2 cautions regarding the inverter – Toshiba Tosvert VF-A5 User Manual
Page 12
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
Braking during power off:
Loads that generate a
negative torque:
Motors with brakes:
The inverter will enter the coast-stop state when the power source is
turned off. The motor will therefore not stop immediately. To stop the
motor immediately, install an auxiliary brake unit. Dynamic braking
units and mechanical braking units are available, so select one that
suits your specific appiication.
The overvoltage protection or overcurrent protection may function and
trip the inverter when used with loads that generate a negative torque,
in this case, a braking resistor that meets the load condition must be
instalied.
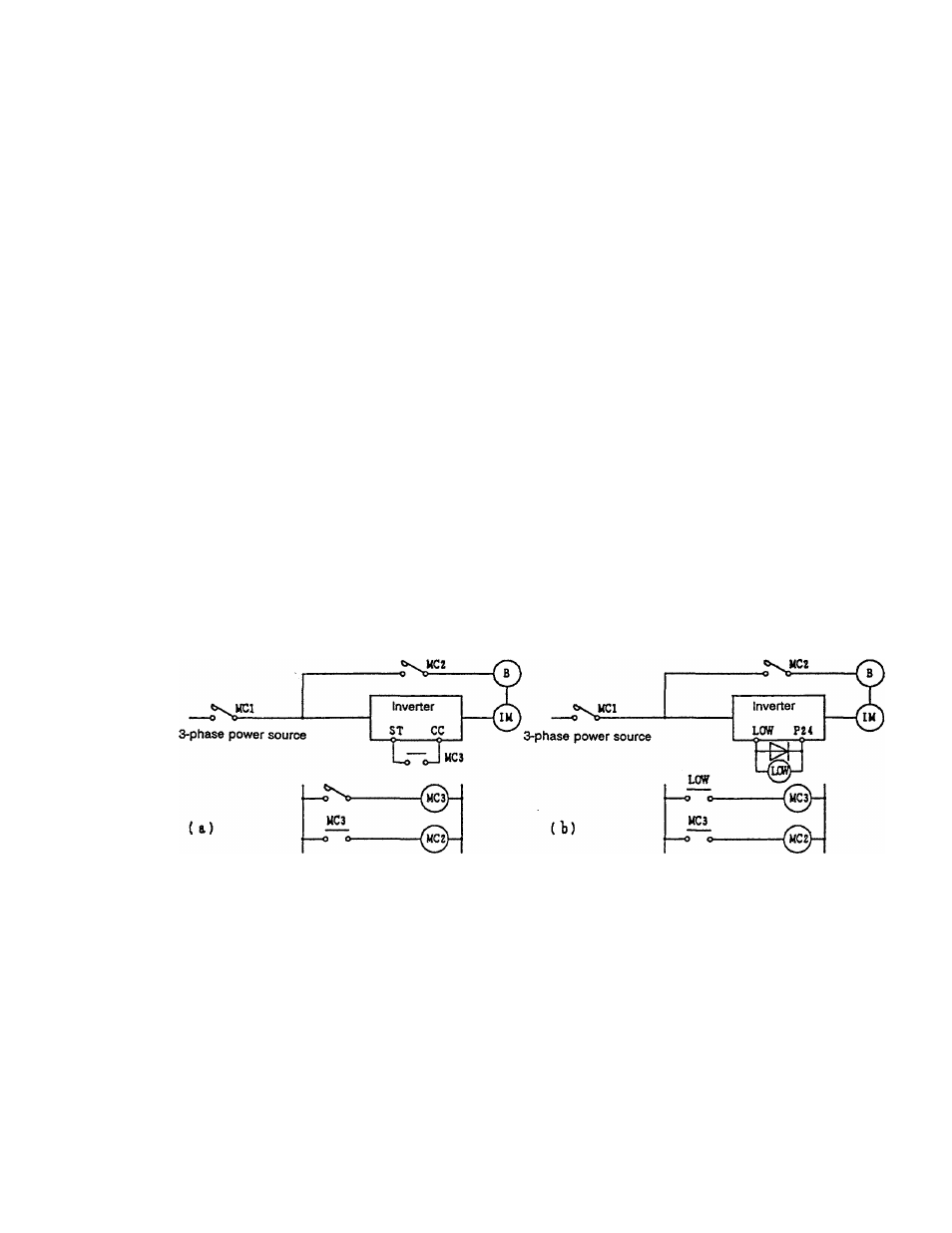
If a motor with a brake is directly connected to the inverter, the
voltage when the motor is started will be low, which may result in the
brake not being released. In this case, separately wire the brake
circuit and motor main circuit. In addition, there is a delay in the time
to when the inverter output stops if the inverter’s ST to CC control
terminal connection is released, so use of the circuit configuration in
Fig. 4-1 is recommended.
In Fig. (a), the brake power is turned ON and OFF via MC2 and MC3.
If a circuit configuration as shown in the drawing is not used, a bound
current may flow during braking and may cause an overcurrent trip.
The brake power can also be turned ON and OFF using the low-
speed signal LOW as shown in Fig. (b).
(Non-excited brake)
Fig.4.1 Circuit configuration for motor with brake
In some cases, such as in hoist applications, turning the brake ON and
OFF by using low-speed detection (LOW terminal function) may be better,
so contact your dealer for further details.
4.2 Cautions Regarding the inverter
Inverter’s overcurrent
protection:
Overcurrent protection is used as the VF-A5 inverter’s protection
function, and the current setting level is set to match the largest
applicable motor. Therefore, when operating a motor that is smaller
than the inverter capacity, the overcurrent level and electronic thermal
protection parameters must be readjusted. (Refer to pages 72, 73.)
