Rockwell Automation 20B PowerFlex 70, PowerFlex 700 Reference Manual User Manual
Page 30
Analog Inputs
30
Rockwell Automation Publication PFLEX-RM001H-EN-P - June 2013
3.
Multiply by the Volts/Hertz ratio
Therefore the command frequency from 0 to 2.5 volts on the analog input will be
15 Hz. After 2.5 volts, the frequency will increase at a rate of 0.16667 volts per
hertz to 7.5 volts. After 7.5 volts on the analog input the frequency command will
remain at 45 Hertz.
Example 2:
Consider the following setup:
•
[Anlg In Config], bit 0 = “0” (voltage)
•
[Speed Ref A Sel] = “Analog In 1”
•
[Analog In1 Hi] = 10V
•
[Analog In1 Lo] = 0V
•
[Speed Ref A Hi] = 50hz
•
[Speed Ref A Lo] = 0hz
•
[Maximum Speed] = 45hz
•
[Minimum Speed] = 15hz
The only change from Example 1 is the [Speed Ref A Hi] is changed to 50 Hz.
The deadband, as it relates to the analog input, can be calculated as follows:
1.
The ratio of analog input volts to frequency (Volts/Hertz) needs to be
calculated. The voltage span on the analog input is 10 volts. The frequency
span is 60 Hz.
2.
Determine the frequency span between the minimum and maximum speed
limits and the Speed Ref A Hi and Lo.
3.
Multiply by the volts/hertz ratio
15 Hz x 0.16667 Volts/Hz = 2.5 Volts
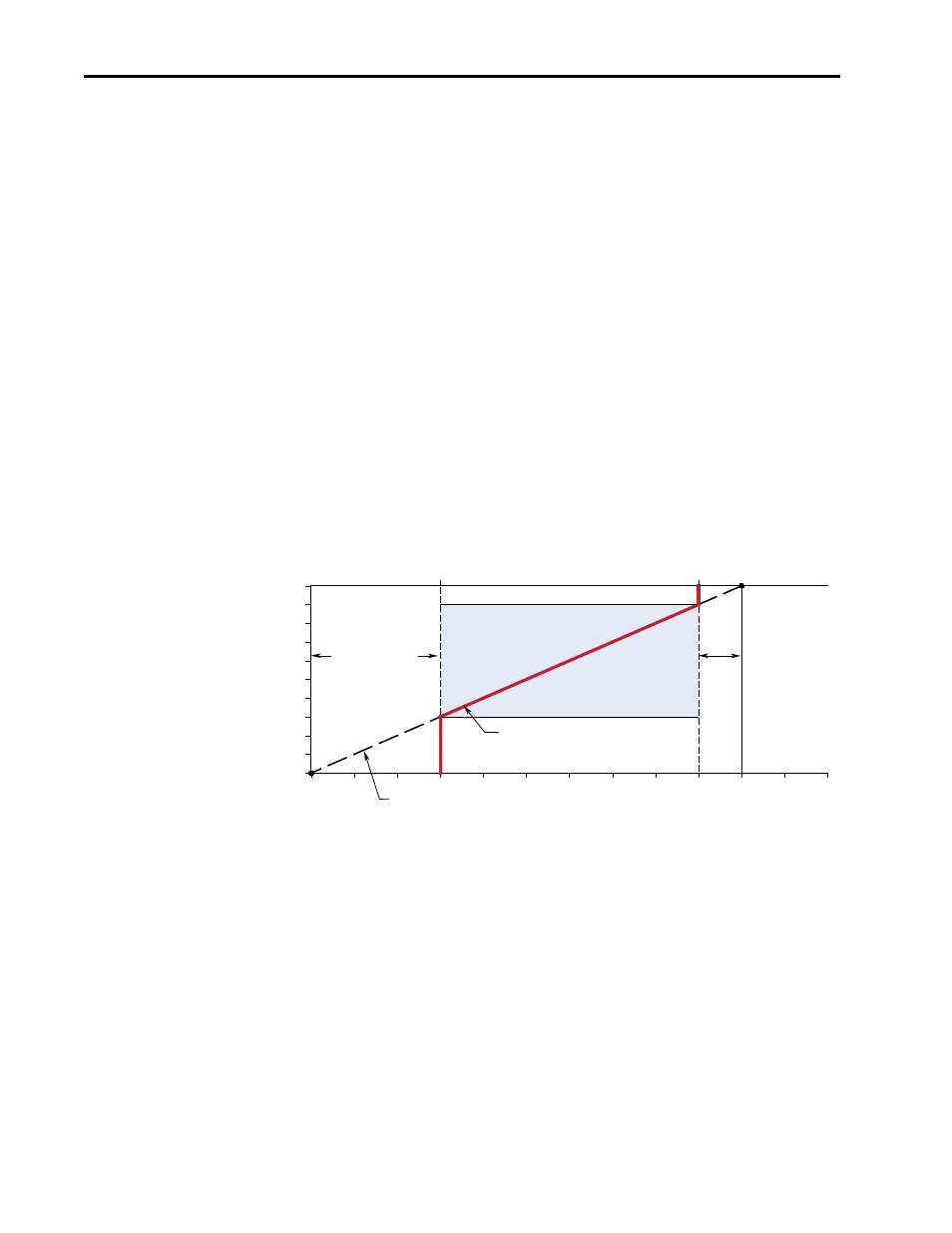
Motor Operating Range
[Maximum Speed]
[Minimum Speed]
Command Frequency
Slope defined by (Analog Volts)/(Command Frequency)
Frequency Deadband
Frequency Deadband
15 Hz
45 Hz
50 Hz
0 Hz
[Speed Ref A Lo]
[Speed Ref A Hi]
10V
0V
[Analog In1 Hi]
[Analog In1 Lo]
0-3 Volts
9-10 Volts
10 Volts/50 Hz = 0.2 Volts/Hz
[Speed Ref A Hi] – [Maximum Speed] = 50 – 45 = 5 Hz and . . .
[Minimum Speed] – [Speed Ref A Lo] = 15 – 0 = 15 Hz
5 Hz x 0.2 Volts/Hz = 1 Volt
15 Hz x 0.2 Volts/Hz = 3 Volts
