Creating a traffic policy – Cisco 15327 User Manual
Page 221
14-13
Ethernet Card Software Feature and Configuration Guide, R7.2
Chapter 14 Configuring Quality of Service
Creating a Traffic Policy
Creating a Traffic Policy
To configure a traffic policy, use the policy-map global configuration command to specify the traffic
policy name, and use the following configuration commands to associate a traffic class, which was
configured with the class-map command and one or more QoS features. The traffic class is associated
with the traffic policy when the class command is used. The class command must be issued after entering
policy-map configuration mode. After entering the class command, you are automatically in policy-map
class configuration mode, which is where the QoS policies for the traffic policy are defined.
When the bandwidth or priority action is used on any class in a policy map, then there must be a class
defined by the match-any command, which has a bandwidth or priority action in that policy map. This
is to ensure that all traffic can be classified into a default class that has some assigned bandwidth. A
minimum bandwidth can be assigned if the class is not expected to be used or no reserved bandwidth is
desired for default traffic.
The QoS policies that can be applied in the traffic policy in policy-map class configuration mode are
shown in
and
.
Example 14-2 Policy-map syntax
policy-map
policy-name
no policy-map
policy-name
Example 14-3 Class command syntax
class
class-map-name
no class
class-map-name
All traffic that fails to meet the matching criteria belongs to the default traffic class. The default traffic
class can be configured by the user, but cannot be deleted.
To create a traffic policy, use the commands in
as needed.
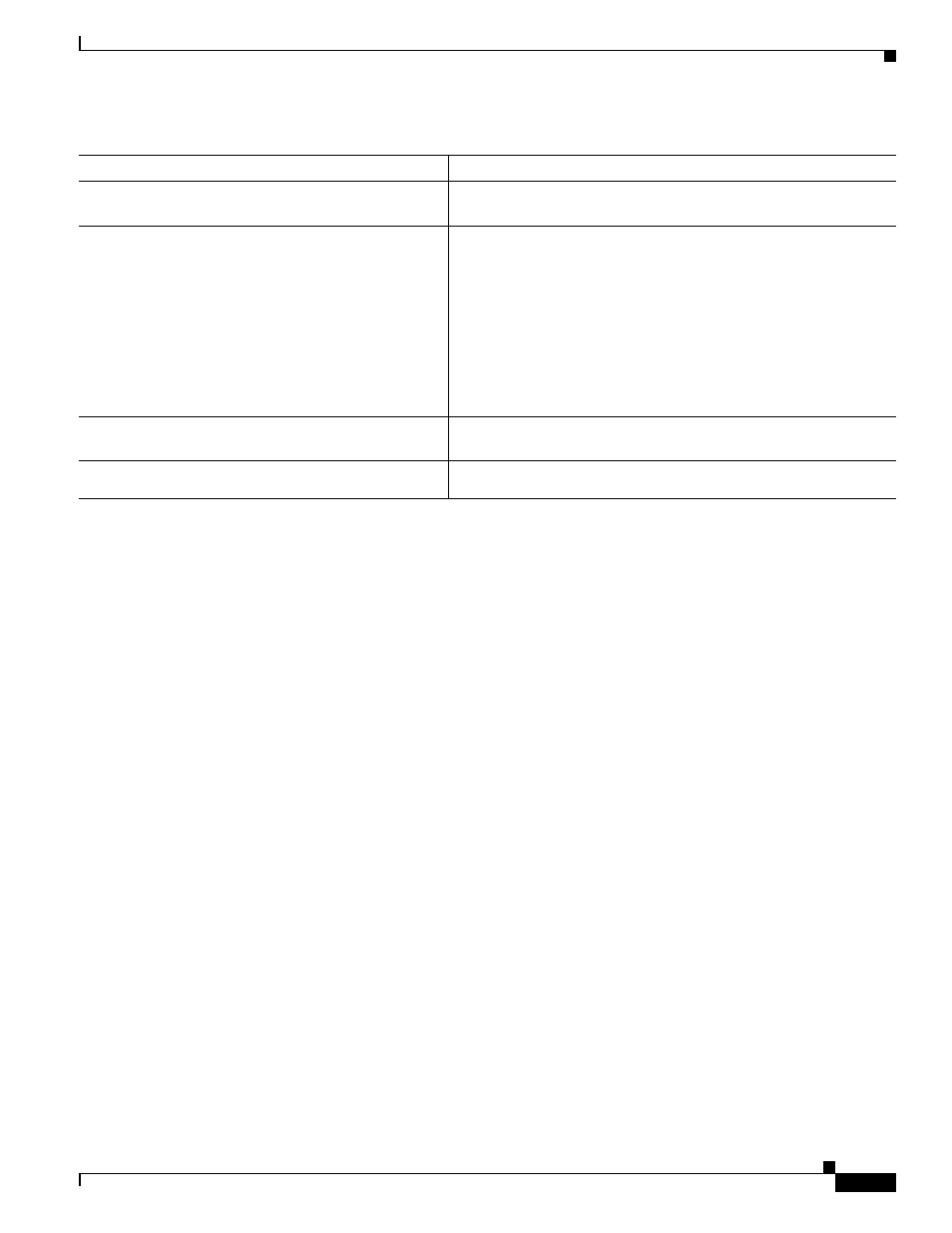
Router(config-cmap)# match cos
cos-number
Specifies the CoS value against whose contents packets are checked
to determine if they belong to the class.
Router(config-cmap)# match input-interface
interface-name
Specifies the name of the input interface used as a match criterion
against which packets are checked to determine if they belong to the
class.
The shared packet ring (SPR) interface used in Cisco proprietary
RPR (SPR1) is a valid interface-name for the ML-Series card. For
more information on the SPR interface, see
“Configuring Cisco Proprietary Resilient Packet Ring.”
The input-interface choice is not valid when applied to the INPUT
of an interface (redundant).
Router(config-cmap)# match ip dscp
ip-dscp-value
Specifies up to eight DSCP values used as match criteria. The value
of each service code point is from 0 to 63.
Router (config-cmap)# match ip precedence
ip-precedence-value
Specifies up to eight IP precedence values used as match criteria.
Table 14-1
Traffic Class Commands (continued)
Command
Purpose
