible transmission capac-
ity. These parameters define the channel capacity.
The main selection criteria for the frequency range to be used include the requirement of a long
range, interference immunity, and the option of applying a customized transmission protocol in
a public frequency band. The focus when selecting the possible communication technologies
is placed on minimizing the size of the transmitting and receiving circuit as well as the power
consumption, on enhancing the transmission safety and the transmission stability, and on sav-
ing costs for the technology involved. Using a wireless connection essentially results in lower
costs, greater flexibility and mobility, and easier handling.
Taking into account the current applicable legislative texts and the available standards and in-
dustry standards, a wireless solution without a generally specified protocol has been selected
for use of the Wtrans system on the 868.4 MHz radio frequency (Europe) or 915 MHz radio fre-
quency (America, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand).
In certain areas, there are strict regulations that apply for this industrial radio frequency with
regard to duty cycle, channel distribution, and transmission power. The various subdivisions
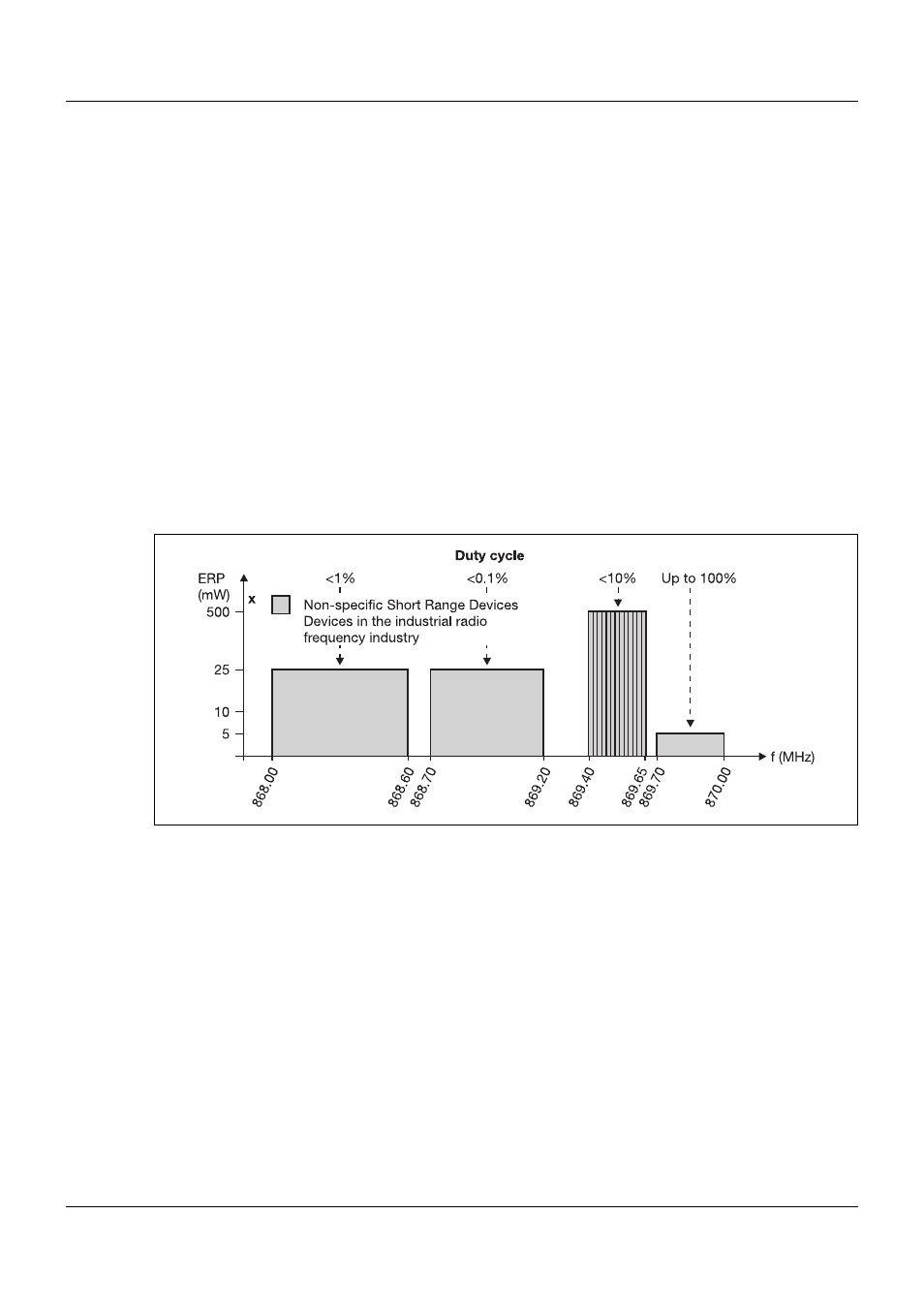
within this frequency band are shown in Figure 2 below.
Figure 2:
Subdivision of the 868 MHz frequency band
The ERP power value (ERP: equivalent radiated power), which is plotted on the Y-axis, repre-
sents the permitted transmission power in relation to a lambda/2 dipole gain. The transmission
power is only generated for a very short period while using the duty cycle, during the transmis-
sion pulse with a small pulse width.
The duty cycle in percent indicates the duration of a transmitter's transmissions based on 1
hour. The overall transmission time can be divided across several transmission intervals. The
duty cycle thus specifies the ratio between the transmission time and the overall time, and is
specified in percent.
The duty cycle is also called the pulse-to-pause ratio or mark-to-space ratio.
