Protocols and standards, How md-vpn works, Share-mdt establishment – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 259: Share-mdt establishment in a pim-dm network
243
Protocols and standards
•
RFC 4684, Constrained Route Distribution for Border Gateway Protocol/MultiProtocol Label
Switching (BGP/MPLS) Internet Protocol (IP) Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
•
draft-rosen-vpn-mcast-08, Multicast in MPLS/BGP IP VPNs
How MD-VPN works
This section describes how the MD-VPN technology is implemented, including the construction of a
share-MDT, delivery of multicast traffic based on the share-MDT, and implementation of multi-AS
MD-VPN.
For a VPN instance, multicast data transmission on the public network is transparent. The MTIs at the
local PE device and the remote PE device form a channel for the seamless transmission of VPN data over
the public network. All that is known to the VPN instance is that the VPN data is sent out of the MTI and
then the remote site can receive the data through the MTI. Actually, the multicast data transmission
process (the MDT transmission process) over the public network is very complicated.
Share-MDT establishment
The multicast routing protocol running on the public network can be PIM-DM, PIM-SM, BIDIR-PIM, or
PIM-SSM. The process of creating a share-MDT is different in these PIM modes.
Share-MDT establishment in a PIM-DM network
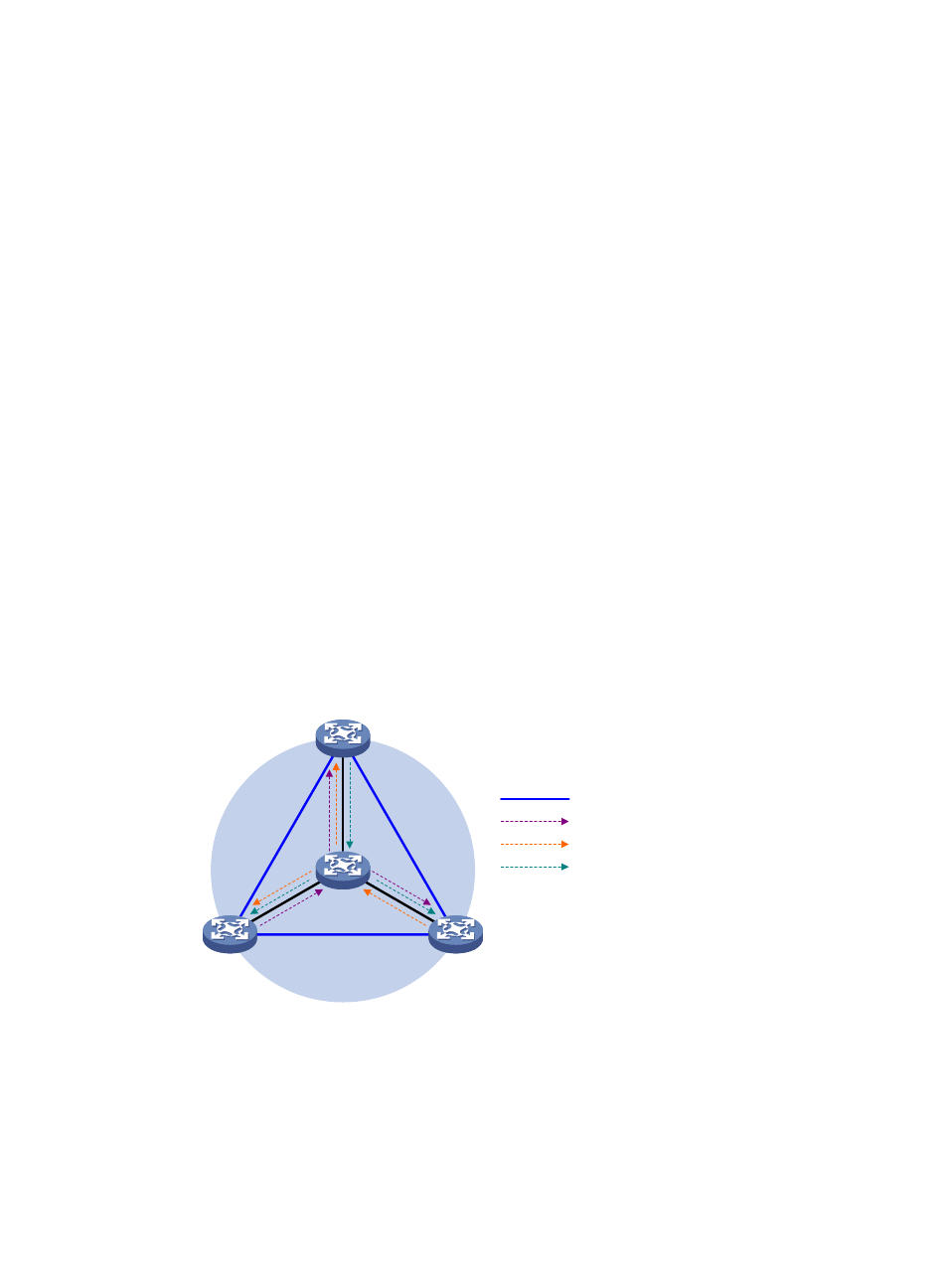
Figure 68 Share-MDT establishment in a PIM-DM network
As shown in
, PIM-DM is enabled in the network and all the PE devices support VPN instance
A. The process of establishing a share-MDT is as follows:
The public network on PE 1 initiates a flood-prune process in the entire public network, with the BGP
interface address (the interface address used to establish the BGP peer) as the multicast source address
and the share-group address as the multicast group address. All the other PE devices that are running
VPN instance A are group members, so that a (11.1.1.1, 239.1.1.1) state entry is created on each device
Public network BGP peers
MD
P
PE 3
PE 2
PE 1
BGP: 11.1.2.1/24
BGP: 11.1.1.1/24
SPT (11.1.1.1, 239.1.1.1)
SPT (11.1.2.1, 239.1.1.1)
SPT (11.1.3.1, 239.1.1.1)
BGP: 11.1.3.1/24
Share-Group: 239.1.1.1
