Executing a global write function – Yaskawa VS-616G5 Modbus Plus Communication Card User Manual
Page 34
7-2 Special MB+ Functions
Executing a Global Write Function
An MSTR global write function (operation code = 5) will write data to all slave devices on the
network. The global write function allows all slave devices on the MB+ network to receive the
data at the same time. When using a MB+ network, an MSTR write function can provide two or
three Data Area Registers.
The first word of global data written to drive is used by the drive to select the commands being
sent to it.
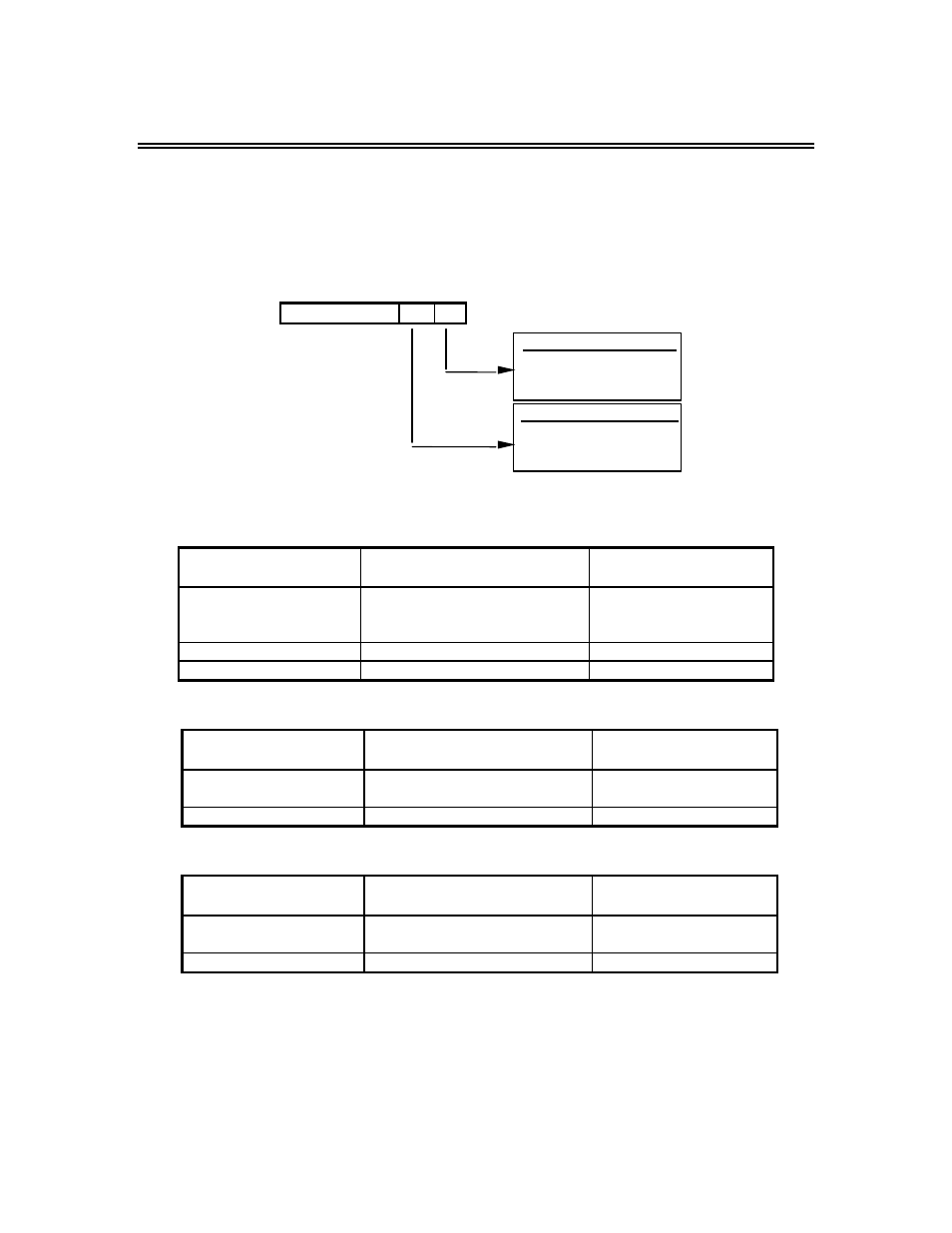
Bit Number
1
0
The following data are considered the three possible cases for Global Write Data:
Case 1: Using Operation Command and Frequency Reference
MSTR Function Data
Area (Register Offset)
Function
VS-616G5 Drive
Register Data Code
4X + 0
3
selecting both operation
command and
frequency reference
4X + 1
operation command
drive register (001h)
4X + 2
frequency reference
drive register (002h)
Case 2: Using Operation Command
MSTR Function Data
Area (Register Offset)
Function
VS-616G5 Drive
Register Data Code
4X + 0
1
selecting the
operation command
4X + 1
operation command
drive register (001h)
Case 3: Using Frequency Reference
MSTR Function Data
Area (Register Offset)
Function
VS-616G5 Drive
Register Data Code
4X + 0
2
selecting the frequency
reference
4X + 1
frequency reference
drive register (002h)
See Appendix A for additional information on data registers 001h and 002h.
An MSTR global write function will take one scan of the PLC ladder logic to complete. An
example of globally writing drive registers can be found in Chapter 9: Example #4 (write global
run/stop and frequency reference).
Operation Command
0 = disabled
1 = enabled
Frequency Reference
0 = disabled
1 = enabled
bit 0
bit 1
