Continuous access synchronous z – HP XP P9500 Storage User Manual
Page 60
Not permitted
Permitted
Product name (Guide name)
Use on THP V-VOLs.
Volume Shredder (HP XP P9000
Volume Shredder for Open and
Mainframe Systems User Guide)
•
Using on pool-VOLs.
•
Using on TSE-VOLs.
•
Increasing the capacity of THP
V-VOL used by Volume Shredder.
•
Reclaiming zero pages of V-VOL
used by Volume Shredder.
Defining base addresses to THP
V-VOLs
Parallel Access Volumes (HP XP P9000
for Compatible Parallel Access
Volumes User Guide)
•
Defining base or alias addresses to
pool-Vols
Defining base addresses to TSE-VOLs.
•
Defining alias addresses to THP
V-VOLs
•
Defining Alias addresses to
TSE-VOLs
Using a THP V-VOL as a Compatible
XRC P-VOL or S-VOL.
Compatible XRC (HP XP P9000 for
Compatible XRC User Guide)
•
Using a THP pool-VOL as a
Compatible XRC P-VOL or S-VOL.
•
Using a THP TSE-VOL as a
Compatible XRC P-VOL or S-VOL.
•
Increasing the capacity of THP
V-VOL used by Compatible XRC.
Using a THP V-VOL as a S-VOL or
T-VOL.
Compatible FlashCopy and
Compatible FlashCopy SE (HP XP
•
Using a pool-VOL as an S-VOL or
T-VOL.
Using a TSE-VOL as a T-VOL.
P9000 for Compatible FlashCopy
Mirroring User Guide )
•
Using a TSE-VOL as an S-VOL.
•
Increasing the capacity of a THP
V-VOL used by Compatible
FlashCopy or Compatible FlashCopy
SE.
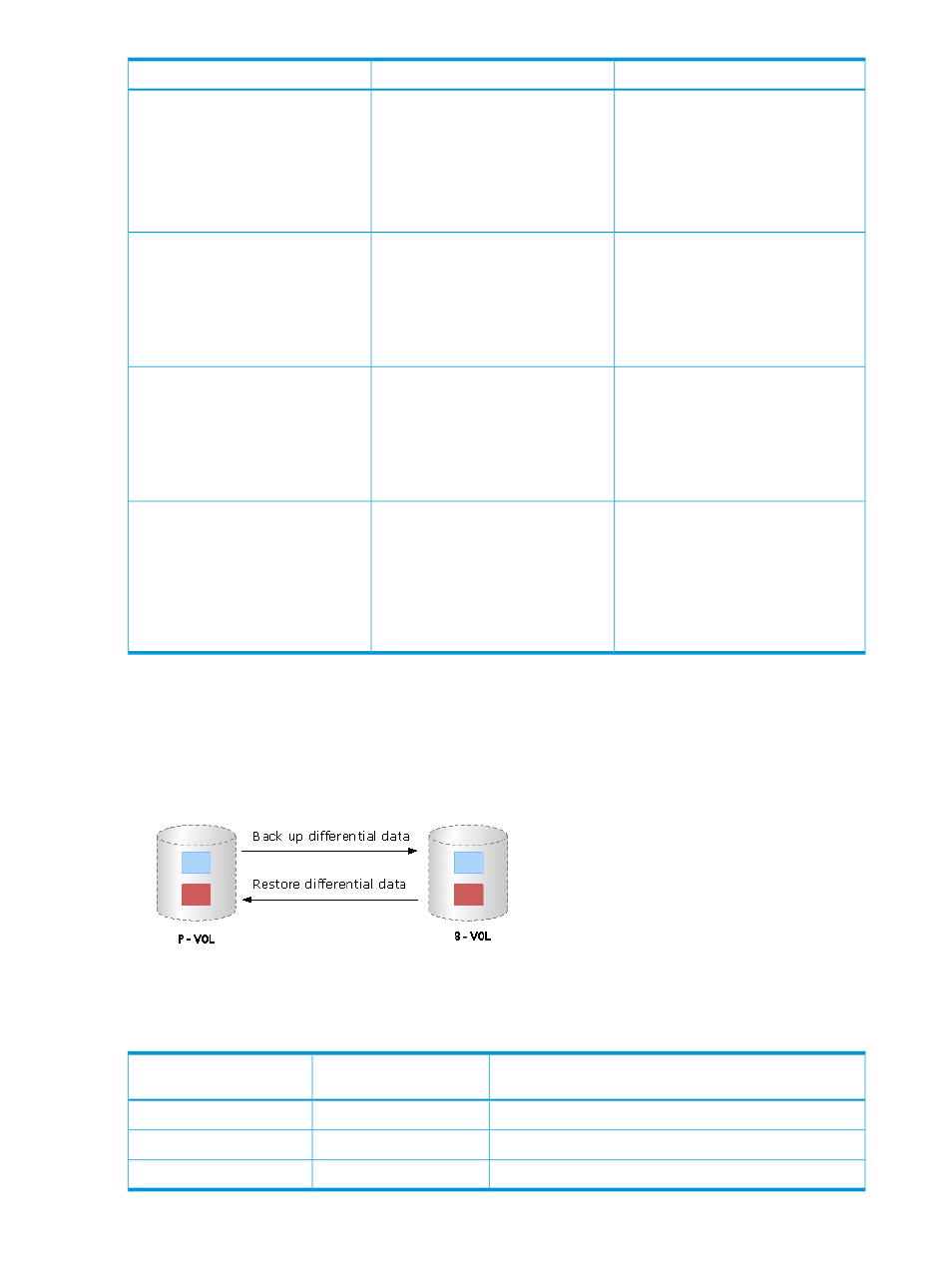
Continuous Access Synchronous Z
You can use Thin Provisioning Z or Smart Tiers Z in combination with Continuous Access
Synchronous Z to replicate V-VOLs. The following figure illustrates the interaction when the
Continuous Access Synchronous Z P-VOL and S-VOL are also V-VOLs.
Figure 1 Thin Provisioning Z or Smart Tiers Z and Continuous Access Synchronous Z
This table shows the supported Continuous Access Synchronous Z and Thin Provisioning Z or Smart
Tiers Z combinations.
Explanation
Continuous Access
Synchronous S-VOL
Continuous Access
Synchronous P-VOL
Supported
THP V-VOLs
THP V-VOLs
Supported
Normal volumes
THP V-VOLs
Supported
THP V-VOLs
Normal volumes
60
Configuring thin provisioning
