1 spi timing description, And t – Rainbow Electronics AT86RF231 User Manual
Page 17
17
8111A–AVR–05/08
AT86RF231
6.1
SPI Timing Description
Pin 17 (CLKM) can be used as a microcontroller master clock source. If the microcontroller
derives the SPI master clock (SCLK) directly from CLKM, the SPI operates in synchronous
mode, otherwise in asynchronous mode.
In synchronous mode, the maximum SCLK frequency is 8 MHz.
In asynchronous mode, the maximum SCLK frequency is limited to 7.5 MHz. The signal at pin
CLKM is not required to derive SCLK and may be disabled to reduce power consumption and
spurious emissions.
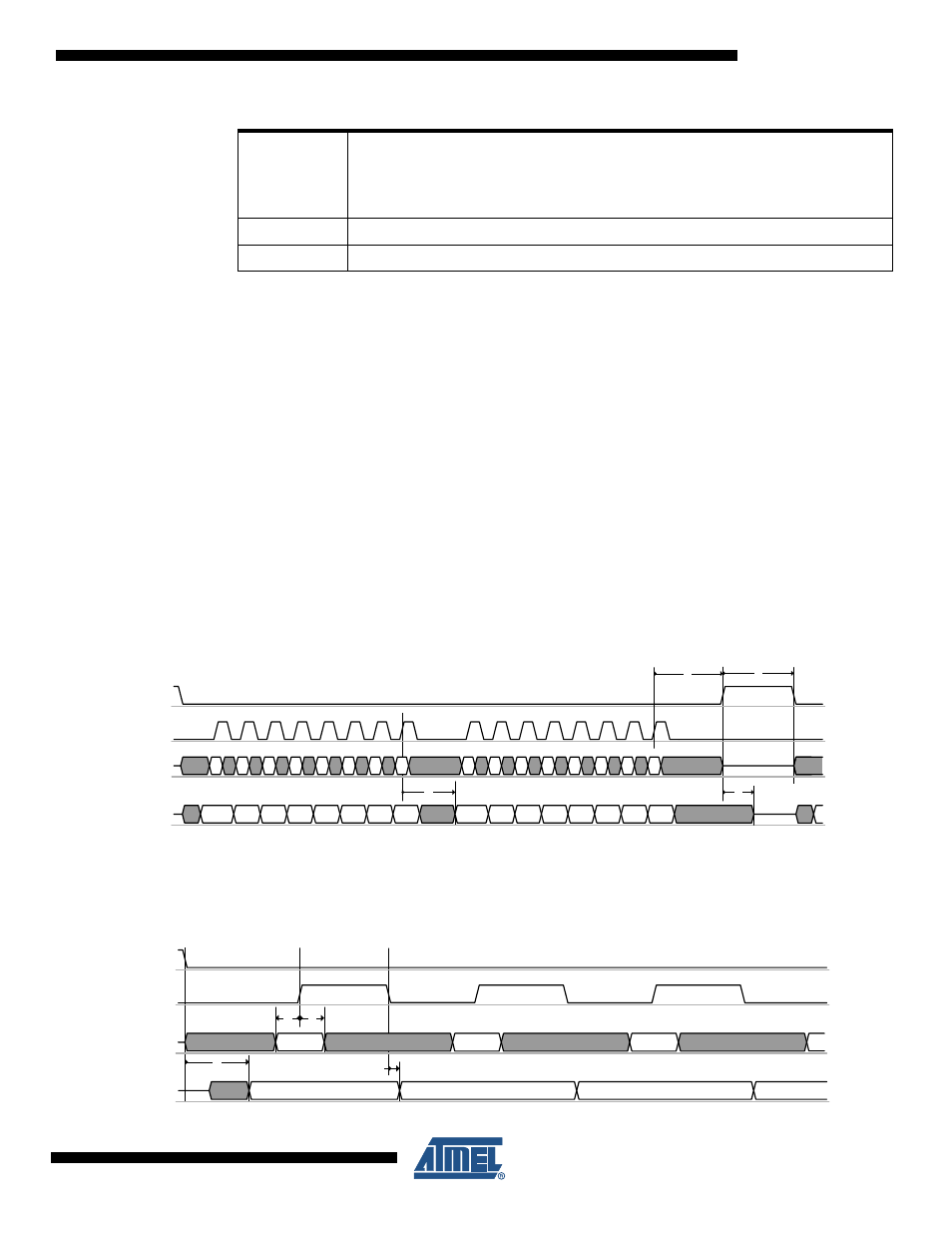
and
illustrate the SPI timing and introduces its
parameters. The corresponding timing parameter definitions t
1
- t
9
“Digital Interface Timing Characteristics” on page 157
Figure 6-2.
SPI Timing, Global Map and Definition of Timing Parameters t
5
, t
6
, t
8
and t
9
Figure 6-3.
SPI Timing, Detailed Drawing of Timing Parameter t
1
to t
4
SLP_TR
Multipurpose control signal (functionality is state dependent, see
-Sleep/Wakeup
enable/disable SLEEP state
-TX
start
BUSY_TX_(ARET) state
-disable/enable CLKM
RX_(AACK)_ON state
/RST
AT86RF231 reset signal, active low
DIG2
Optional, IRQ_2 (RX_START) for RX Frame Time Stamping, see
Table 6-1.
Signal Description of Microcontroller Interface (Continued)
SCLK
t
8
MOSI
6
7
5
4
3
2
1
0
6
7
5
4
3
2
1
0
MISO
Bit 6 Bit 5
Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Bit 4
Bit 6 Bit 5
Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Bit 4
Bit 7
t
6
Bit 7
t
5
/SEL
t
9
Bit 7
Bit 6
t
1
t
2
Bit 5
t
4
t
3
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
SCLK
MOSI
MISO
/SEL
