Yokogawa Button Operated MV2000 User Manual
Page 51
1-44
M-4660
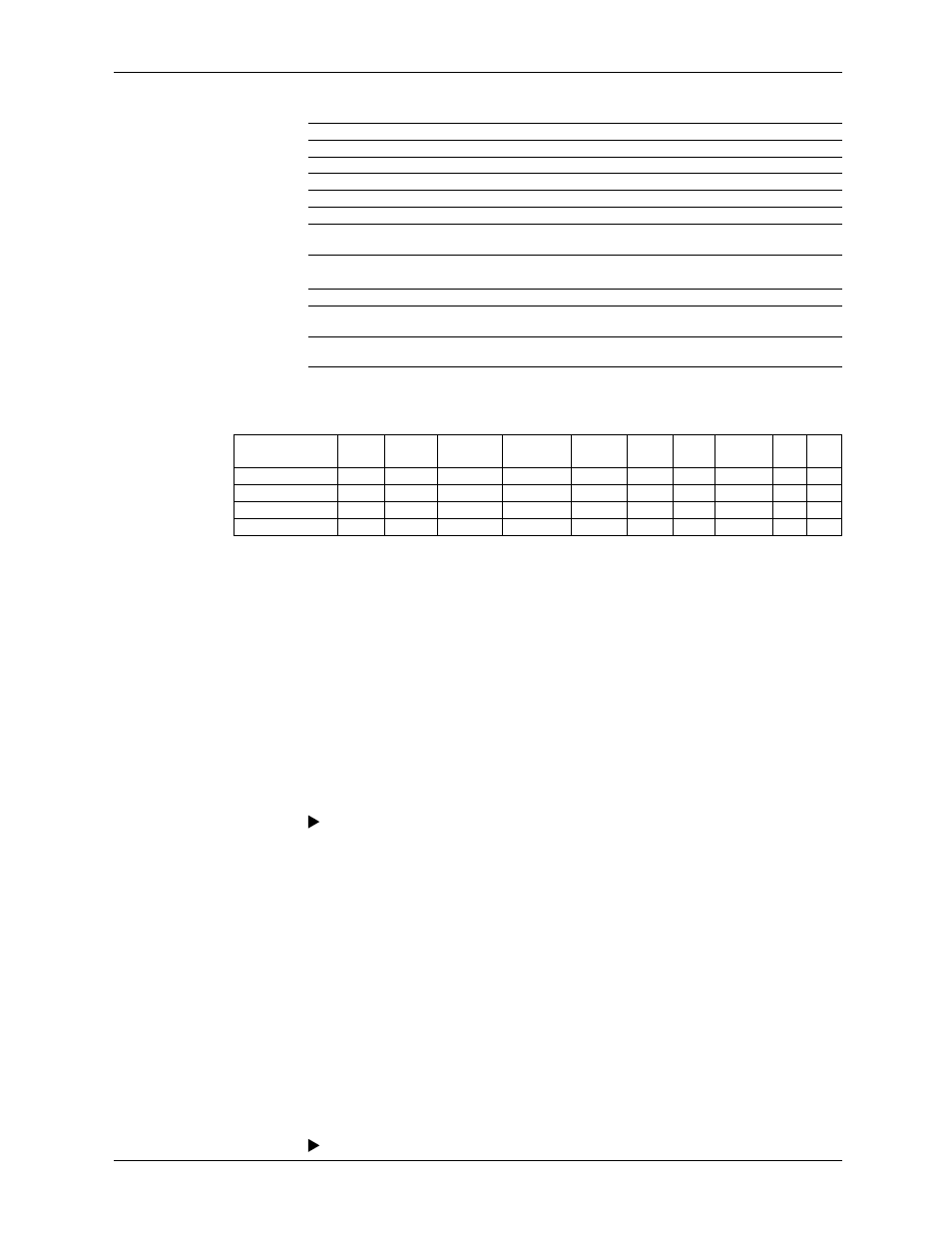
• Data That Can Be Used in Equations
The data listed below can be used in equations.
Data
Notation
Description
Measurement channel data
001, etc.
Specify by channel number.
Computation channel data*
101, etc.
Specify by channel number.
External input channel data*
201, etc.
Specify by channel number.
Constants
K01 to K60
Set to numeric values.
Communication input data
C01 to C60
Data set through communications.
Status of remote control*
input
D01 to D08**
The value is 1 when remote control input is
ON and 0 when it is OFF.
Pulse input*
P01 to P08
Counts the number of pulses per scan interval.
Q01 to Q08**
Counts the number of pulses per second.
Internal switch status
S01 to S30
1 or 0.
Alarm output relay* status
I01 to I36
The value is 1 when activated and 0 when
deactivated.
Flag
F01 to F08
1 or 0. Set the flag using the event action
function (for details, see section 1.7).
* This is an option.
** Values such as 01 are terminal numbers.
The table below shows the data that can be used with TLOG, CLOG, and PRE.
Checked data is usable.
Data
Math Func.
Meas.
CH
Comp.
CH
Ext.
input CH
Constant Comm.
Input
Remote Pulse Internal
Switch
Relay Flag
TLOG
CLOG
PRE
Other Functions
For example, TLOG.SUM(S01), CLOG.AVE(001.002.K01), and PRE(S01) are not allowed.
• Order of Operation
Computation functions are performed every scan interval, starting with the smallest
channel number.
Example: If you specify 102 = 101 + 103, the value of the previous scan interval is
used for the 103 value.
• How Computation Functions Handle Units
In computations, measured values are handled as values without units. For example,
if the measured data from channel 001 is 20 mV and the measured data from channel
002 is 20 V, the computed result of 001 + 002 is 40.
• How Computed Data Is Displayed
You can set a span for the computed data displayed on each computation
channel. Computation channels can be displayed on all operation screens, just like
measurement channels.
For configuration instructions, see section 10.3.
• Alarms
You can set a maximum of four different alarms on each computation channel. The
alarm types are high limit alarm (H), low limit alarm (L), delay high limit alarm (T), and
delay low limit alarm (t).
• How Computed Data Is Saved
Just as with measured data, computation channel computed data can be saved as
display data, event data, manually sampled data, and report data.
• Computation Data Dropout
A computation data dropout occurs if a mathematical operation is not completed within
the scan interval.
• The computation icon in the status display section turns yellow.
• When a computation data dropout occurs, the computed data of the scan interval in
which the dropout occurred is set to the same value as the data immediately before
the dropout.
• If computation data dropout occurs frequently, reduce the load on the CPU by
reducing the number of computation channels or by setting a longer scan interval.
For operating instructions, see section 10.4.
1.9 Computation and Report Functions (/M1 and /PM1 options)
