Flow control operation example, Selecting the proper threshold value – Altera SerialLite II IP Core User Manual
Page 41
3–18
Chapter 3: Parameter Settings
Link Layer Configuration
SerialLite II MegaCore Function
January 2014
Altera Corporation
User Guide
Flow Control Operation Example
shows an example of a flow control operation.
Selecting the Proper Threshold Value
defines the specification value for flow control internal latency,
as mentioned in the previous example. Use this information to determine the
minimum FIFO threshold size avoiding starvation during the flow control.
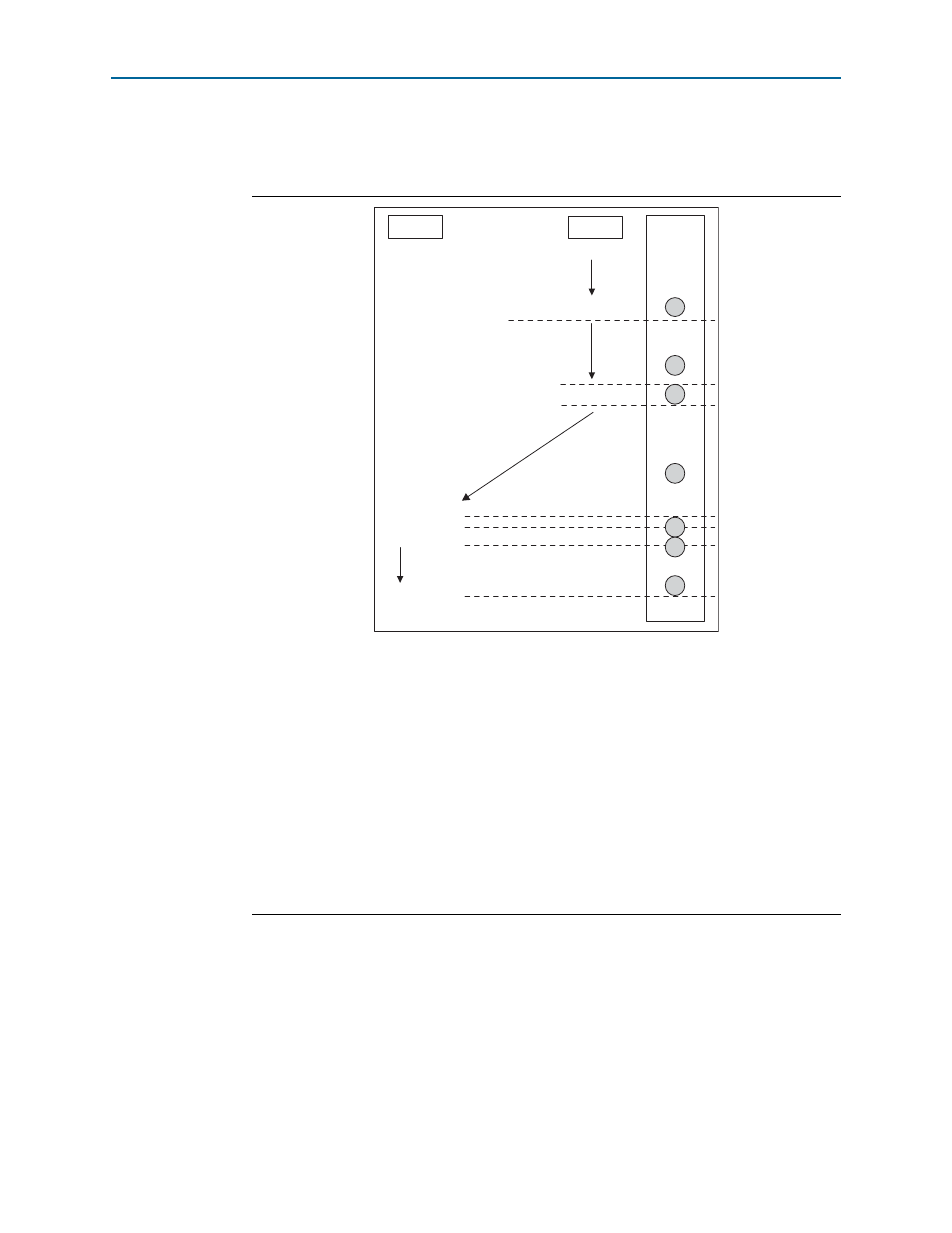
Figure 3–12. Typical Flow Diagram of FC Operation
Notes to
(1) Near transmitter starts sending data to far receiver when the link is up. The FIFO inside the far receiver reads the data.
When the user logic on the receiving end of the link is reading the data out of the FIFO slower than the rate at which
the data is being written into the FIFO, the FIFO starts to fill.
(2) The far receiver FIFO fill level breaches the flow control threshold value.
(3) The far transmitter generates and sends the flow control packet with a FC_TIME pause request amount. There is some
internal transmit latency (tlate_fc_transmit) for the flow control packet to hit the serial link.
(4) The flow control packet reaches the near receiver after some wire delay period (t_wd).
(5) There is some latency for the flow control packet to come from the serial link until the near receiver completes
processing the packet (tlate_fc_receive).
(6) The near transmitter stops sending data to the far receiver either as soon as the flow control packet is received, or
after the current active segment has been sent (for Priority packet with Retry-on Error enabled) for the specified
pause duration. This latency accounts for the amount of additional data that has been already transmitted before the
PAUSE
request was received (tlate_stop_data).
(7) After the pause quantum time specified by the users expires, the pause stops and the near transmitter continues
sending the data (assuming that no other pause requests have been received).
Near End
Far End
Data transmitted by
Near Transmitter
Read Ongoing
Time
1
3
4
2
7
FIFO read rate < Data transmit rate
FIFO fills
Threshold hits;
Pause generated and transmitted
by Far Transmitter
5
6
Pause received by Near Receiver;
Pause starts,
Near Transmitter stops sending data
Pause count expires,
Near Transmitter resumes sending data
Wire delay
