Creating an rpf route – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 78
62
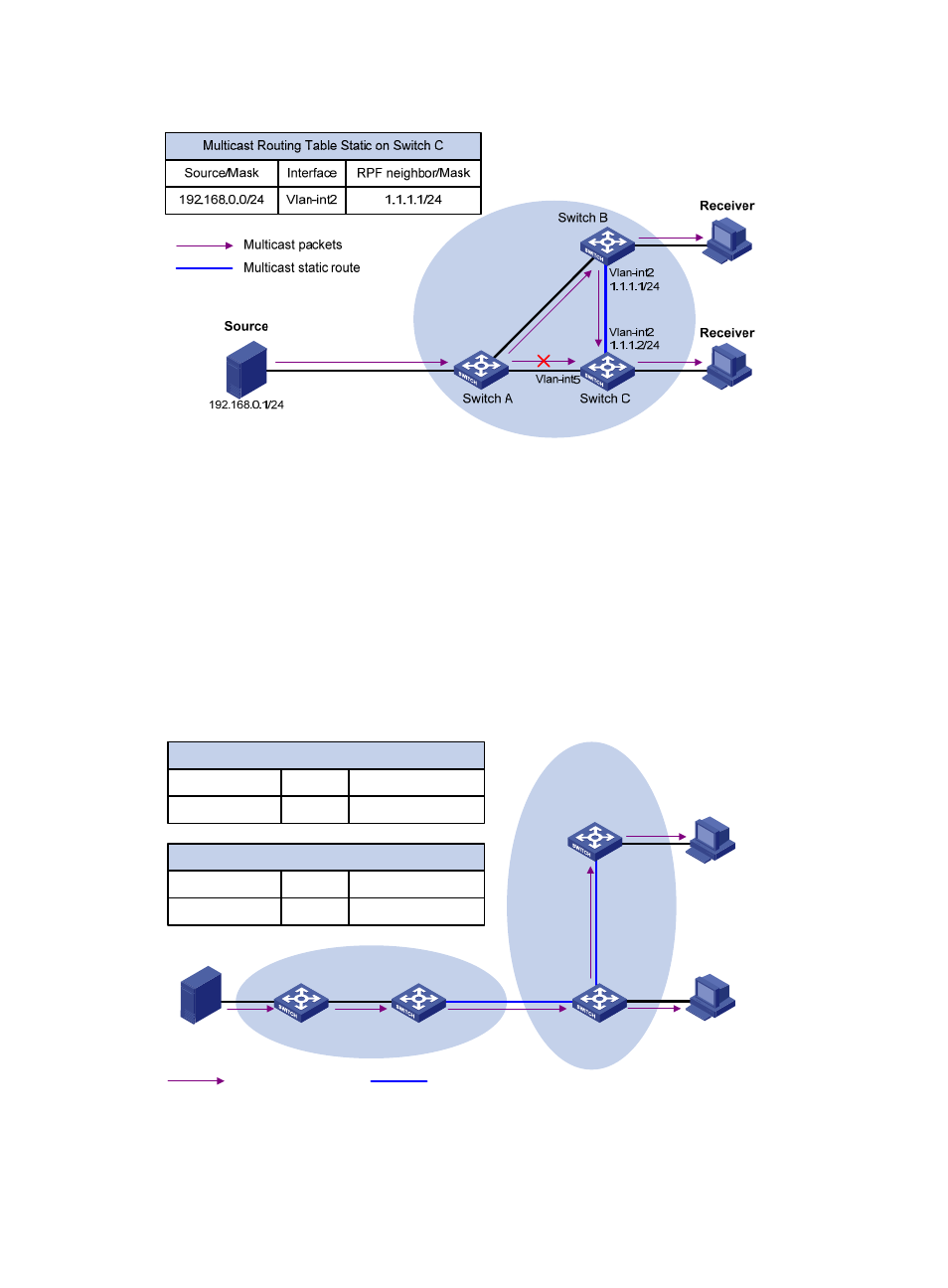
Figure 24 Changing an RPF route
As shown in
, when no static multicast route is configured, Switch C's RPF neighbor on the path
back to Source is Switch A. The multicast information from Source travels along the path from Switch A
to Switch C, which is the unicast route between the two routers; with a static multicast route configured on
Switch C and with Switch B as Switch C's RPF neighbor on the path back to Source, the multicast
information from Source travels from Switch A to Switch B and then to Switch C.
Creating an RPF route
When a unicast route is blocked, multicast traffic forwarding might be stopped due to lack of an RPF
route. By configuring a static multicast route for a given multicast source, you can create an RPF route so
that a multicast routing entry is created to guide multicast traffic forwarding regardless of whether a
unicast route is available.
Figure 25 Creating an RPF route
As shown in
, the RIP domain and the OSPF domain are unicast isolated from each other.
When no static multicast route is configured, the hosts (Receivers) in the OSPF domain cannot receive the
multicast packets that the multicast source (Source) sent in the RIP domain. After you configure a static
Vlan-int2
1.1.1.2/24
Vlan-int5
1.1.1.1/24
Vlan-int5
2.2.2.2/24
Vlan-int2
2.2.2.1/24
Source
192.168.0.1/24
Source/Mask
Multicast Routing Table Static on Switch C
192.168.0.0/24
Interface
Vlan-int2
RPF neighbor/Mask
1.1.1.1/24
Source/Mask
Multicast Routing Table Static on Switch D
192.168.0.0/24
Interface
Vlan-int2
RPF neighbor/Mask
2.2.2.2/24
OSPF domain
RIP domain
Switch A
Switch B
Switch C
Switch D
Receiver
Receiver
Multicast packets
Multicast static route
