Rjc of tc input – Yokogawa Button Operated MV2000 User Manual
Page 261
12-22
M-4660
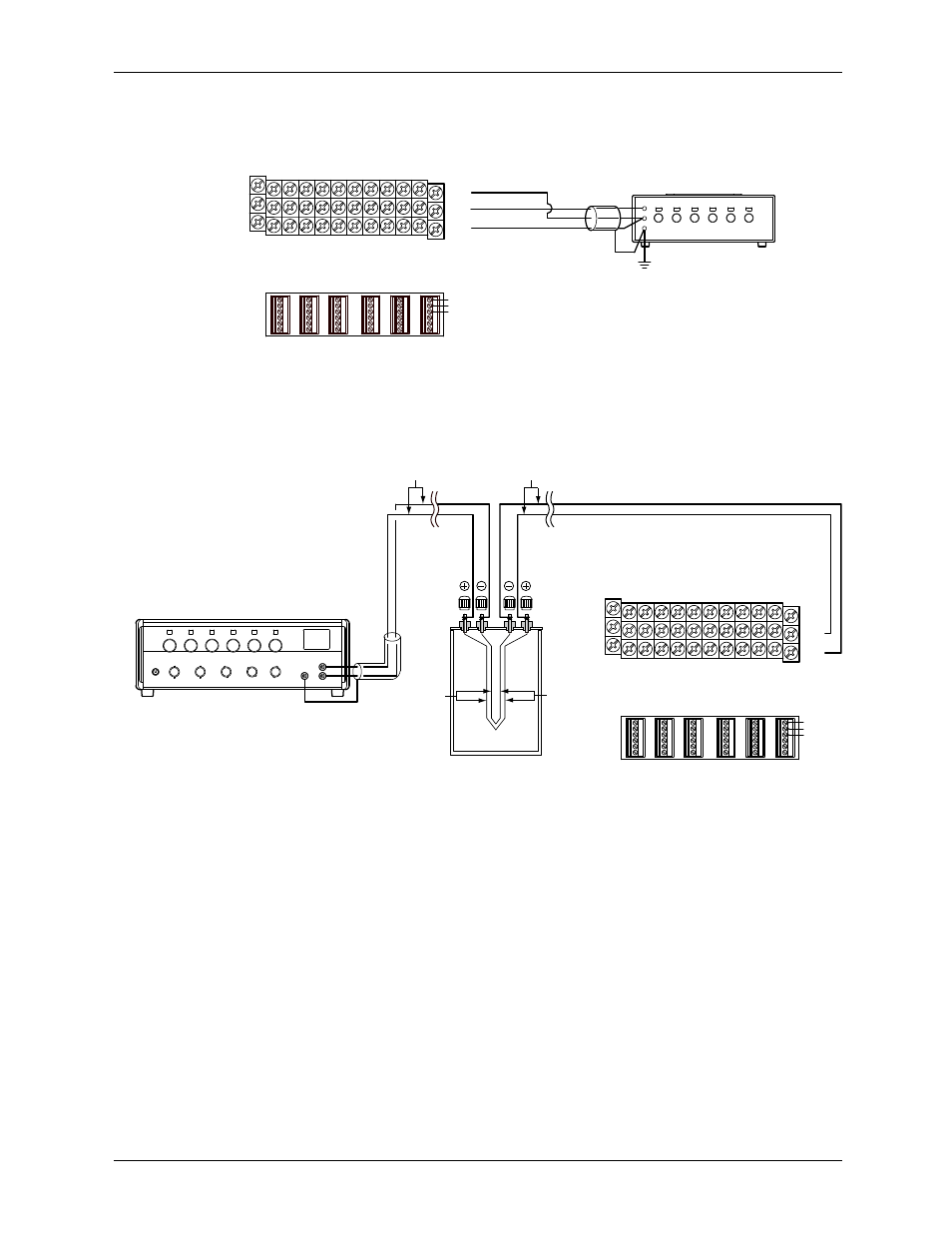
Temperature Measurement When Using an RTD (Example for the RD-
MV1012)
Decade resistance box
The resistances of the three lead wires should be equal.
b
B
A
Input terminal
Screw terminal
Clamp terminal
CH1
CH2
CH3
CH4
CH5
CH6
CH7
CH8
CH9
CH11
CH10
CH12
+/A
/b
–/B
CH5 CH3 CH1
CH6 CH4 CH2
CH9 CH7
CH10
CH11
CH12
CH8
/b
+/A
–/B
–
Temperature Measurement When Using a Thermocouple (Example for the
RD-MV1012)
Thermocouple wires or
TC extension wires
Thermocouple
wires
Copper
wires
Copper wires
DC voltage standard
–
+
+
–
(0°C standard temperature device
ZC-114/ZA-10 by Coper Electronics)
Input terminal
Screw terminal
Clamp terminal
CH1
CH2
CH3
CH4
CH5
CH6
CH7
CH8
CH9
CH11
CH10
CH12
+/A
/b
–/B
CH5 CH3 CH1
CH6 CH4 CH2
CH9 CH7
CH10
CH11
CH12
CH8
/b
+/A
–/B
RJC of TC Input
As the measurement terminal of the MV is generally at room temperature, the actual
output of the thermocouple is different from the values given on the thermoelectromotive
force table based on 0°C. The MV performs compensation by measuring the temperature
at the input terminal and adding the corresponding thermoelectromotive force to the
actual output of the thermocouple. Therefore, when the measurement terminal is shorted
(equivalent to the case when the detector tip is 0°C), the measured value indicates the
temperature of the input terminal.
When calibrating the MV, this compensation voltage (thermoelectromotive force of 0°C
reference corresponding to the input terminal temperature) must be subtracted from the
output of the standard generator before application. As shown in the figure, by using the
0°C standard temperature device to compensate the reference junction at 0°C, you can
input the thermoelectromotive force of 0°C reference from the DC voltage standard and
perform the calibration.
12.4 Calibrating the MV
