14< principle of operation, Toshiba, Figure 14.1 principle of operation – Toshiba LF494 User Manual
Page 143
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
TOSHIBA
6 F 8 A 0 7 7 4
14< Principle of Operation
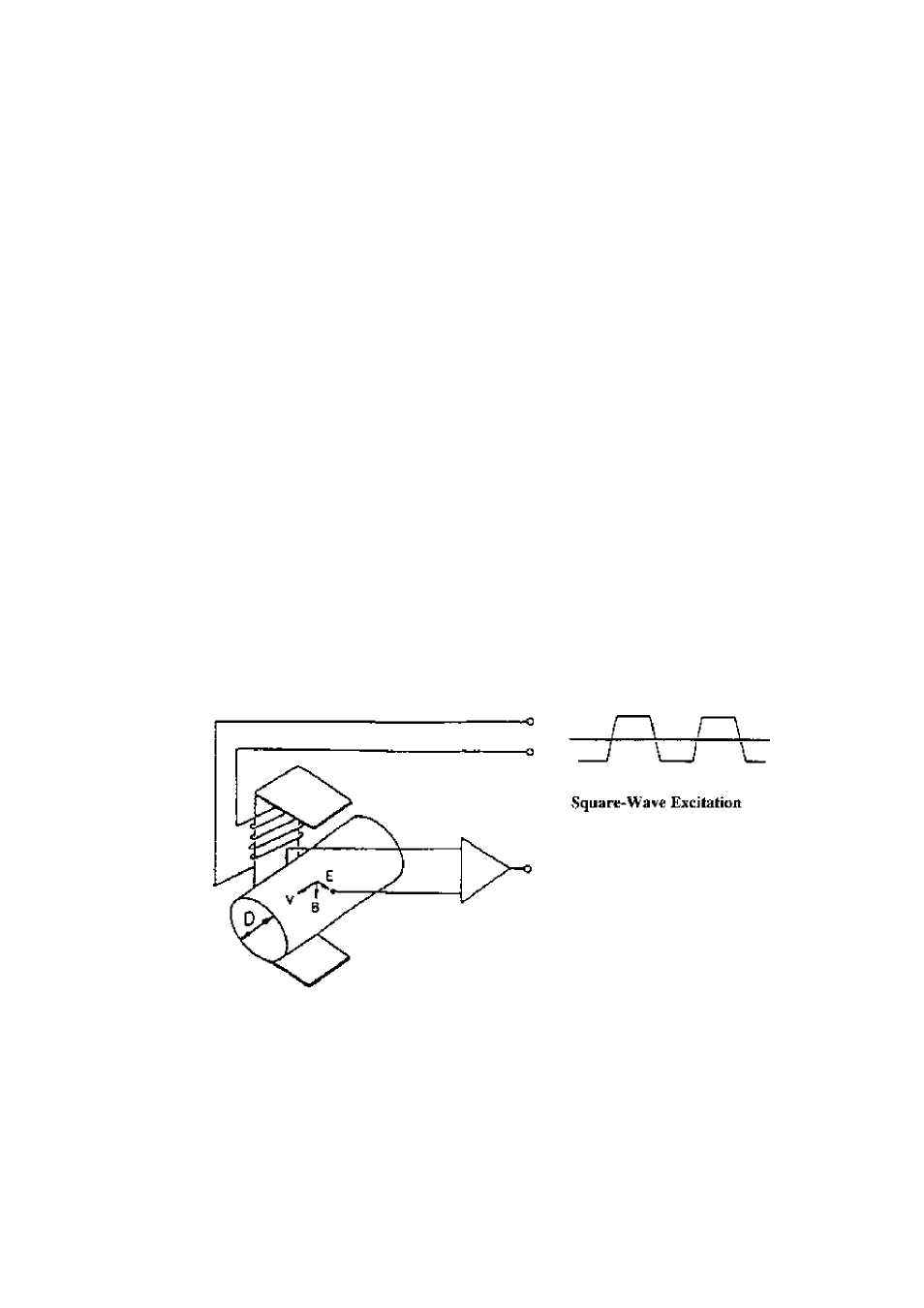
The opori^tiiig principle of the electromagnetic flowmeter is based on Faraday's T^w of
electromagjiciic induction and it is designed to measure the volumetric flow rate of fluid. An
insulated pipe of diameter D is placed vertically lo ihe direction of a magnelic field with
flux density B (see Figure 14.]), When an electrically conductive fluid flows in the ptpe^ an
electrode voltage E is induced between a pair of electrodes placed at right angles to the
direction of magnetic field. The electrode voltage E is directly proportional to the average
fluid velocity V.
The following expression is applicable to the voltage.
E = K x B x D x V [ V ] ...... {Eq. U,l)
Volumetric flow rate Q [mVs] is:
Q =
X V ...................... (Eq. 14.2)
\ 1 =
induced electrode voltage [V]
K = constant
B = magnetic flux density ['!']
D = meter pipe diameter [mj
V = fluid velocity [ni''s]
Using the Equation 14.1 and 14.2
4
E = K x T 3 x D x
71
x Q
...........(Eq,14.3)
X D
Therefore, volumetric flow rate is directly proportional to the induced voltage.
Figure 14.1 Principle of Operation
The 1.F494/LF404 electromagnetic flowmeter uses the square-wave excitation method,
which provides long-term stable operation. With square-wave c.xcitation, the LI 494/LF404
offers reliable measurement without being affected by clcclrostatio or electromagnetic
interference, or electroehcniical polarization bclwccii the electrodes and the fluid to be
measured.
-
142 -
