Interlogix NS3502-8P-2S User Manual User Manual
Page 115
IFS NS3502-8P-2S User Manual
115
VLAN can also provide a level of security to your network. IEEE 802.1Q VLAN will only deliver packets
between stations that are members of the VLAN. Any port can be configured as either tagging or
untagging.
The untagging feature of IEEE 802.1Q VLAN allows VLAN to work with legacy switches that don't
recognize VLAN tags in packet headers.
The tagging feature allows VLAN to span multiple 802.1Q-compliant switches through a single
physical connection and allows Spanning Tree to be enabled on all ports and work normally.
Some relevant terms:
-
Tagging - The act of putting 802.1Q VLAN information into the header of a packet.
-
Untagging - The act of stripping 802.1Q VLAN information out of the packet header.
■
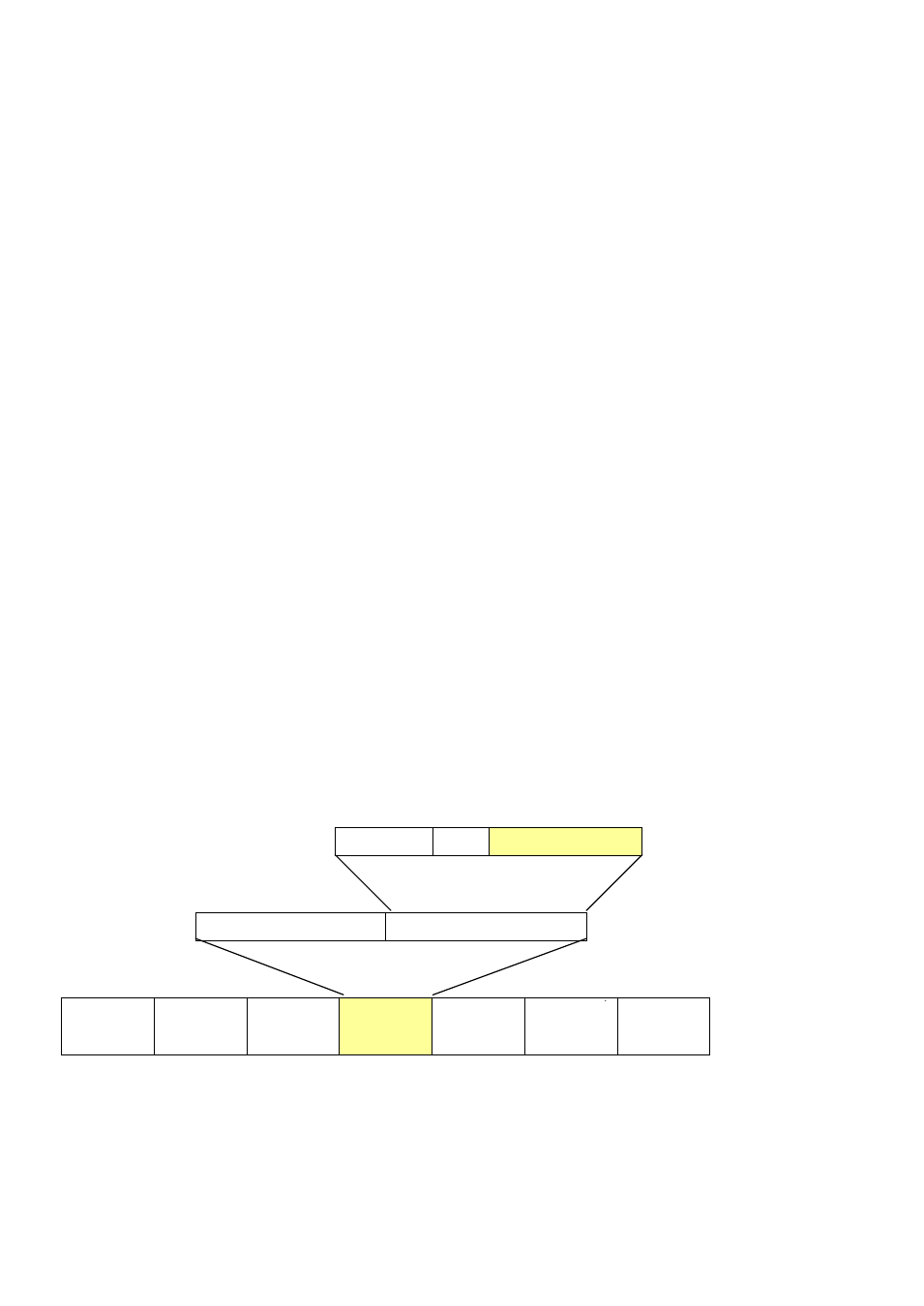
802.1Q VLAN Tags
The figure below shows the 802.1Q VLAN tag. There are four additional octets inserted after the source
MAC address. Their presence is indicated by a value of 0x8100 in the Ether Type field. When a packet's
Ether Type field is equal to 0x8100, the packet carries the IEEE 802.1Q/802.1p tag. The tag is contained
in the following two octets and consists of 3 bits of user priority, 1 bit of Canonical Format Identifier
(CFI - used for encapsulating Token Ring packets so they can be carried across Ethernet backbones),
and 12 bits of VLAN ID (VID). The 3 bits of user priority are used by 802.1p. The VID is the VLAN
identifier and is used by the 802.1Q standard. Because the VID is 12 bits long, 4094 unique VLAN can be
identified.
The tag is inserted into the packet header making the entire packet longer by 4 octets. All of the
information originally contained in the packet is retained.
802.1Q Tag
User Priority
CFI
VLAN ID (VID)
3 bits
1 bits
12 bits
TPID (Tag Protocol Identifier)
TCI (Tag Control Information)
2 bytes
2 bytes
Preamble
Destination
Address
Source
Address
VLAN TAG
Ethernet
Type
Data
FCS
6 bytes 6 bytes
4 bytes 2 bytes
46-1500 bytes
4 bytes
The Ether Type and VLAN ID are inserted after the MAC source address, but before the original Ether
Type/Length or Logical Link Control. Because the packet is now a bit longer than it was originally, the
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) must be recalculated.
