7 internal registers, 8 selecting peripherals vs. general purpose i/o, Internal registers -7 – Intel PXA255 User Manual
Page 37: Selecting peripherals vs. general purpose i/o -7
Intel® PXA255 Processor Developer’s Manual
2-7
System Architecture
2.7
Internal Registers
All internal registers are mapped in physical memory space on 32-bit address boundaries. Use
word access loads and stores to access internal registers. Internal register space must be mapped as
non-cacheable.
Byte and halfword accesses to internal registers are not permitted and yield unpredictable results.
Register space where a register is not specifically mapped is defined as reserved space. Reading or
writing reserved space causes unpredictable results.
The processor does not use all register bit locations. The unused bit locations are marked reserved
and are allocated for future use. Write reserved bit locations as zeros. Ignore the values of these bits
during reads because they are unpredictable.
2.8
Selecting Peripherals vs. General Purpose I/O
Most peripherals connect to the external pins through GPIOs. To use a peripheral connected
through a GPIO, the software must first configure the GPIO so that the desired peripheral is
connected to its pins. The default state of the pins is GPIO inputs.
To allocate a peripheral to a pin, disable the GPIO function for that pin, then map the peripheral
function onto the pin by selecting the proper alternate function for the pin. Some GPIOs have
multiple alternate functions. After a function is selected for a pin, all other functions are excluded.
For this reason some peripherals are mapped to multiple GPIOs, as shown in
Alternate Functions” on page 4-2
. Multiple mapping does not mean multiple instances of a
peripheral - only that the peripheral is connected to the pins in several ways.
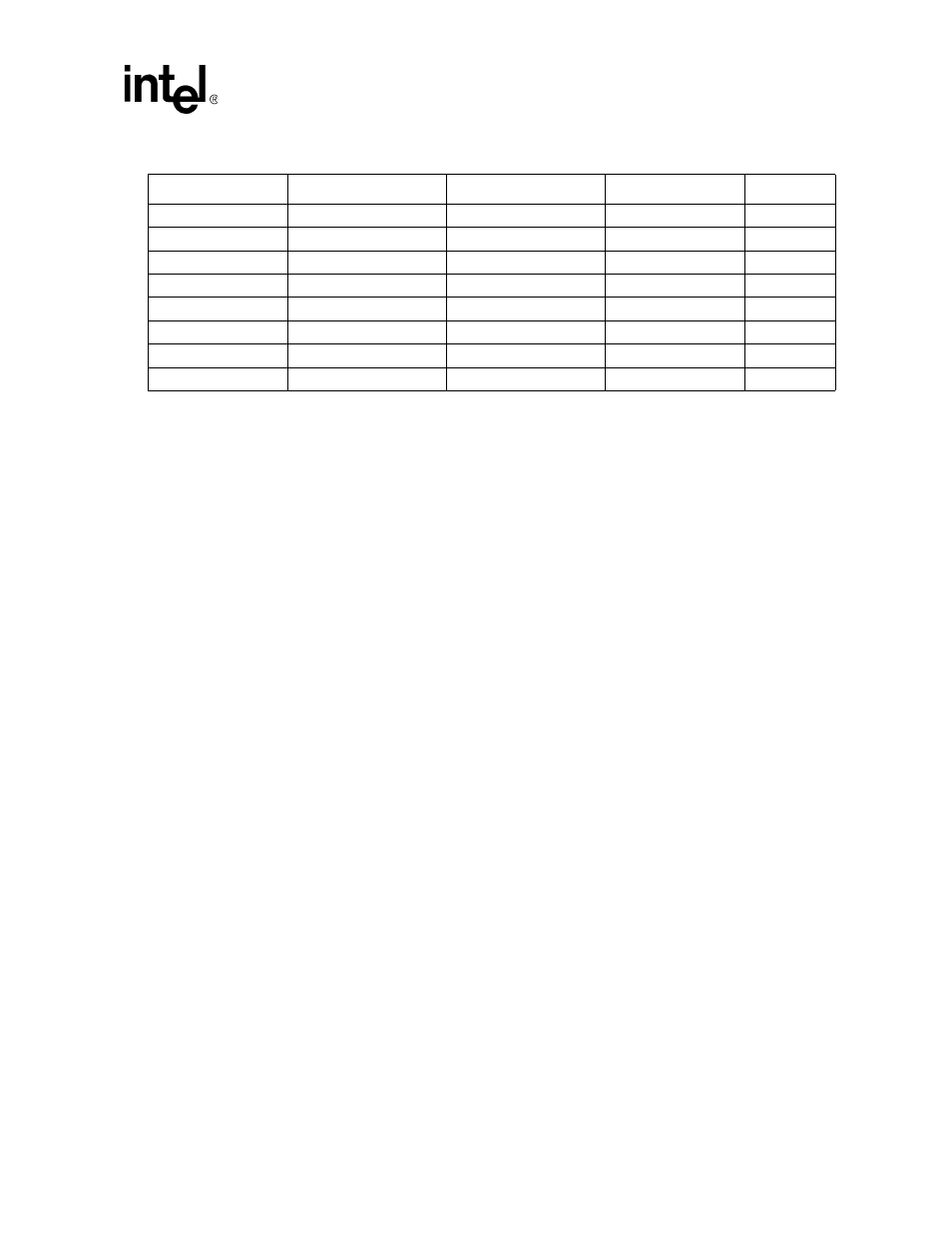
PWM
reset
reset
reset
reset
Interrupt Controller
reset
reset
reset
reset
GPIO
reset
reset
reset
reset
Power Manager
preserved
reset
reset
reset
SSP
reset
reset
reset
reset
NSSP
reset
reset
reset
reset
MMC
reset
reset
reset
reset
Clocks
preserved (except CP14)
preserved (except CP14)
reset (except OSCC)
reset
Table 2-4. Effect of Each Type of Reset on Internal Register State (Sheet 2 of 2)
Unit
Sleep Mode
GPIO Reset
Watchdog Reset
Hard Reset
