Simple point aggregation – Pitney Bowes MapInfo Vertical Mapper User Manual
Page 177
Chapter 10: Aggregating Data
User Guide
175
Simple Point Aggregation
Simple point aggregation is useful for quickly grouping points that are virtually coincident or that are
separated by relatively small gaps. For example, when soil samples are collected, you may need to
take several samples at each sample site. When creating a surface of this data, you may want to
average all of the samples taken at each site before proceeding with the surface creation. It may
also be desirable to aggregate data that has poor reproducibility over a large area and achieve a
more smoothing or averaging effect.
Simple point aggregation is also used as a preliminary data smoothing technique for TIN creation in
the Triangulation with smoothing interpolation method, for natural neighbour region creation in the
natural neighbour interpolation method, and in the kriging interpolation. Here, highly variable data
points spaced closely together can be aggregated and new values calculated using a statistical
expression. For example, if two points are very closely spaced, even a small difference in z-value
will generate a steep slope between them. This slope affects the interpolated surface for a significant
distance beyond the two points, creating unwanted rises and dips.
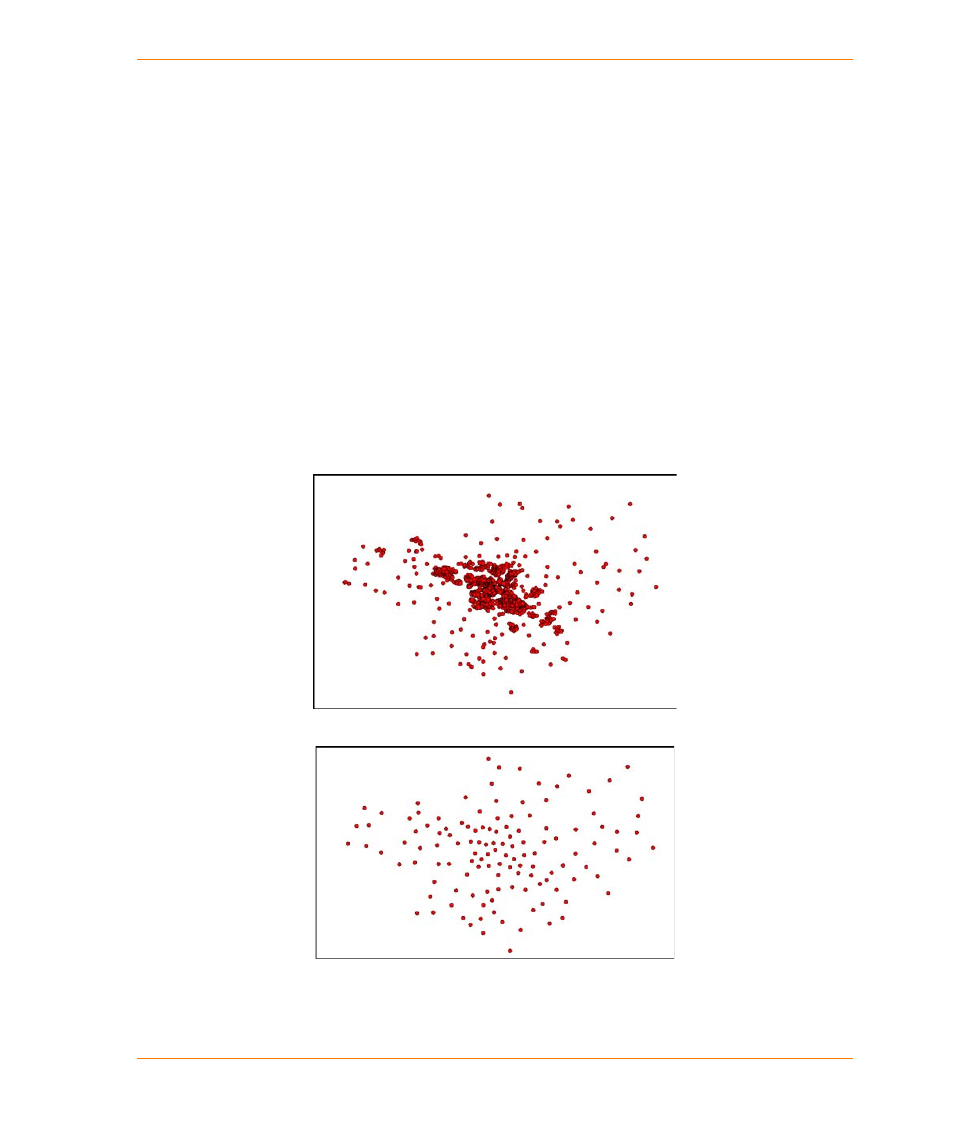
Simple point aggregation uses a coincident point distance value for spatially aggregating points.
This means you need to specify how close the points will be before they are considered coincident.
The result of simple point aggregation is shown in the next two figures.
Original distribution of points.
Distribution of points after simple point aggregation.
