Assigning multiple strings, Assigning multiple strings 416, Table 15-2 – Nortel Networks WEB OS 212777 User Manual
Page 416: Real server content 416
Web OS 10.0 Application Guide
416
n
Chapter 15: Content Intelligent Switching
212777-A, February 2002
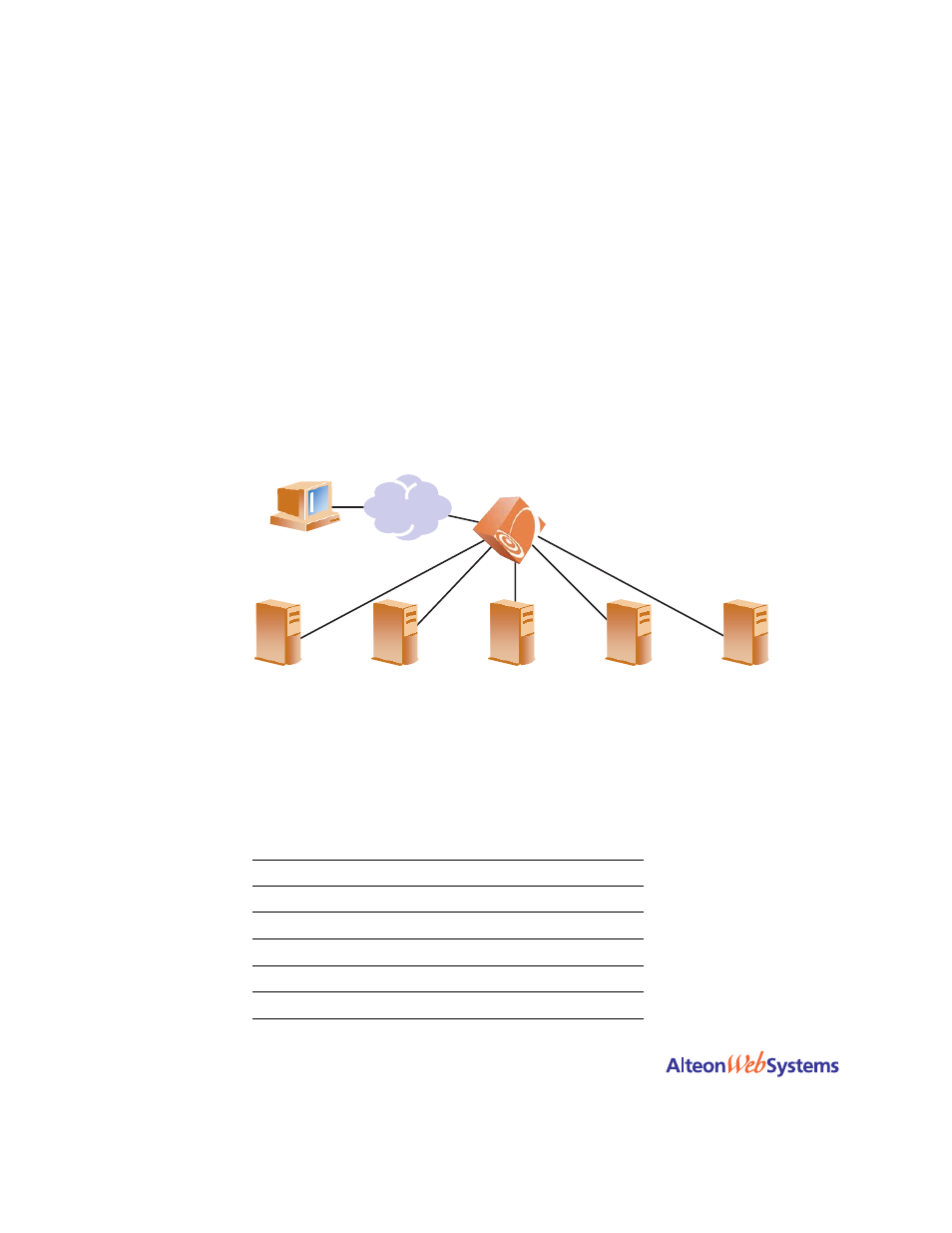
Assigning Multiple Strings
shows an example of a company providing content for two large customers: Cus-
tomers A and B. Customer A uses
www.a.com
as their domain name, and Customer B uses
www.b.com
.
The company has a limited number of public IP addresses and wishes to assign them on a very
conservative basis. As a result, the company implements virtual hosting by advertising a single
virtual server IP address that includes both customers’ Web sites. Additionally, the hosting
company assigns only one service (HTTP port 80) to support the virtual server.
The virtual hosting company wishes to maintain the flexibility to allow different types of con-
tent to be placed on different servers. To make most efficient use of their server resources, they
separate their servers into two groups, using their fastest servers to process dynamic content
(such as .cgi files) and their slower servers to process all static content (such as .jpg files).
Figure 15-8 Content Precedence Lookup Multiple Strings Example
To configure content precedence lookup for the example in
, the hosting company
groups all the real servers into one real server group even though different servers provide ser-
vices for different customers and different types of content. In this case, the servers are set up
for the following purpose:
Table 15-2 Real Server Content
Server
Customer
Content
Server 1
Customer A
Static .jpg files
Server 2
Customer A
Static .jpg files
Server 3
Customer A
Dynamic .cgi files
Server 4
Customer B
Static .jpg files
Server 5
Customer B
Dynamic .cgi files
Web Switch
Real Servers
Client
Internet
1
2
3
4
5
Host: www.a.com
URL: *.jpg
Host: www.a.com
URL: *.jpg
Host: www.a.com
URL: *.cgi
Host: www.b.com
URL: *.jpg
Host: www.b.com
URL: *.cgi
