Table 3 parts to be measured – Hitachi J300U Series User Manual
Page 87
10-6
Table 3 Parts to be measured
Measurement
item
Parts to be
measured
Measuring instrument
Remarks
Reference
value
Supply voltage
E
1
Supply current
I
1
Supply power
W
1
Supply power
factor
Pf
1
Output voltage
E
0
Output current
I
0
Output power
W
0
Output power
factor
Pf
0
Moving-iron type
voltmeter or rectifier
type voltmeter
Fundamental
wave effective
value
Moving-iron type
ammeter
Total effective
value
Electrodynamic type
wattmeter
Total effective
value
Calculate the supply power factor from the measured supply voltage, E
1
,
supply current I
1
and supply power W
1
.
Between U and V, V and
W, W and U
(E
U
)(E
V
)(E
W
)
Rectifier type
voltmeter
Total effective
value
U, V, W (I
U
)(I
V
)(I
W
)
Moving-iron type
ammeter
Total effective
value
Between U and V, V
and W
(W
01
)(W
02
)
Electronic type
wattmeter
Total effective
value
Calculate the output power factor from the output voltage E, output current I,
and output power W.
Pf
1
=
× 100 (%)
3 E
1
I
1
W
1
Pf
0
=
× 100(%)
3 E
0
I
0
W
0
W
11
W
12
E
R
E
S
E
T
U
General
purpose
inverter
Power
supply
Motor
V
W
U(T1)
W
01
W
02
I
U
I
V
I
W
E
U-V
E
V-W
E
W-V
W
V
R
T
S
I
R
I
S
R
T
S
I
T
Between R and S, S and
T, T and R (E
R
)(E
S
)(E
T
)
R, S, T (I
R
)(I
S
)(I
T
)
Between R and S, S and
T (W
11
)(W
12
)
(L1)
(L2)
(L3)
(T2)
(T3)
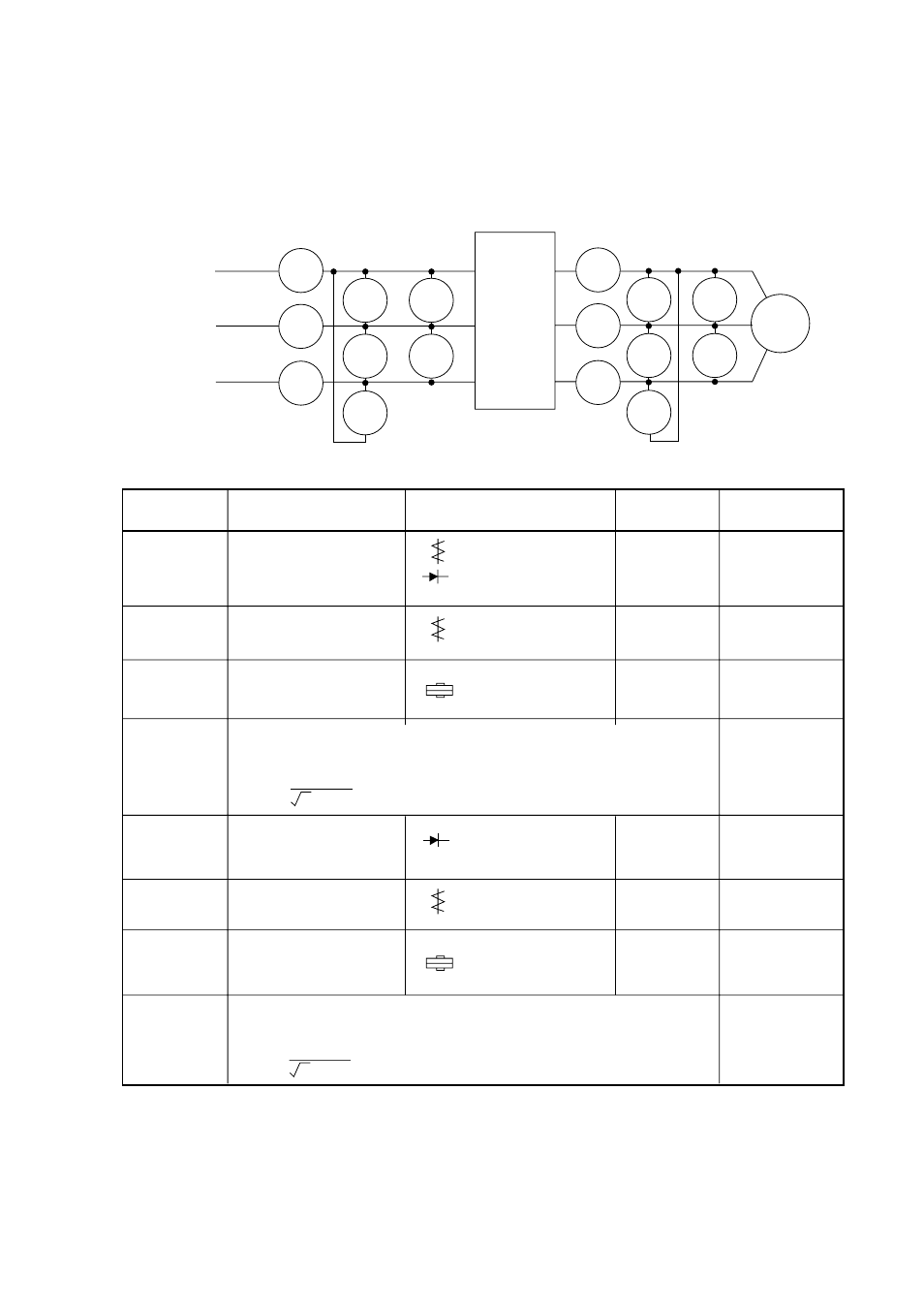
10.3
Measurement Method for I/O Voltage, Current, and Power
General measuring instruments for I/O voltage, current, and power are indicated below. The
voltage to be measured is the fundamental wave effective voltage and the power to be meas-
ured is the total effective value.
NOTE 1: Use a meter indicating a fundamental wave effective value for voltage, and meters
indicating total effective values for current and power.
NOTE 2: The inverter output waveform is a distorted wave, and low frequencys may cause
errors. However, the measuring instruments and methods indicated above provide
comparatively accurate values.
NOTE 3: A tester (general purpose) may not be suited often to measurement of a distorted
wave.
