Chapter 4: electrical installation – Horner APG XL4 OCS User Manual
Page 23
MAN0964-01-EN
CH.4
June 29, 2012
Page 23 of 122
CHAPTER 4: ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
Note: The datasheet is the first document you need to refer to for model-specific information
related to XL4 OCS models such as pin-outs, jumper settings, and other key installation
information. Visit our website to obtain datasheets, user documentation, and updates.
4.1
Grounding Definition
Ground: The term Ground is defined as a conductive connection between a circuit or piece of equipment
and the earth. Grounds are fundamentally used to protect an application from harmful interference
causing either physical damage such as by lightning or voltage transients or from circuit disruption often
caused by radio frequency interference (RFI).
4.2
Ground Specifications
Ideally, a ground resistance measurement from equipment to earth ground is 0 ohms. In reality it typically
is higher. The U.S. National Electrical Code (NEC) states the resistance to ground shall not exceed
twenty-five (25) ohms. Horner APG recommends less than fifteen (15) ohms resistance from our
equipment to ground. Resistance greater than twenty-five (25) ohms can cause undesirable or harmful
interference to the device.
4.3
How to Test for Good Ground
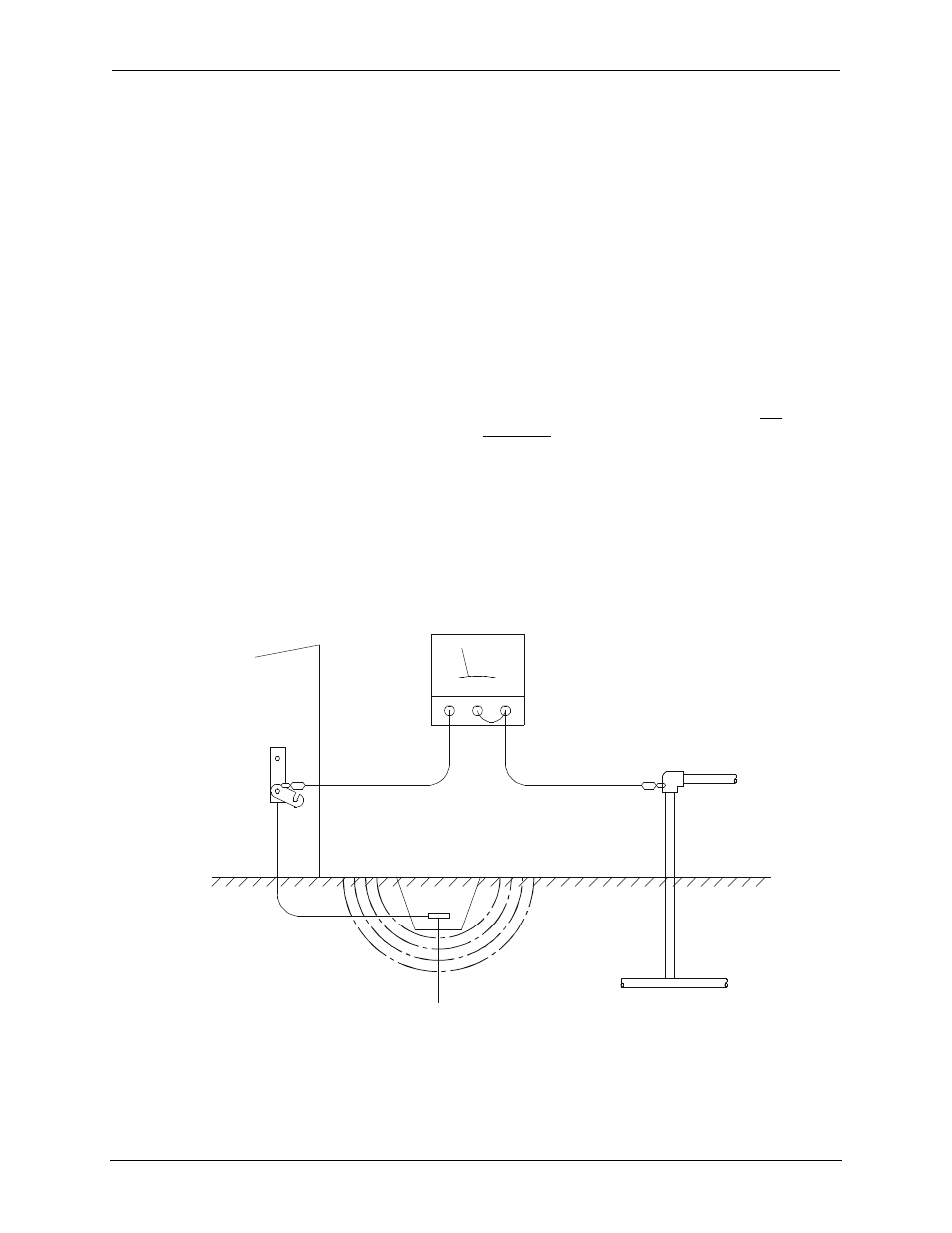
In order to test ground resistance, a Ground Resistance Tester must be used. A typical Ground
Resistance Meter Kit contains a meter, two or three wire leads, and two ground rods. Instructions are
supplied for either a two-point or three-point ground test.
Figure 4.1 shows a two-point ground connection test.
Figure 4.1 – Two-Point Ground Connection Test
METAL WATER PIPE OR
OTHER GOOD GROUND
GROUND ROD
GROUND
DISCONNECTED
FROM SERVICE
GROUND RESISTANCE METER
