2 how ospf works, 3 interfaces and virtual links – ZyXEL Communications XGS-4728F User Manual
Page 274
Chapter 32 OSPF
XGS-4728F User’s Guide
274
The following table describes the four classes of OSPF routers.
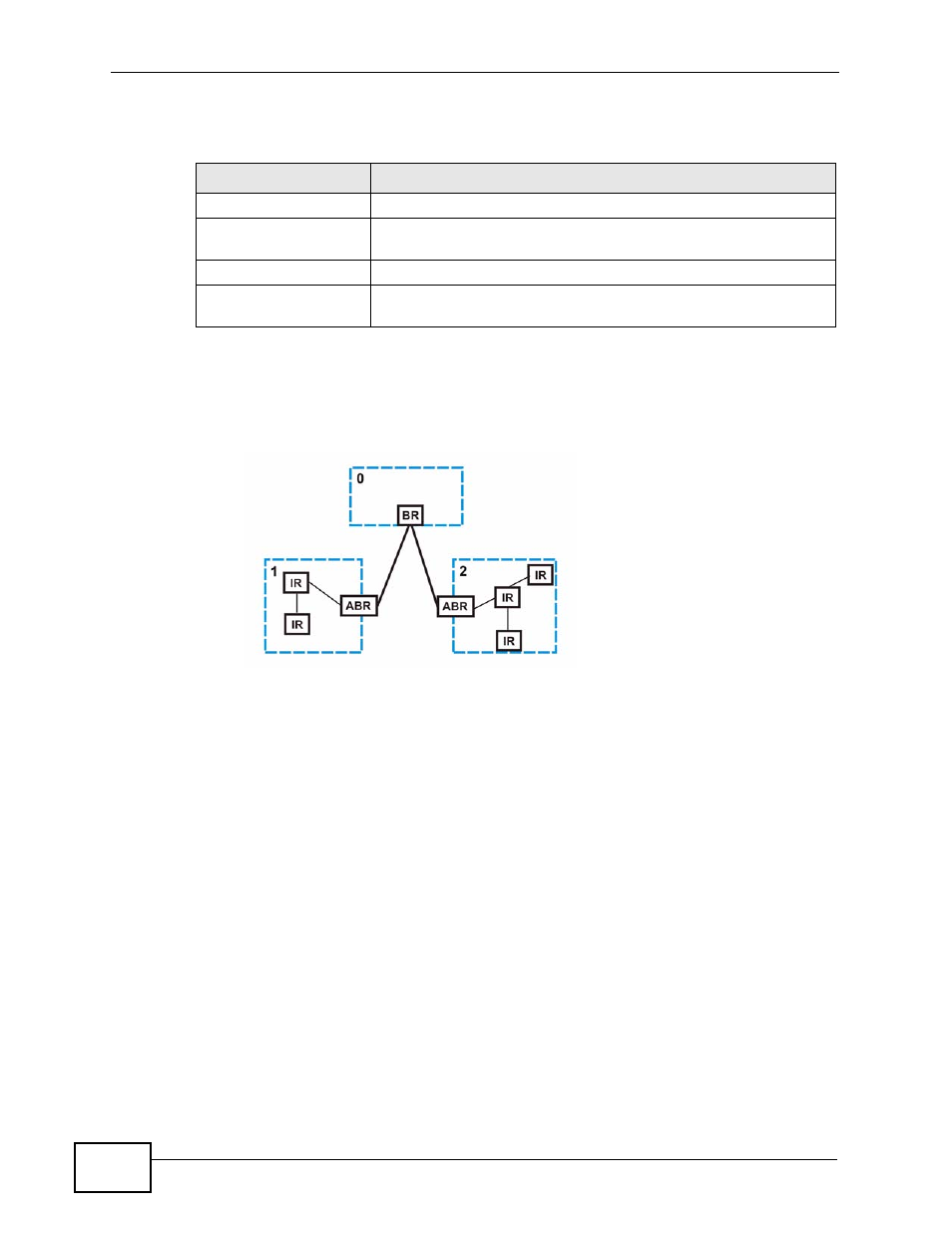
The following figure depicts an OSPF network example. The backbone is area 0
with a backbone router. The internal routers are in area 1 and 2. The area border
routers connect area 1 and 2 to the backbone.
Figure 146 OSPF Network Example
32.1.2 How OSPF Works
Layer 3 devices exchange routing information to build a synchronized link state
database within the same AS or area. The link state database contains records of
router IDs, their associated links and path costs. Each device can then use the link
state database and Dijkstra algorithm to compute the least cost paths to network
destinations.
Layer 3 devices build a synchronized link state database by exchanging Hello
messages to confirm which neighbor (layer 3) devices exist and then they
exchange database descriptions (DDs) to create the link state database. The link
state database is constantly updated through LSAs (Link State Advertisements).
32.1.3 Interfaces and Virtual Links
An OSPF interface is a link between a layer 3 device and an OSPF network. An
interface has state information, an IP address and subnet mask associated with it.
Table 95 OSPF: Router Types
TYPE
DESCRIPTION
Internal Router (IR)
An Internal or intra-area router is a router in an area.
Area Border Router
(ABR)
An Area Border Router connects two or more areas.
Backbone Router (BR)
A backbone router has an interface to the backbone.
AS Boundary Router
An AS boundary router exchanges routing information with
routers in other ASs.
