2 input, App index, Measurement channels – Yokogawa Button Operated MV2000 User Manual
Page 10: Input types and computation functions
1-3
M-4660
Feature Overview
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
App
Index
1.2
Input
Measurement Channels
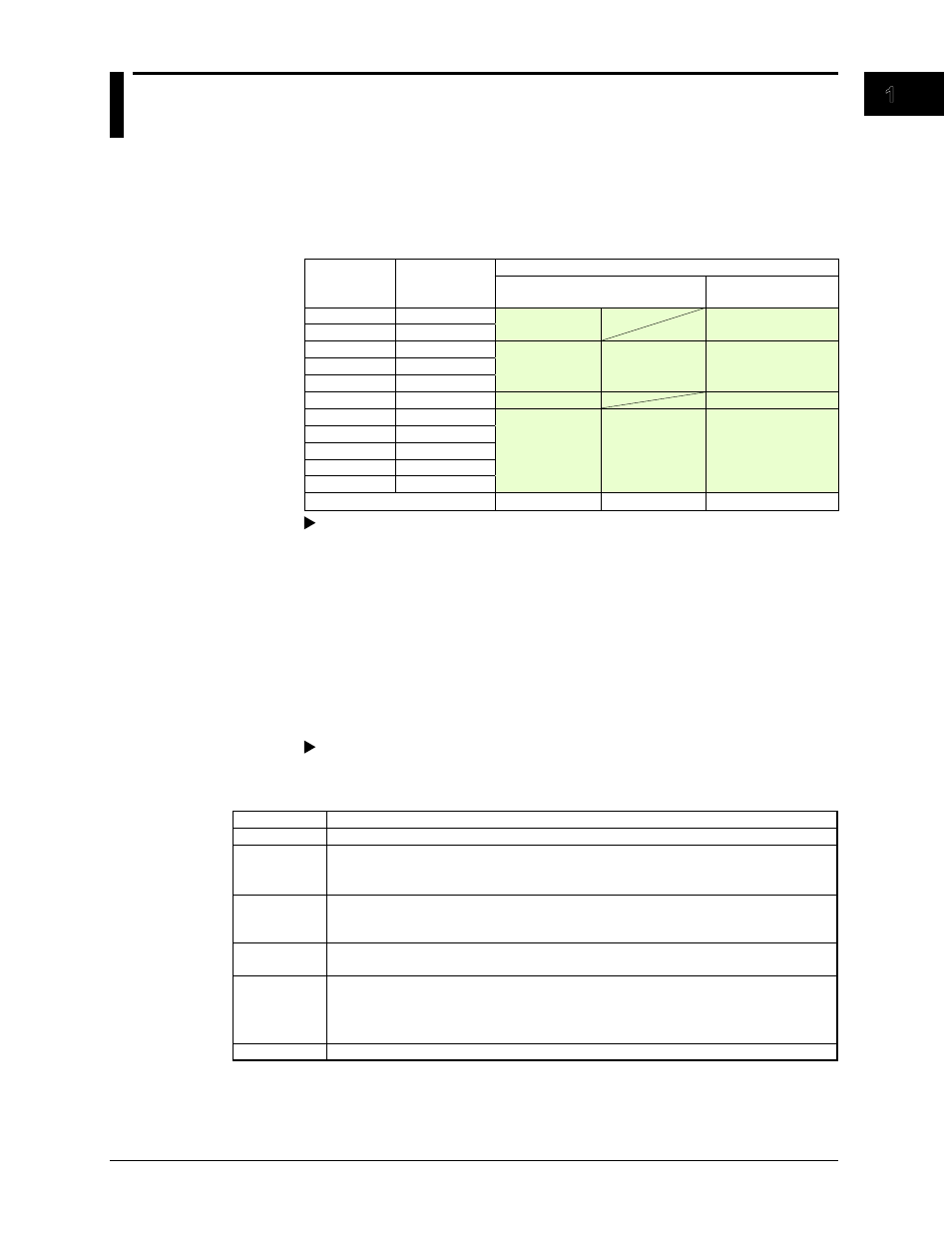
• Number of Channels vs. Scan Interval
The MV acquires data by sampling measurement channel input signals at the set scan
interval. The following is a list of the scan intervals available with different numbers of
channels.
Model
Number of
Measurement
Channels
Scan Interval
Normal Mode
Fast Sampling Mode
RD-MV1004
4
125 ms, 250 ms
25 ms
RD-MV1008
8
RD-MV1006
6
1 s, 2 s, 5 s
2 s, 5 s
125 ms
RD-MV1012
12
RD-MV1024
24
RD-MV2008
8
125 ms, 250 ms
25 ms
RD-MV2010
10
1 s, 2 s, 5 s
2 s, 5 s
125 ms
RD-MV2020
20
RD-MV2030
30
RD-MV2040
40
RD-MV2048
48
A/D converter integration time
60 Hz/50 Hz
100 ms
600 Hz (fixed)
For configuration instructions, see section 3.1.
• A/D Converter Integration Time
The MV uses an A/D converter to convert sampled analog signals to digital signals.
You can effectively eliminate the influence of power supply noise by setting the A/
D converter’s integration time to the same length as or to an integral multiple of the
power source period.
• Because 100 ms is an integral multiple of both 16.7 ms and 20 ms, you can effectively
eliminate the influence of power supply noise from both 50- and 60-Hz frequencies by
setting the integration time to 100 ms.
• Power supply noise elimination is less effective in fast sampling mode than it is in normal
mode. When measuring in an environment susceptible to power supply noise, we
recommend that you measure in normal mode.
For configuration instructions, see section 3.1.
Input Types and Computation Functions
You can measure the following types of input.
Input Type
Description
DC voltage
You can measure DC voltages in the range of ±20 mV to ±50 V.
DC current
You can measure a DC current signal by converting it to a voltage signal using a shunt
resistor attached to the input terminal.
1
The converted signal can be measured within the DC voltage range (see above).
Thermocouple
You can measure temperatures using these thermocouple types: R, S, B, K, E, J, T, N,
W, L, U, and WRe3-25. It is also possible to measure using other thermocouples, such as
PR40-20 and PLATINEL.
2
RTD
You can measure temperatures using RTD types Pt100 and JPt100. It is also possible to
measure using other RTD types such as Cu10 and Cu25,
3
and Pt50 and Ni100.
2
ON/OFF input
You can display contact input or voltage input signals correlated to 0% or 100% of the
display range.
Contact input: A closed contact is ON (1). An open contact is OFF (0).
Voltage input: Less than 2.4 V is OFF (0). 2.4 V or more is ON (1).
Pulse input
4
You can count pulses.
1 Shunt resistor sold separately. For example, you can use a 250-Ω shunt resistor to convert a 4- to 20-mA
signal to a 1- to 5-V signal.
2 /N3 option
3 /N1 option
4 /PM1 option
