1 measuring wheel and encoder selection, Measuring wheel and encoder selection -32, Flyingsaw – Lenze EVS93xx FlyingSaw User Manual
Page 45
FlyingSaw
Functions
Prepared Solution Servo PLC / ECSxA 1.1 EN
page 3-32
3.8.1 Measuring wheel and encoder selection
In order to achieve an exact cutting result, the flying saw requires the speed of the material
path. For this purpose, in practice often a measuring wheel in combination with an incremental
encoder is used. The measuring wheel is pressed on the material path by means of a spring, so
that no slip can develop between the material path and the measuring wheel. Like this, the
incremental encoder connected to the measuring wheel measures the speed of the material.
Usually incremental encoders with two tracks with zero pulse, shifted by 90 degrees, are used
to be able to use the so-called quadruple evaluation that provides for a resolution improvement.
The resolution can further be increased by using measuring wheels with a small diameter or by
mounting a gearbox between the measuring wheel and the incremental encoder, increasing the
speed of the incremental encoder.
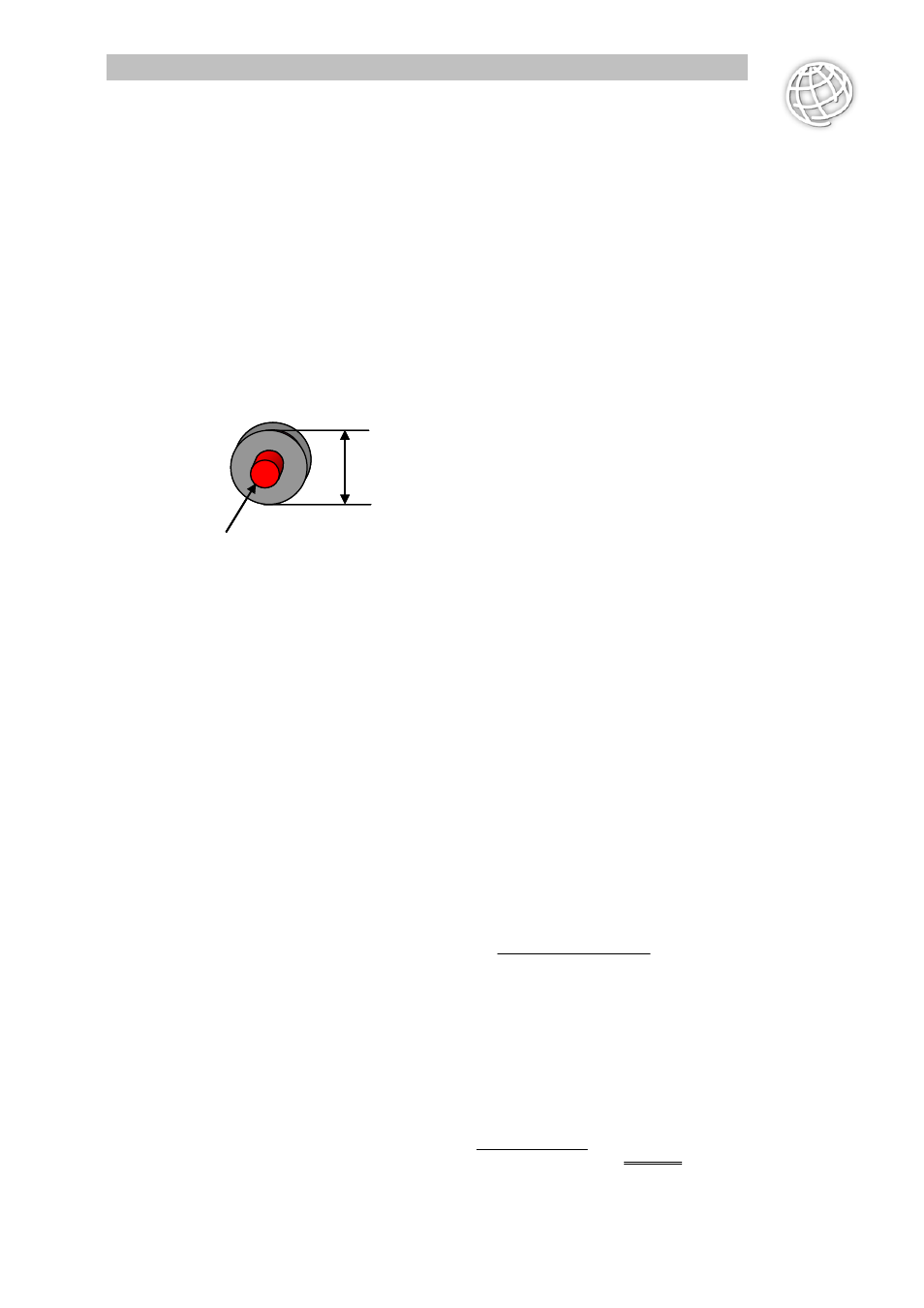
Durchmesser
Impulsgeber
Durchmesser
Impulsgeber
In practice it has been shown that the resolution of the registration of the material position has
to be 10 times higher than the cutting accuracy required. This means that if a cutting accuracy
of 1 mm is to be achieved, the encoder at least has to provide 10 position encoder increments
for a material feed of 1 mm. Here one can benefit from the quadruple evaluation brought about
by the use of incremental encoders. During the position registration each edge of the position
tracks is evaluated, by which the resolution of the position is quadrupled. (A 1024-pulse encoder
provides 4096 edges per revolution.) Therefore one position encoder increment corresponds to
the 1/(4 pulse number)-th part of a revolution.
Example:
Cutting accuracy required:
0.5 mm
Diameter of impeller:
200 mm
Circumference of impeller:
628.32 mm
The measuring wheel is directly coupled to the incremental encoder.
Calculation of the required edges per revolution to achieve the required accuracy of 0.5 mm:
wheel
Measuring
wheel
Measuring
i
accuracy
required
U
edges
of
number
_
_
min
_
10
_
_
⋅
⋅
=
where:
Number of edges
min
= minimum required number of edges of incremental encoder
U
Measuring wheel
= circumference of measuring wheel
i
Measuring wheel
= gearbox ratio between the measuring wheel and incremental encoder
12566,4
1
5
,
0
32
,
628
10
_
_
min
=
⋅
⋅
=
mm
mm
edges
of
number
diameter
encoder
