3 snmpv3, 1 snmpv3 engine id – Planet Technology SGSD-1022 User Manual
Page 101
User’s Manual of SGSD-1022 / SGSD-1022P
SGSW-2840 / SGSW-2840P
101
These are legacy notifications and therefore when used for SNMP Version 3 hosts, they
must be enabled in conjunction with the corresponding entries in the Notification View
4.3.3 SNMPv3
Configuring SNMPv3 Management Access
To configure SNMPv3 management access to the switch, follow these steps:
1.
If you want to change the default engine ID, it must be changed first before configuring other parameters.
2.
Specify read and write access views for the switch MIB tree.
3.
Configure SNMP user groups with the required security model (i.e., SNMP v1, v2c or v3) and security level (i.e.,
authentication and privacy).
4.
Assign SNMP users to groups, along with their specific authentication and privacy passwords.
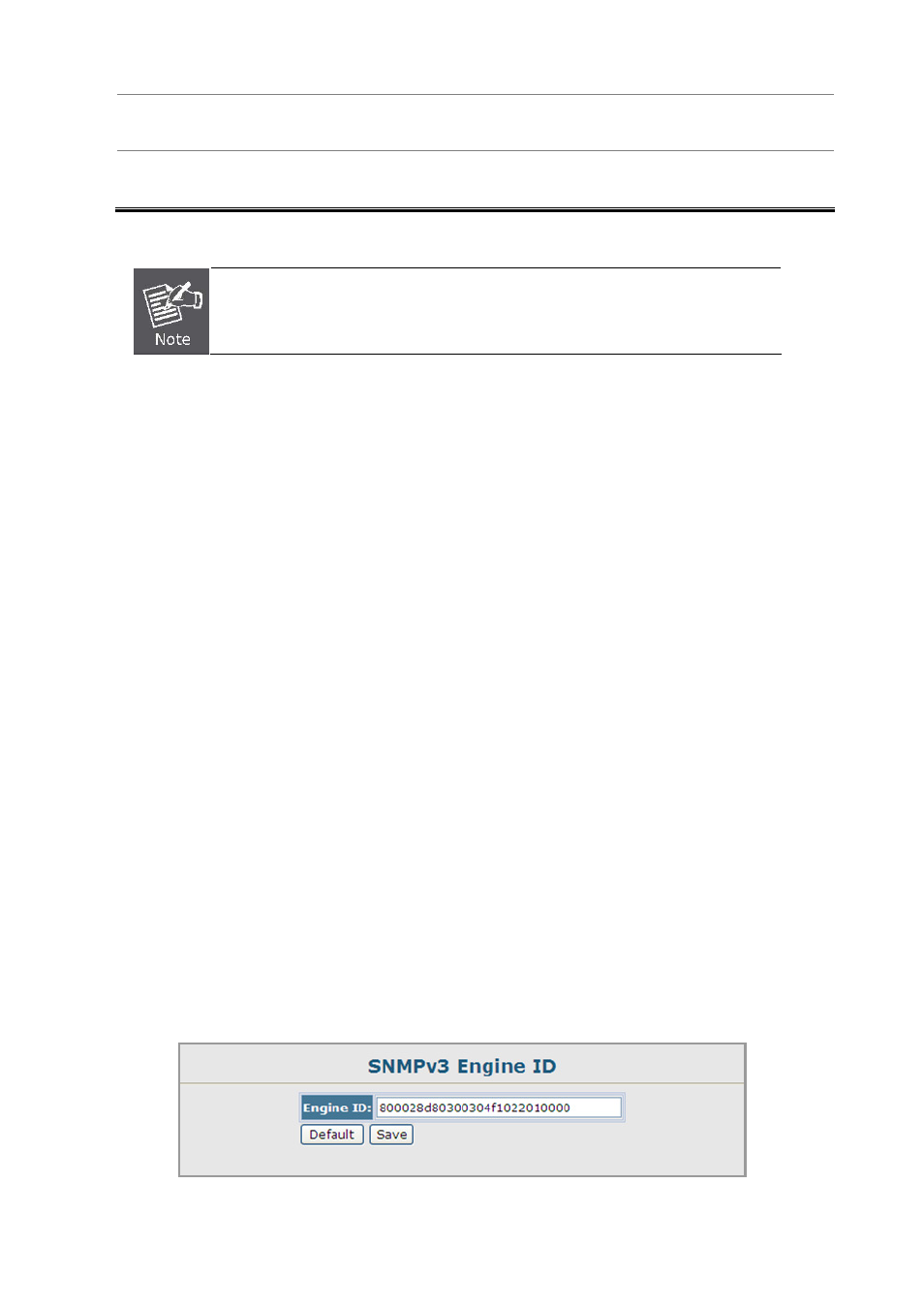
4.3.3.1 SNMPv3 Engine ID
A SNMPv3 engine is an independent SNMP agent that resides on the switch. This engine protects against message replay,
delay, and redirection. The engine ID is also used in combination with user passwords to generate the security keys for
authenticating and encrypting SNMPv3 packets.
A local engine ID is automatically generated that is unique to the switch. This is referred to as the default engine ID. If the local
engine ID is deleted or changed, all SNMP users will be cleared. You will need to reconfigure all existing users.
A new engine ID can be specified by entering 10 to 64 hexadecimal characters. If an odd number of characters are specified,
the last character is dropped. For example, entering the value “12345678901” sets the engine ID as “1234567890”.
Figure 4-3-4 SNMPv3 Engine ID page screenshot
Traps
community string is submitted during the SNMP access authentication process.
(Default: Enabled)
• Enable Link-up and
Link-down Traps
Issues a notification message whenever a port link is established or broken.
(Default: Enabled)
