Figure 13 – Rockwell Automation 20B PowerFlex 70, PowerFlex 700 Reference Manual User Manual
Page 58
Bus Regulation
58
Rockwell Automation Publication PFLEX-RM001H-EN-P - June 2013
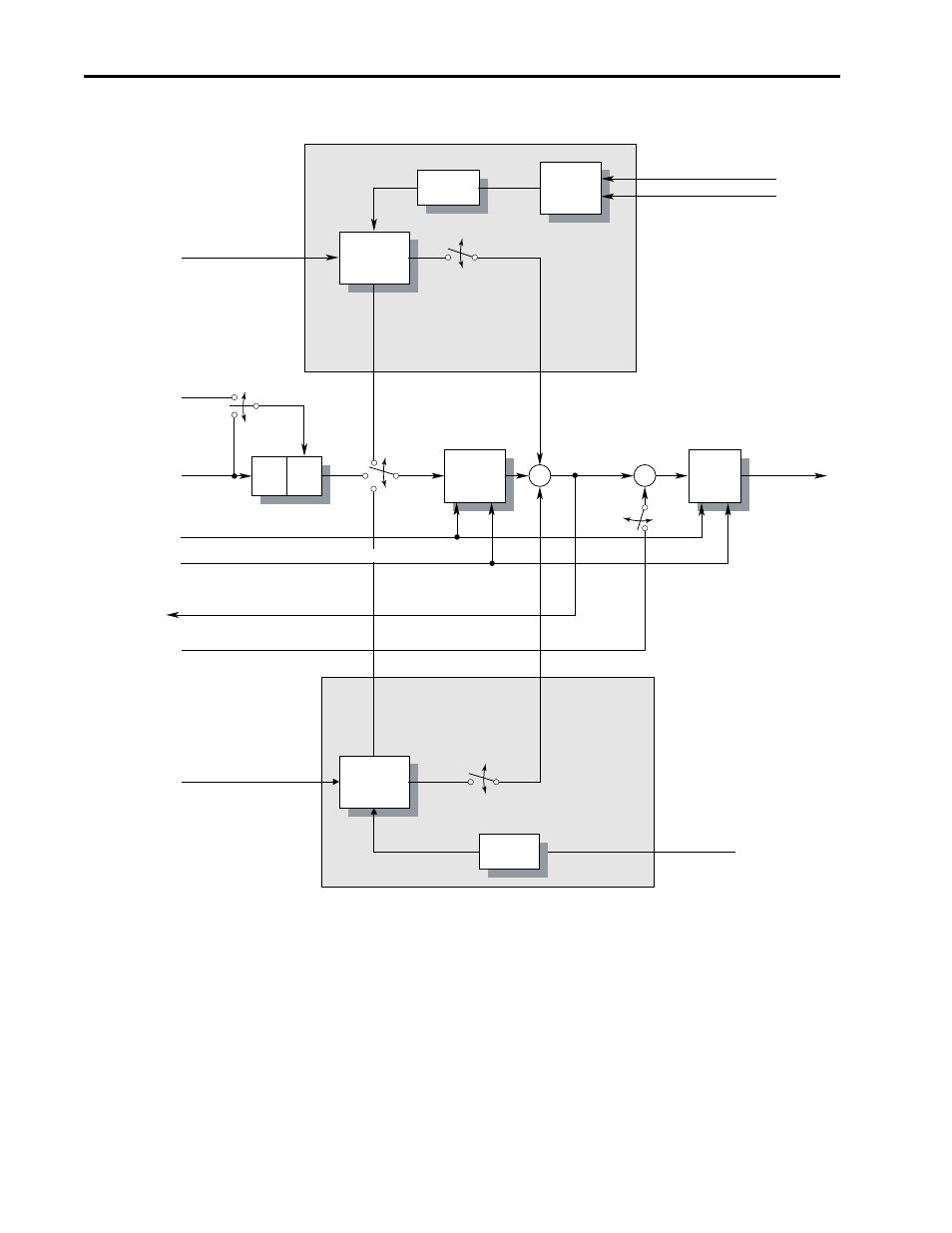
Figure 13 Bus Voltage Regulator, Current Limit and Frequency Ramp.
The derivative term senses a rapid rise in the bus voltage and activates the bus
regulator prior to actually reaching the bus voltage regulation set point Vreg. The
derivative term is important since it minimizes overshoot in the bus voltage when
bus regulation begins thereby attempting to avoid an over-voltage fault. The
integral channel acts as the acceleration or deceleration rate and is fed to the
frequency ramp integrator. The proportional term is added directly to the output
of the frequency ramp integrator to form the output frequency. The output
frequency is then limited to a maximum output frequency.
Bus voltage regulation is the highest priority of the three components of this
controller because minimal drive current will result when limiting the bus voltage
and therefore, current limit will not occur.
Bus Voltage Regulator
Current Limit
Magnitude
Calculator
Frequency
Ramp
(Integrator)
Frequency
Limits
Current Limit Level
U Phase Motor Current
W Phase Motor Current
Propor
tion
al Ch
annel
Frequency
Reference
Acc/Dec Rate
Integ
ra
l Ch
annel
Bus Reg
I Limit,
No Bus Reg
Propor
tion
al Ch
annel
I Limit,
No Bus Reg
Maximum Frequency, Minimum Speed, Maximum Speed, Overspeed Limit
Frequency Set Point
+
+
+
+
+
Output Frequency
Frequency Reference (to Ramp Control, Speed Ref, etc.)
Speed Control (Slip Comp, Process PI, etc)
Bus Voltage Regulation Point, V
reg
Bus Reg On
Bus Voltage (Vbus)
PI Gain Block
Speed
Control
Mode
0
No Limit
Limit
SW 1
SW 2
SW 3
SW 4
SW 5
Derivative
Gain Block
Jerk
Ramp
Jerk
Clamp
No Limit
PI Gain Block
Derivative Gain
Block
Integ
ra
l Ch
annel
