Understanding redundant interconnect, Characteristics of ri on the ml-series card, Figure 17-15 – Cisco 15327 User Manual
Page 289
17-37
Ethernet Card Software Feature and Configuration Guide, R7.2
Chapter 17 Configuring Cisco Proprietary Resilient Packet Ring
Understanding Redundant Interconnect
Understanding Redundant Interconnect
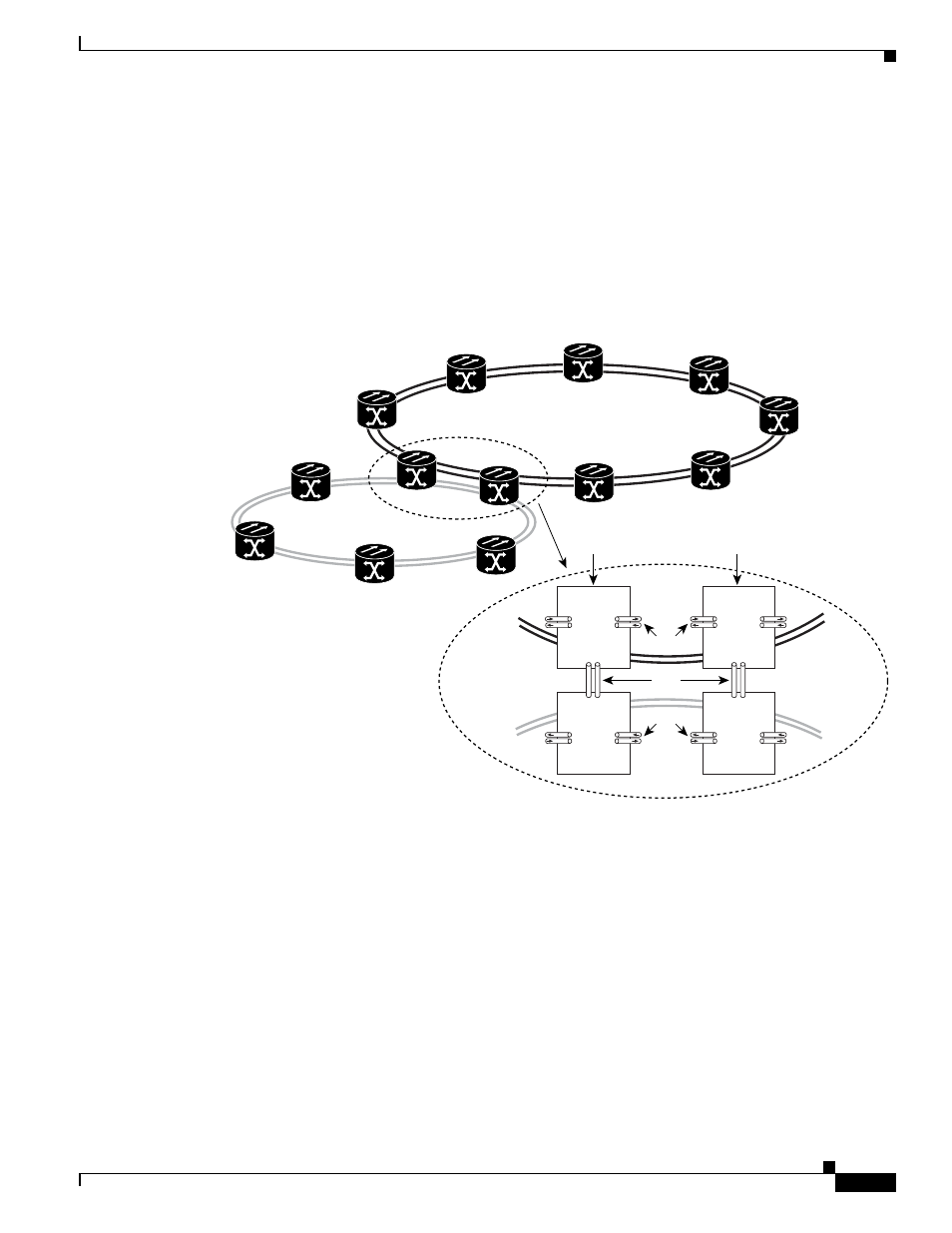
Ring interconnect (RI) is a mechanism to interconnect RPRs, both RPR-IEEE and Cisco proprietary
RPR, for protection from failure. It does this through redundant pairs of back-to-back Gigabit Ethernet
connections that bridge RPR networks. One connection is the active node and the other is the standby
node. During a failure of the active node, link, or card, the detection of the failure triggers a switchover
to the standby node.
illustrates an example of RPR RI.
Figure 17-15
RPR RI
Characteristics of RI on the ML-Series Card
RI on the ML-Series card has these characteristics:
•
Supported only on Gigabit Ethernet
•
Provisioned by identifying peer RPR MACs as either primary or standby
•
Uses an OAM frame to flush the spatially aware sublayer (SAS) table and MAC table at the add
stations
•
Provides protection between individual RPRs, including:
–
Two RPRs
–
Two Cisco proprietary RPRs
–
A Cisco proprietary ring and an IEEE 802.17 ring
GEC
151968
Primary
pair
A
ML1000-2
West
East
B
ML1000-2
West
East
C
ML1000-2
West
East
D
ML1000-2
West
East
OC-N
OC-N
Secondary
pair
