Performing simple point aggregation – Pitney Bowes MapInfo Vertical Mapper User Manual
Page 178
Simple Point Aggregation
176
Vertical Mapper 3.7
Performing Simple Point Aggregation
You can use simple point aggregation to quickly group points that are virtually coincident or that are
separated by relatively small gaps.
1. From the Vertical Mapper menu, choose the Data Aggregation > Simple Point Aggregation
command.
2. From the Select Table to Aggregate list in the Select Table and Column dialog box, choose a
point table.
3. From the Select Column list, choose a column of data to transfer to the aggregated file.
4. Enable the Ignore Records Containing Zero check box to include only non-zero records.
5. Click the Next button.
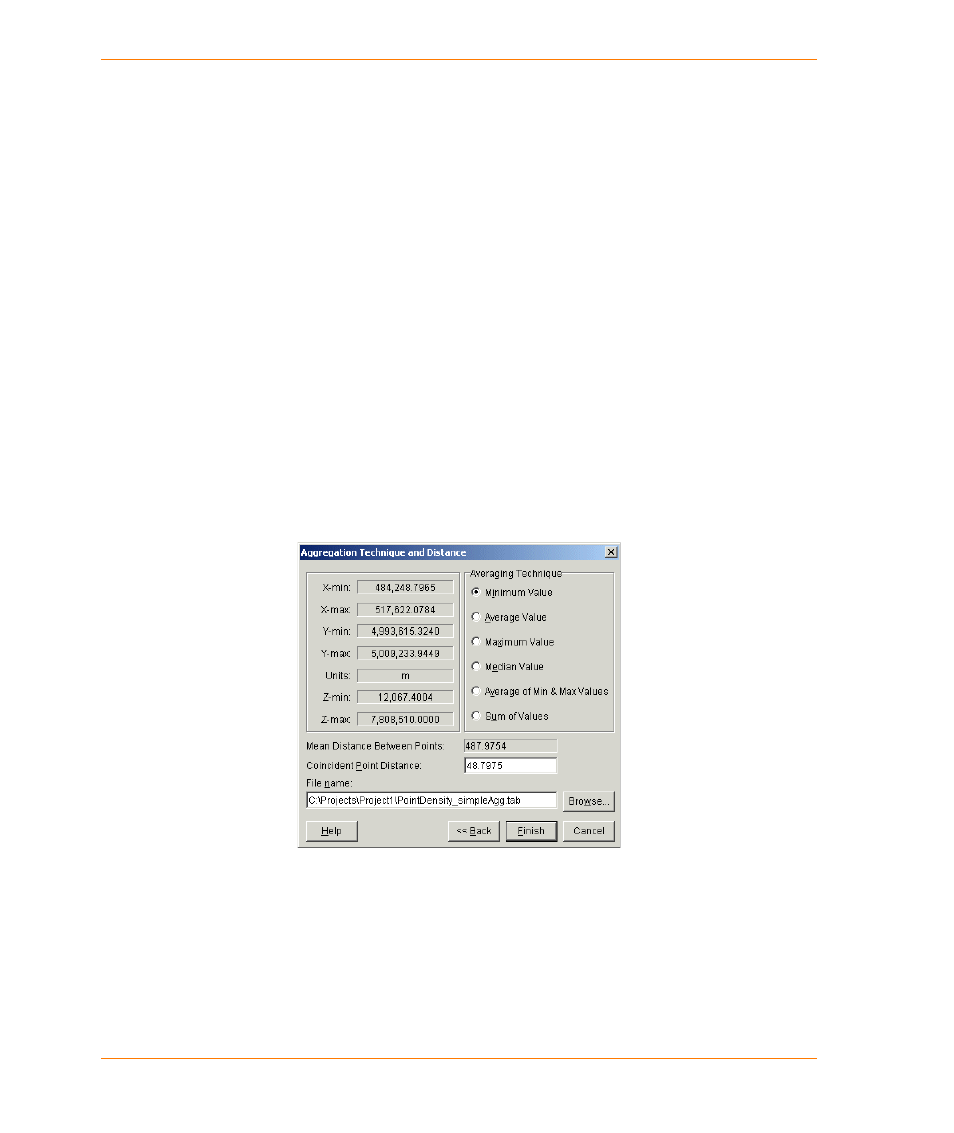
6. In the Aggregation Technique and Distance dialog box, choose an averaging technique.
7. In the File Name box, type a new file name or accept the default.
8. Click the Finish button.
Exploring the Aggregation Technique and Distance Dialog Box
The left side of the Aggregation Technique and Distance dialog box summarizes the spatial
characteristics of the point file including the file extents, the z-value range, and the coordinate
system units. The right side of the dialog box contains settings that control the statistical processing
of the passed values.
The Averaging Technique section enables you to choose one of six statistical methods to
determine the z-value of the aggregated points.
•
Minimum Value: The minimum value is the lowest value within the “same point” distance of the
aggregated coordinate.
•
Average Value: The average value is determined by averaging all valid points within the “same
point” distance of the aggregated coordinate.
•
Maximum Value: The maximum value is the highest value within the “same point” distance of
the aggregated coordinate.
