Telnet and web communications, Preliminar y – Extron Electronics MGP 462xi Series User Manual
Page 57
4-5
MGP Series • Software Configuration and Control
PRELIMINAR
Y
E24 — Privilege violation
E26 — Maximum number of users connected has been exceeded
E27 — Invalid event number
E28 — Bad filename/File not found
Telnet and Web communications
The MGP can also be controlled via an IP connection using either Telnet (port 23)
or a Web browser (port 80). The ASCII and URL commands listed in the tables
later in this chapter perform the same functions, but are encoded differently to
accommodate the requirements of each port (Telnet or browser).
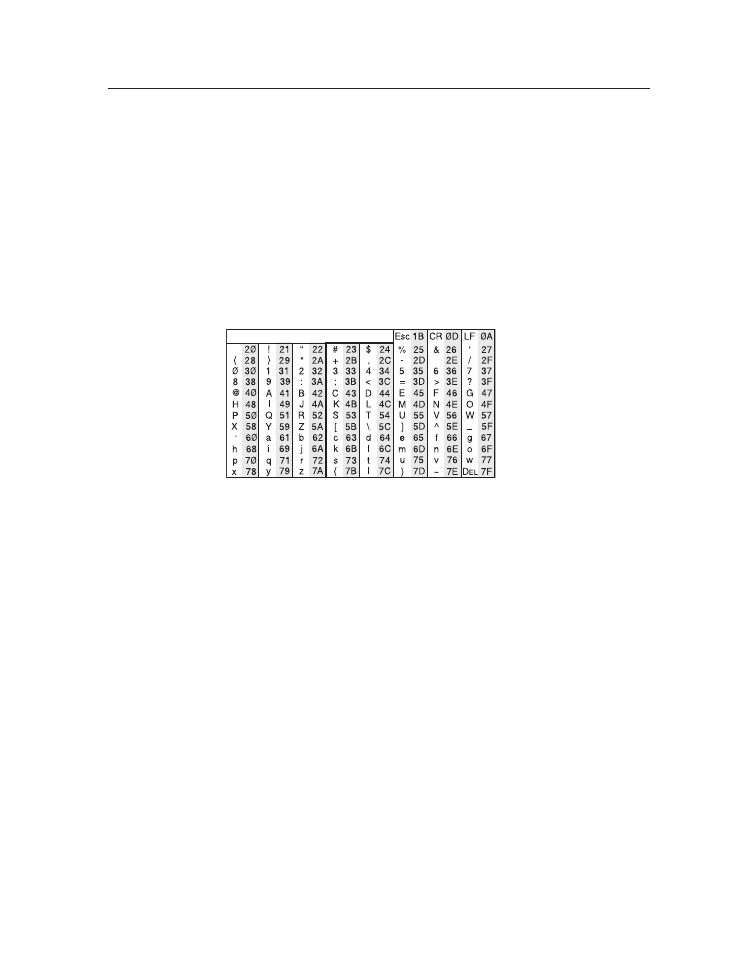
The ASCII to hexadecimal (hex) character conversion table below is for use with the
Command/response table for SIS commands, beginning on page 4-10.
ASCII to HEX Conversion Table
•
ASCII to hexadecimal character conversion table
The command/response tables list valid ASCII (for Telnet) command codes, the
corresponding URL encoded (for Web browsers) command codes, the processor’s
responses to the host, and a description of the command’s function or results from
executing the command.
• Upper- and lowercase letters may be used interchangeably in the command
field unless otherwise specified.
• Commands may be sent back-to-back without spaces; for example, 2*2!2*0B.
• Numbers can be entered as 1 digit, or as 2 or 3 digits with leading zeros; for
example, 8V = 08V = 008V.
• There are a few differences in how to enter the commands depending on
whether you are using Telnet or a Web browser.
m
For control via a Web browser, all non-alphanumeric characters must be
represented as the hexadecimal equivalent, %xx, where xx represents the
two-character hex byte. For example, a comma (,) would be represented
as %2C.
m
When using these commands through a Web browser, the URL reference
is used to shorten the examples. “URL” refers to the full URL of the
control interface and Web page reference, including all path information;
for example, http://192.168.100.10/myform.htm.
