Iscsi initiator perspective, 47 example: single mpx100 iscsi port ip addressing, Figure 46 – HP EVA Array iSCSI Connectivity Option User Manual
Page 98: Eva ip network, Mp x 1 0 0
M
P
X
1
0
0
FC1
GE2
GE1
FC2
50:…..f6:78
Lun 0,1,2,3
T=Iqn.1996…..f678
Lun 0,1,2,3
T=Iqn.1996…..f67c
Lun 0,1,2,3
50:…..f6:7c
Lun 0,1,2,3
T=Iqn.1996…..f678
Lun 0,1,2,3
T=Iqn.1996…..f67c
Lun 0,1,2,3
EVA
IP
Network
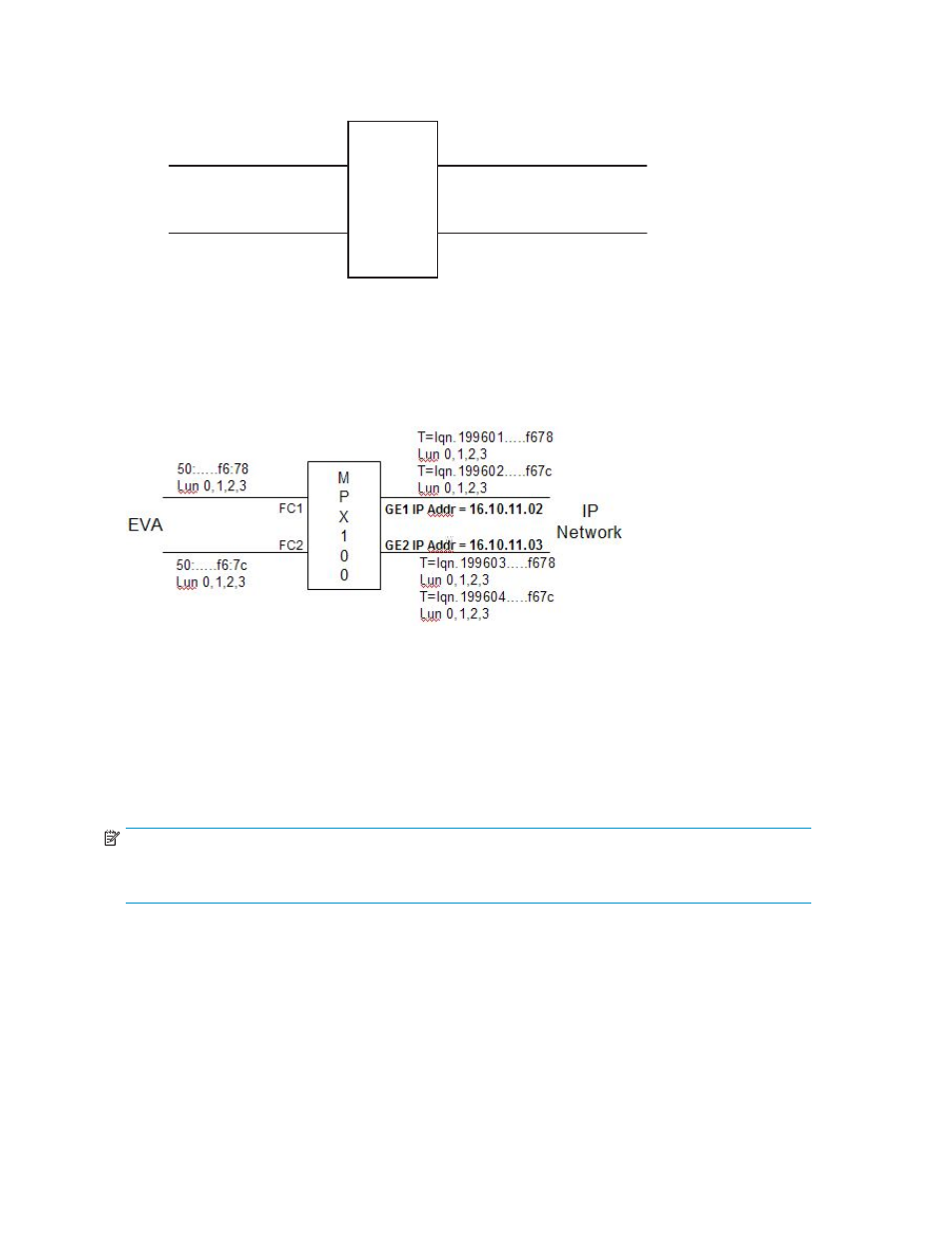
Figure 46 Example: Fibre Channel to IP port/target translation
The iSCSI Initiator discovers the targets presented out of the mpx100/100b GE ports by discovering the
GE port's IP addresses and logging in to the target (see
).
Figure 47 Example: Single mpx100 iSCSI port IP addressing
Each iSCSI GbE port has duplicate paths to the LUN because each GE port is presenting two unique
targets with the same LUN information. Each unique target should be considered an iSCSI path to the LUN.
iSCSI Initiator perspective
Because of the mpx100's/100b's ability to present multiple Fibre Channel targets through one physical
iSCSI GbE connection, it is possible for the iSCSI Initiator to connect—and use—more virtual paths than
are physically available on the FC/IP networks.
NOTE:
Using the iSCSI target discovery process, it is up to the iSCSI Initiator to determine how many targets to
log in to, bearing in mind that one target equals one path.
For the preceding examples,
shows all the paths available to an iSCSI Initiator connected
to both iSCSI GbE Ports of the mpx100/100b.
98
Setting up the iSCSI Initiator for multipathing
