How gslb works, How gslb works 291, Foo corp. california foo corp. denver client site – Nortel Networks WEB OS 212777 User Manual
Page 291
Web OS 10.0 Application Guide
Chapter 12: Global Server Load Balancing
n
291
212777-A, February 2002
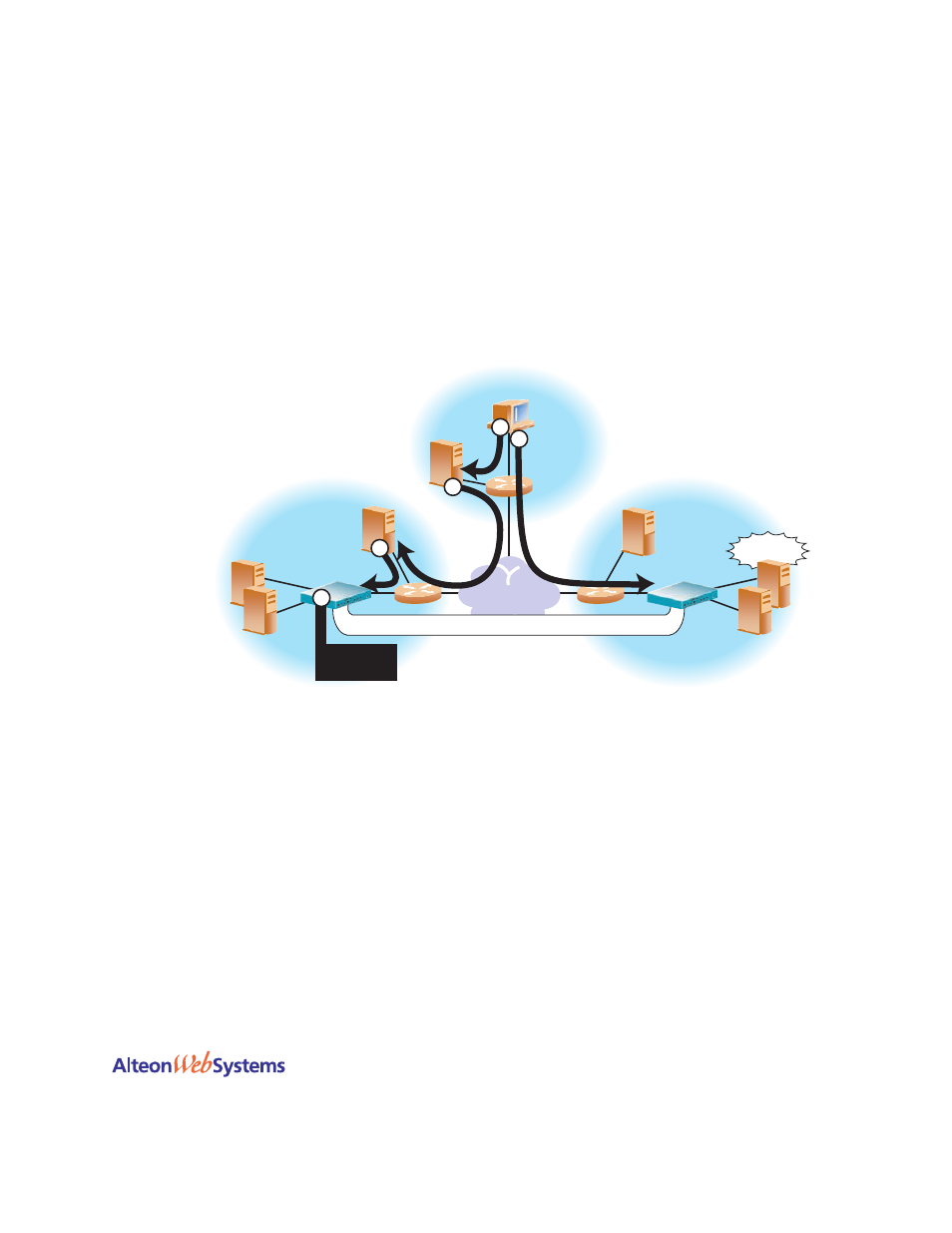
How GSLB Works
GSLB is based on the Domain Name System (DNS) and proximity by source IP address. In the
example in
, a client is using a browser to view the Web site for the Foo Corporation
at “www.foocorp.com.” The Foo Corporation has two Web sites: one in California, and one in
Denver, each with identical content and available services. Both Web sites have an Alteon Web
switch configured for GSLB. These switches are also configured as the Authoritative Name
Servers for “www.foocorp.com.”
Figure 12-1 DNS Resolution with Global Server Load Balancing
The DNS resolution for GSLB is described in detail in the following procedure:
1.
The client Web browser requests the “www.foocorp.com” IP address from the local DNS.
2.
Client’s DNS asks its upstream DNS, which in turn asks the next, and so on, until the
address is resolved.
Eventually, the request reaches an upstream DNS server that has the requested IP address
information on hand or the request reaches one of the Foo Corporation’s DNS servers.
3.
The Foo Corporation’s California DNS has been configured to use the local Web switch
with GSLB software as the authoritative name server for “www.foocorp.com.”
Internet
Foo Corp. California
Foo Corp. Denver
Client Site
DNS
DNS
Web
Servers
Web
Servers
DNS
Switches regularly exchange performance information
Web Switch
Web Switch
Best Service!
4
3
2
1
5
DNS response
lists best site's
IP address first
DNS
Request
HTTP
Request
