Software mode control, 1 control port description, 1 spi mode – Cirrus Logic CS8422 User Manual
Page 43: Figure 22.control port timing in spi mode, Control port description
DS692F2
43
CS8422
9. SOFTWARE MODE CONTROL
9.1
Control Port Description
The control port is used to access the registers, allowing the CS8422 to be configured for the desired oper-
ational modes and formats. The operation of the control port may be completely asynchronous with respect
to the audio sample rates. However, to avoid potential interference problems, the control port pins should
remain static if no operation is required.
The control port has two modes: SPI and I²C, with the CS8422 acting as a slave device. SPI Mode is se-
lected if there is a high to low transition on the AD0/CS pin, after the RST pin has been brought high. I²C
Mode is selected by connecting the AD0/CS pin through a resistor to VL or DGND, thereby permanently
selecting the desired AD0 bit address state.
9.1.1
SPI Mode
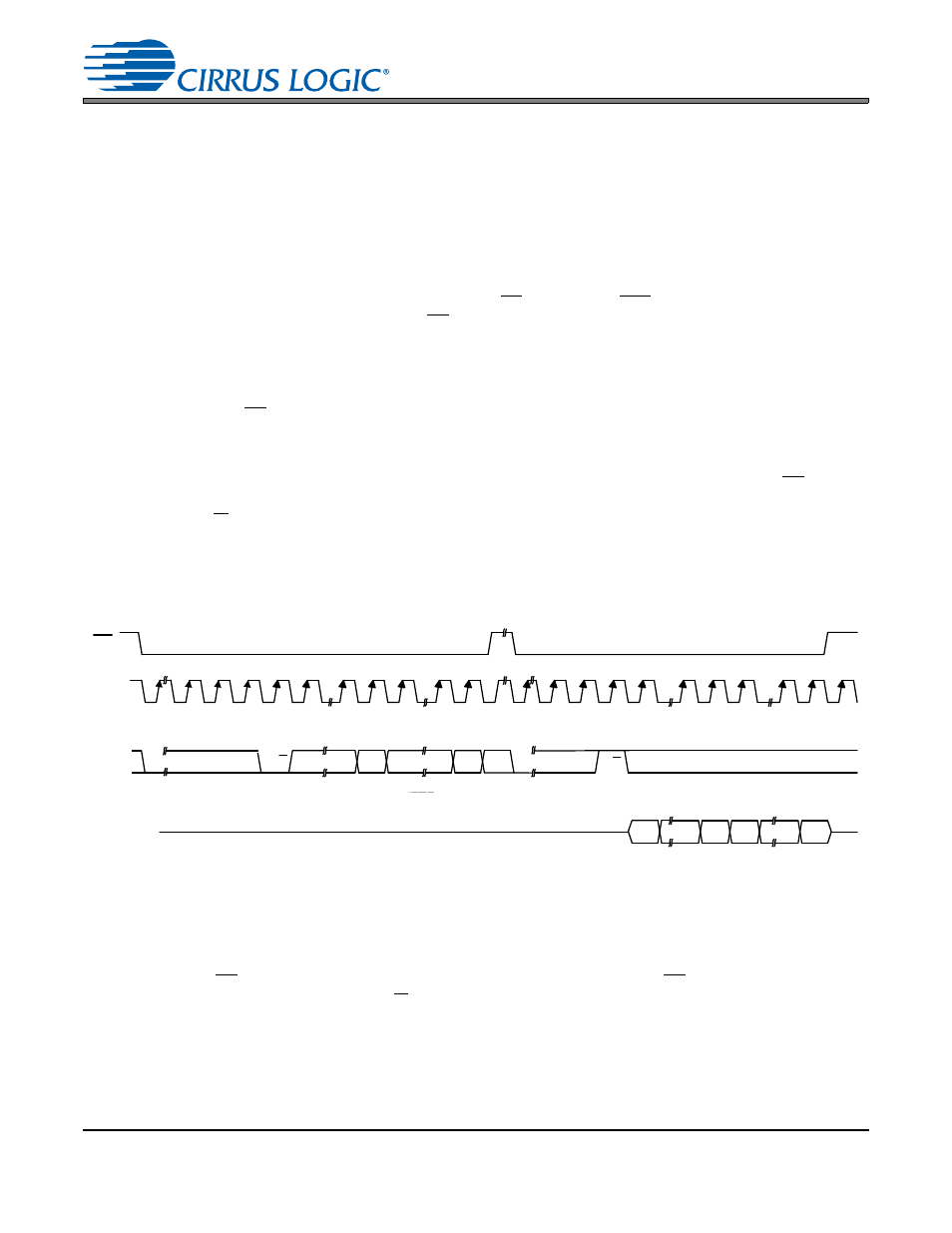
In SPI Mode, CS is the CS8422 chip select signal, CCLK is the control port bit clock (input into the CS8422
from the microcontroller), CDIN is the input data line from the microcontroller, CDOUT is the output data
line to the microcontroller. Data is clocked in on the rising edge of CCLK and out on the falling edge.
shows the operation of the control port in SPI Mode. To write to a register, bring CS low. The
first seven bits on CDIN form the chip address and must be 0010000. The eighth bit is a read/write indi-
cator (R/W), which should be low to write. The next eight bits include the 7-bit Memory Address Pointer
(MAP), which is set to the address of the register that is to be updated. The next eight bits are the data
which will be placed into the register designated by the MAP. During writes, the CDOUT output stays in
the Hi-Z state. It may be externally pulled high or low with a 20 k
resistor, if desired.
To read a register, the MAP has to be set to the correct address by executing a partial write cycle which
finishes (CS high) immediately after the MAP byte. To begin a read, bring CS low, send out the chip ad-
dress and set the read/write bit (R/W) high. The next falling edge of CCLK will clock out the MSB of the
addressed register (CDOUT will leave the high impedance state). The MAP automatically increments, so
data for successive registers will appear consecutively.
M A P
MSB
LSB
DATA
b y te 1
b y te n
R/W
R/W
A D D R E S S
C H IP
ADDRESS
C H I P
C D I N
C C L K
CS
C D O U T
MSB
LSB MSB
LSB
0010000
0010000
MAP = Memory Address Pointer, 8 bits, MSB first
High Impedance
Figure 22. Control Port Timing in SPI Mode
