Share-mdt establishment in a pim-ssm network, Characteristics of a share-mdt, Share-mdt-based delivery – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 262
246
Share-MDT establishment in a PIM-SSM network
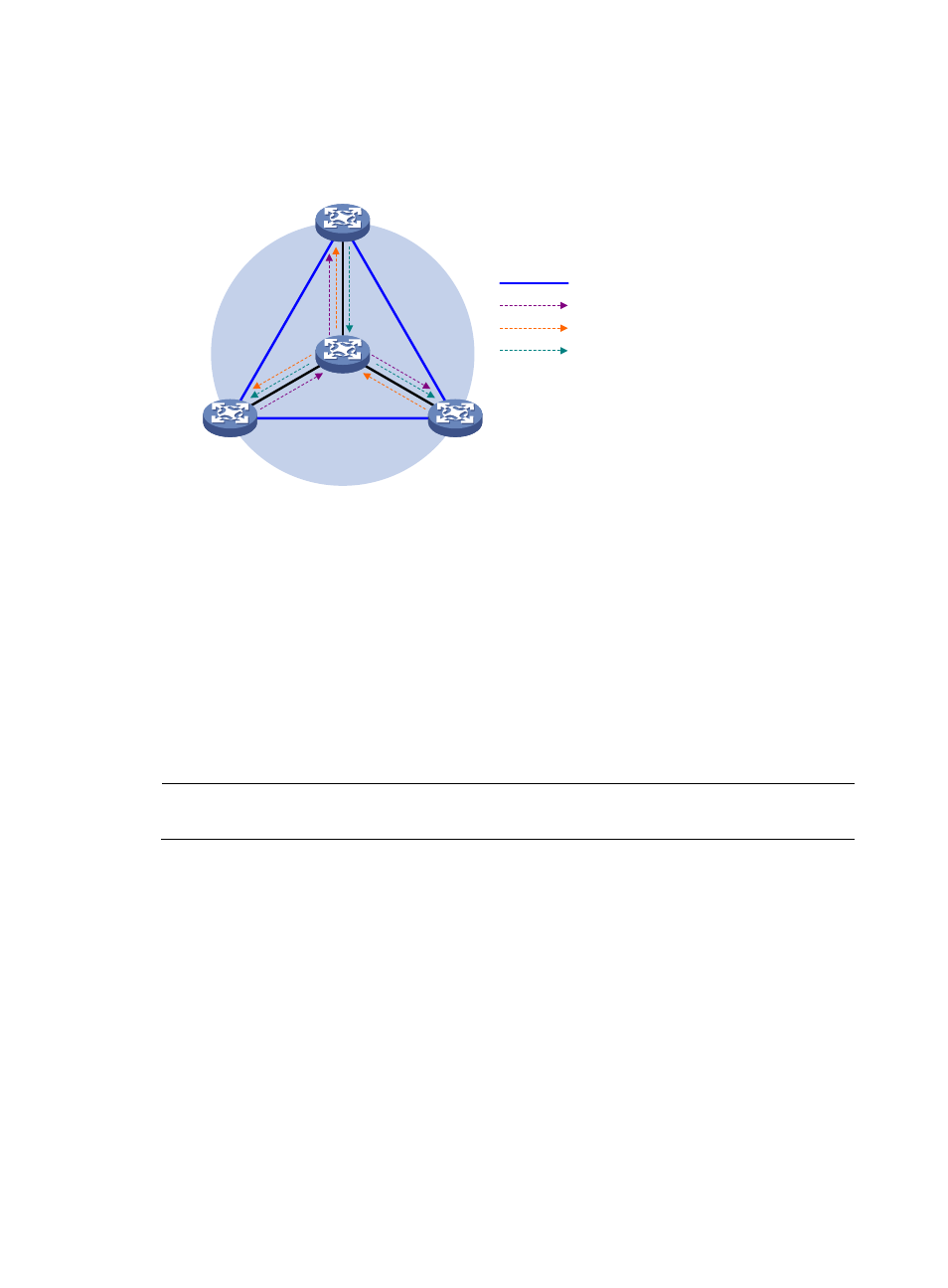
Figure 71 Share-MDT establishment in a PIM-SSM network
As shown in
, PIM-SSM is enabled in the network and all the PE devices support VPN instance
A. The process of establishing a share-MDT is as follows:
The public network on PE 1 sends the local BGP MDT routing information, including its BGP interface
address and the share-group address, to PE 2 and PE 3. PE 2 and PE 3 perform the same operation to
exchange their BGP MDT routing information with one another. After receiving the BGP MDT information
from PE 1, PE 2 and PE 3 respectively send a subscribe message for channel subscription hop by hop
toward the BGP interface of PE 1. A (11.1.1.1, 232.1.1.1) entry is created on devices on the path toward PE
1 on the public network. Thus an SPT is created in the network, with PE 1 as its root, PE 2 and PE 3 as
its leaves.
At the same time, PE 2 and PE 3 respectively initiate a similar SPT establishment process. Finally, three
independent SPTs are established in the MD. In the PIM-SS M network, the three independent SPTs
constitute a share-MDT.
NOTE:
In PIM-SSM, subscribe messages are used equivalent to join messages.
Characteristics of a share-MDT
A share-MDT is characterized as follows, no matter what PIM mode is running on the public network:
•
All PE devices that support this VPN instance join the share-MDT.
•
All VPN multicast packets that belong to this VPN, including protocol packets and data packets, are
forwarded along the share-MDT to every PE device on the public network, even if they have no
active receivers downstream.
Share-MDT-based delivery
A share-MDT can be used for delivering multicast packets, including both multicast protocol packets and
multicast data packets. However, the transmission processes for these two types of multicast packets are
different.
Public instance BGP peers
MD
P
PE 3
PE 2
PE 1
BGP: 11.1.2.1/24
BGP: 11.1.1.1/24
SPT (11.1.1.1, 232.1.1.1)
SPT (11.1.2.1, 232.1.1.1)
SPT (11.1.3.1, 232.1.1.1)
BGP: 11.1.3.1/24
Share-Group: 232.1.1.1
