Rockwell Automation 1747-BSN Backup Scanner Module User Manual
Page 77
Publication 1747-UM010B-EN-P - September 2003
Configuration and Programming 5-15
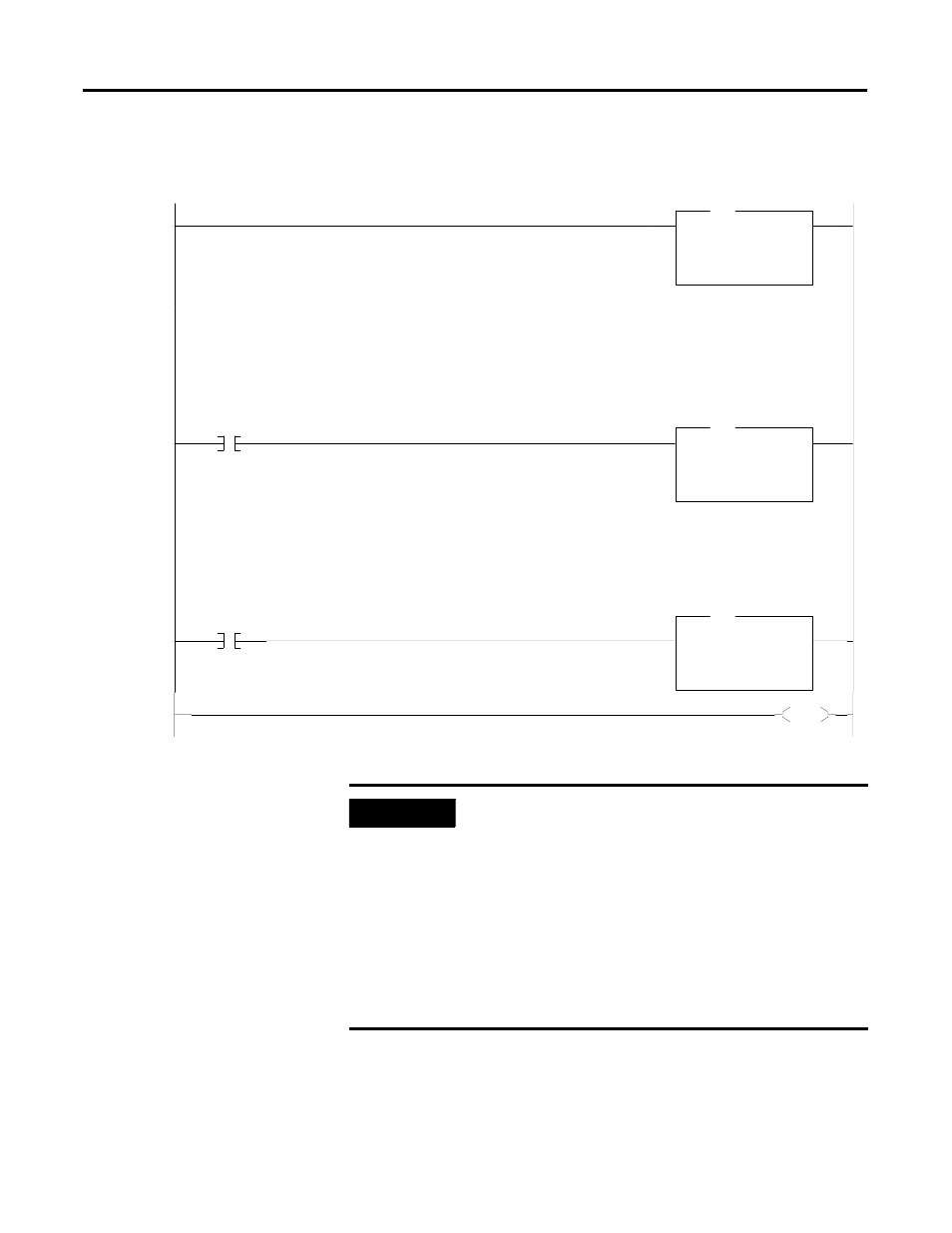
COP
Copy File
Source
#M1:1.100
Dest
#B3:0
Length
4
COP
COP
Copy File
Source
#M1:1.110
Dest
#N10:0
Length
64
COP
MOVE
Source
B3:3
0000000000000000
Dest
N10:64
0
MOV
B3
13
B3
12
END
To decrease program scan time, copy the first four words of the M1 file to a binary file and use these addresses throughout the
program to access block transfer done, error, data, etc. information without interrupting the program scan many times.
Examine B3/13 (B3: 0/13), an internal storage bit, to determine when a block transfer is done. Note that examining multiple individual
M-file bits directly (every scan) can measurably increase processor scan time
Examine B3/12 (an internal storage bit) to determine if a BT error occurred. Buffer the BT status from B3:3 if an error does occur.
BT DONE
IMPORTANT
If you are using an SLC 5/02 processor, M file data
cannot be directly monitored. To monitor M files, you
must move the M file words into an SLC file that can
be monitored, e.g., an integer “N” file. SLC 5/03 or
later processors allow you to monitor M files directly.
However, do not address M file bits more than
necessary throughout your application program. The
processor accesses M files like immediate I/O.
Therefore, excessive addressing of M files can greatly
increase SLC processor scan time. For more
information on M files, refer to Appendix B.
