Spanning-tree – Planet Technology SGSD-1022 User Manual
Page 542
User’s Manual of SGSD-1022 / SGSD-1022P
SGSW-2840 / SGSW-2840P
542
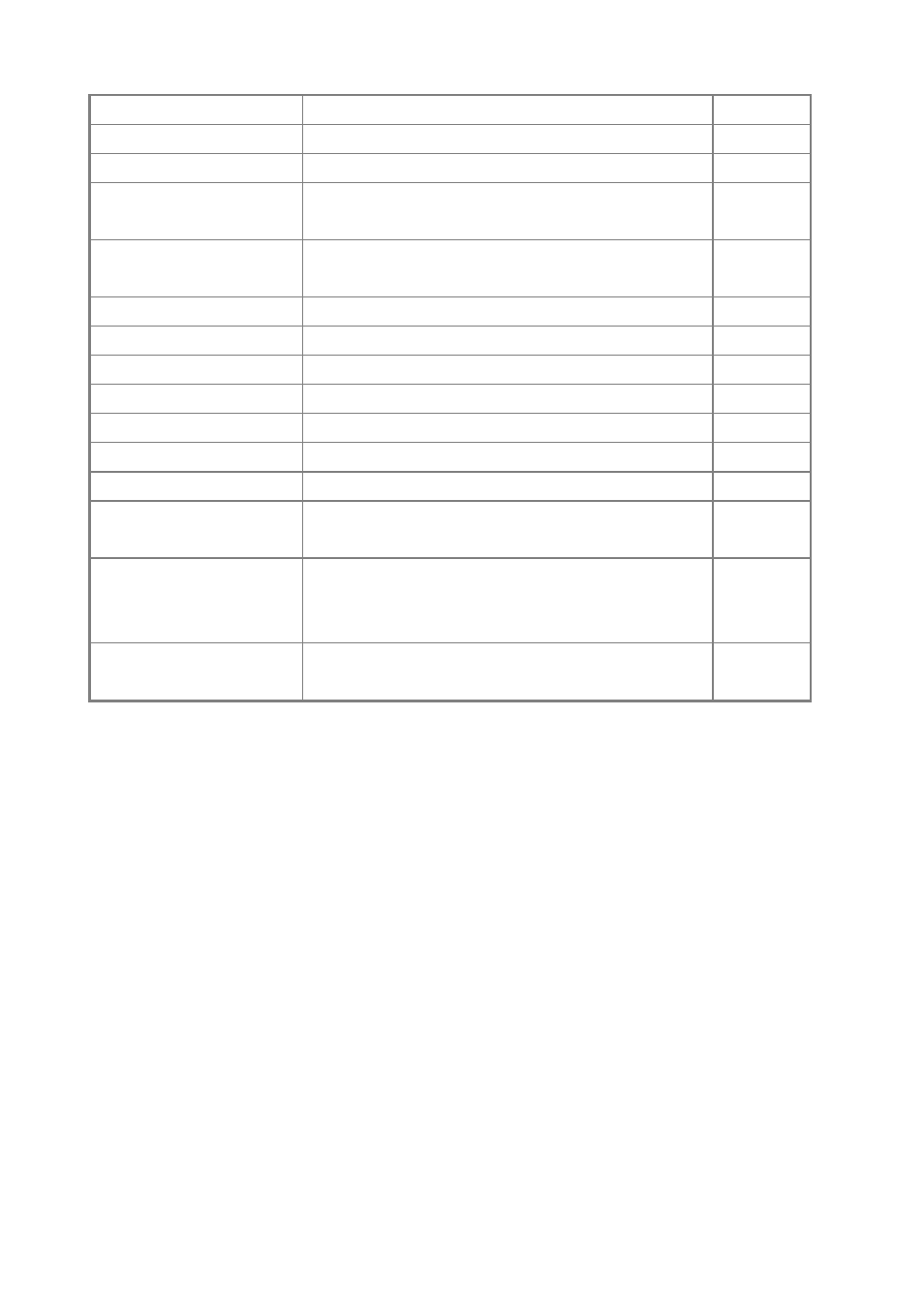
mst priority
Configures the priority of a spanning tree instance
MST
name
Configures the name for the multiple spanning tree
MST
revision
Configures the revision number for the multiple spanning tree
MST
max-hops
Configures the maximum number of hops allowed in the region
before a BPDU is discarded
MST
spanning-tree
spanning-disabled
Disables spanning tree for an interface
IC
spanning-tree cost
Configures the spanning tree path cost of an interface
IC
spanning-tree port-priority
Configures the spanning tree priority of an interface
IC
spanning-tree edge-port
Enables fast forwarding for edge ports
IC
spanning-tree portfast
Sets an interface to fast forwarding
IC
spanning-tree link-type
Configures the link type for RSTP/MSTP
IC
spanning-tree mst cost
Configures the path cost of an instance in the MST
IC
spanning-tree mst port-priority
Configures the priority of an instance in the MST
IC
spanning-tree
protocol-migration
Re-checks the appropriate BPDU format
PE
show spanning-tree
Shows spanning tree configuration for the common spanning
tree (i.e., overall bridge), a selected interface, oran instance
within the multiple spanning tree
PE
show spanning-tree mst
configuration
Shows the multiple spanning tree configuration
PE
Table 5-62 Spanning Tree Commands
spanning-tree
This command enables the Spanning Tree Algorithm globally for the switch. Use the no form to disable it.
Syntax
[no] spanning-tree
Default Setting
Spanning tree is enabled.
Command Mode
Global Configuration
Command Usage
The Spanning Tree Algorithm (STA) can be used to detect and disable network loops, and to provide backup links
between switches, bridges or routers. This allows the switch to interact with other bridging devices (that is, an
STA-compliant switch, bridge or router) in your network to ensure that only one route exists between any two stations on
the network, and provide backup links which automatically take over when a primary link goes down.
Example
