Pid loop setup – Super Systems 9205 Series User Manual
Page 29
Series 9205 Operations Manual Rev A
28
Digital IN 4 Assignment: The value for the digital input 4 assignment. Clicking on the value will allow the
user to change the value, which can be either event or Start Burnoff.
Burnoff Minimum Millivolts Alarm Setpoint: The minimum millivolt value that must be reached in order for
the “Insufficient mV drop during BO” alarm not to be generated. If the millivolt value does not drop below
the minimum, the alarm will be generated.
Burnoff Maximum Temperature Rise Limit: The maximum number of degrees that the temperature is
allowed to increase before the “Excessive TC rise during BO” alarm is generated.
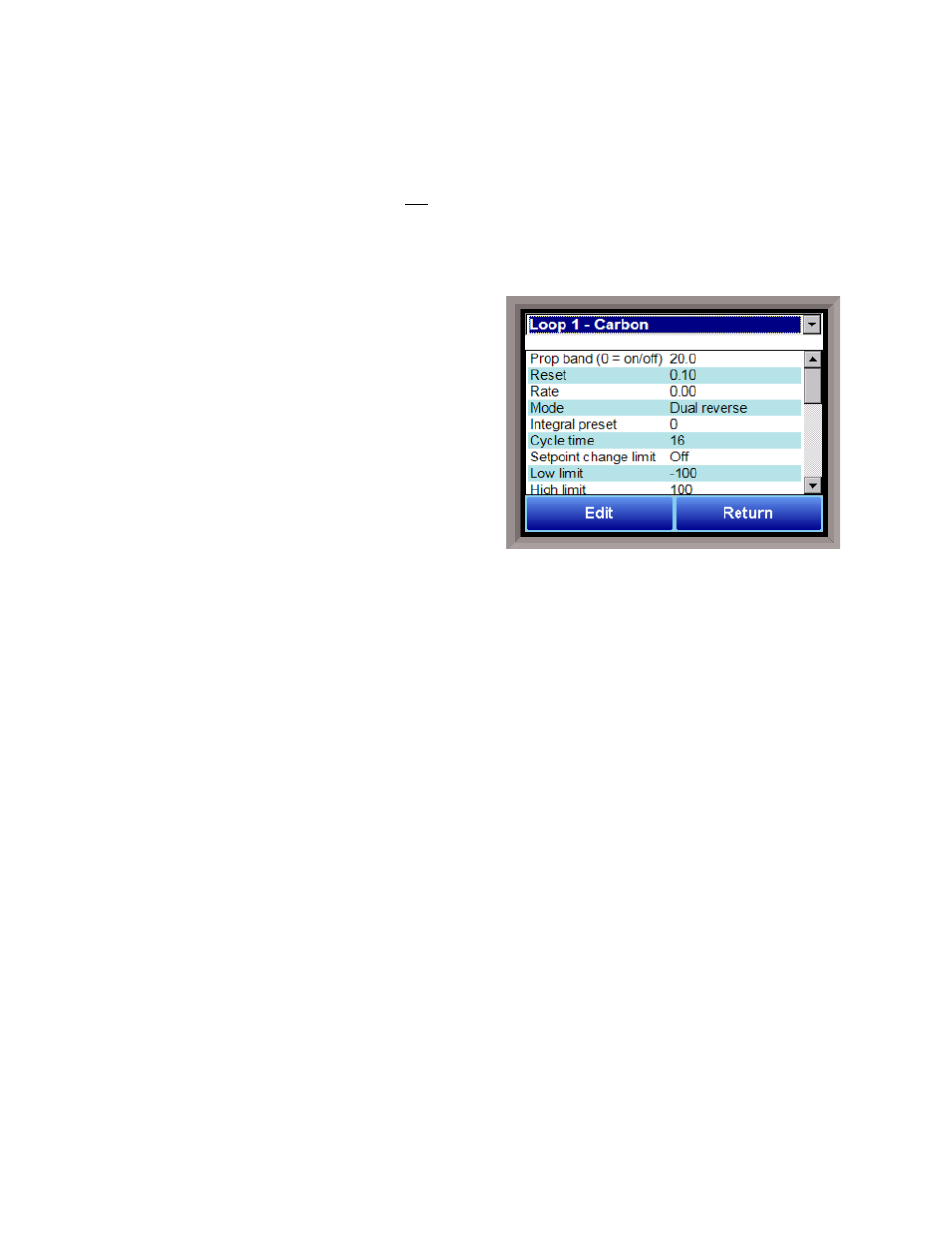
PID Loop Setup
PID is the tuning parameters entered for each Process
Variable loop.
Prop Band (0 for On/Off)
Proportional Band determines the response to the
current error. The Proportional Band is the percent of
the range of the process variable that will produce
100% output and is the inverse of the proportional gain.
A low Proportional Band value results in a larger
change in output for a given error. Conversely, a high
Proportional Band value results in a smaller change in
output for a given error. If the Proportional Band is too
small, control may oscillate or be otherwise unstable.
If the Proportional Band is too large the control action may be too sluggish in response to changes within
the system. Note: If the Proportional Band is set to 0.0, only on/off control is performed. The range 0 –
3276.0.
Reset
Reset determines the influence of past errors. The Reset, or integral action (expressed in repeats per
minute), sums the error between the process variable and setpoint over time and adds this accumulated
output to the proportional output. A “proportional only” controller generally operates with steady-state
error because some error is required to produce control output. The goal of integral action is to drive the
steady-state error to zero and eliminate this droop.
The range 0 – 327.67.
Rate
Rate adjusts the response to future errors.
The Rate, or derivative action (expressed in minutes), is used to
predict system behavior and has a dampening effect. The more the controller tries to change the process
variable the harder the derivative will work to counter that effort. This dampening effect can be valuable in
reducing overshoot but is most often useful when trying to improve control on systems with significant and
predicable lag.
The range 0 – 327.67. NOTE: The rate is not typically used for carbon control.
Control Mode
This is the mode of the loop. The values are: Dual Reverse, Single Reverse, Dual Direct, or Single Direct.
Dual – This has two output relays which can increase and decrease to achieve the SP.
Single – This has one relay which works in only one direction to achieve the SP.
Direct - If the PV - SP equals a positive number and the output would bring the PV down toward setpoint
that is direct.
Reverse – If the PV - SP equals a negative number and the output would bring the PV up toward setpoint
then that is reverse
