Logging in through ssh – H3C Technologies H3C SecBlade LB Cards User Manual
Page 35
25
Step Command
Remarks
2.
Specify the source IPv4
address or source interface
for outgoing Telnet packets.
telnet client source { interface
interface-type interface-number | ip
ip-address }
Optional.
By default, no source IPv4 address
or source interface is specified.
The LB product automatically
selects a source IPv4 address.
3.
Exit to user view.
quit
N/A
4.
Use the LB product to log in to
a Telnet server.
•
Log in to an IPv4 Telnet server:
telnet remote-host
[ service-port ] [ vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ] [ source
{ interface interface-type
interface-number | ip
ip-address } ]
•
Log in to an IPv6 Telnet server:
telnet ipv6 remote-host [ -i
interface-type
interface-number ]
[ port-number ] [ vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ]
Use either command.
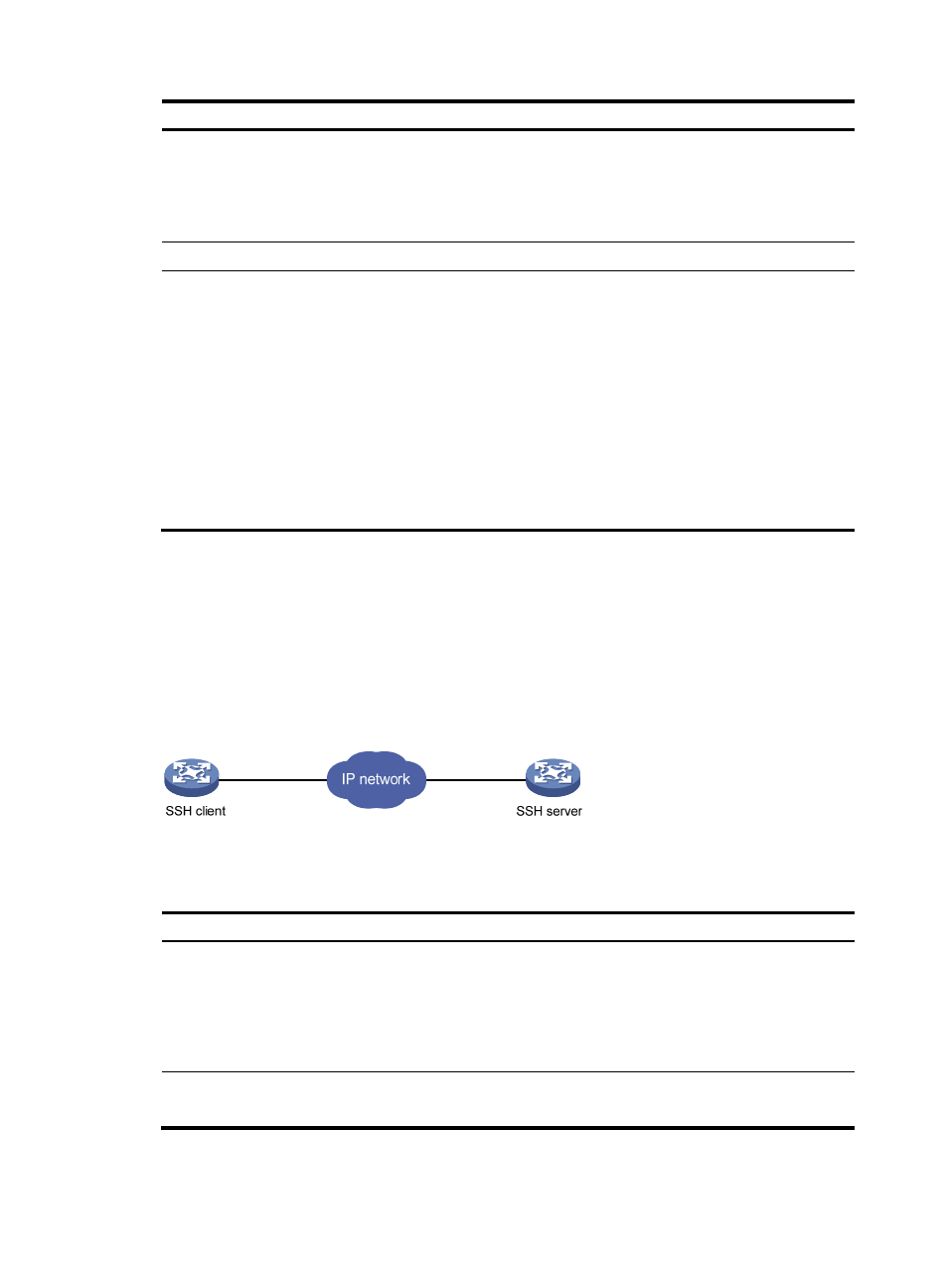
Logging in through SSH
SSH offers a secure approach to remote login. By providing encryption and strong authentication, it
protects devices against attacks such as IP spoofing and plain text password interception. You can use an
SSH client to log in to the LB product operating as an SSH server for remote management, as shown
in
. You can also use the LB product as an SSH client to log in to an SSH server.
Figure 21 SSH login diagram
shows the SSH server and client configuration required for a successful SSH login.
Table 7 SSH server and client requirements
Device role
Requirements
SSH server
Assign an IP address to a Layer 3 interface, and make sure the interface and
the client can reach each other. By default, the LB module has the IP address
192.168.0.1/24 configured for the interface GigabitEthernet 0/1 and
L1000-A has the same IP address configured for the interface GigabitEthernet
0/0.
Configure the authentication mode and other settings.
SSH client
If a host operates as an SSH client, run the SSH client program on the host.
Obtain the IP address of the Layer 3 interface on the server.
