Cs42l56 – Cirrus Logic CS42L56 User Manual
Page 12
12
DS851F2
CS42L56
2.2 µF
Note 1
**
Note 2
2.2 µF
Note 1
1 µF
GND/Thermal Pad
VL
0.1 µF
+1.65 V to +3.63 V
RESET
R
p
LRCK
MCLK
SCLK
+VHPFILT
VDFILT
LINEREF
SDIN
SDOUT
Digital Audio
Processor
FLYC
FLYN
-VHPFILT
2.2 µF
2.2 µF
**
**
VCP
LINEOUTA
LINEOUTB
0.1 µF
VA
+1.65 V to +2.75 V
0.1 µF
VLDO
2.2 µF
VQ
AGND
NPO/C0G dielectric capacitors.
1000 pF
AFILTA
AFILTB
1000 pF
2.2 µF
*
*
HPOUTB
HPOUTA
Headphone Out
Left & Right
33
0.1 µF
HPDETECT
33
0.1 µF
47 k
HPREF
FILT+
+1.65 V to +2.75 V
FLYP
2.2 µF
**
**
Note 1
Notes:
1. The headphone amplifier’s output power and distortion are rated using the nominal capacitance shown. Larger capacitance
reduces the ripple on the internal amplifiers’ supplies and in turn reduces the amplifier’s distortion at high output power levels.
Smaller capacitance may not sufficiently reduce ripple to achieve the rated output power and distortion. Since the actual value
of typical X7R/X5R ceramic capacitors deviates from the nominal value by a percentage specified in the manufacturer’s data
sheet, capacitors should be selected based on the minimum output power and maximum distortion required.
2. The headphone amplifier’s output power and distortion are rated using the nominal capacitance shown and using the default
charge pump switching frequency. The required capacitance follows an inverse relationship with the charge pump’s switching
frequency. When increasing the switching frequency, the capacitance may decrease; when lowering the switching frequency,
the capacitance must increase. Since the actual value of typical X7R/X5R ceramic capacitors deviates from the nominal value
by a percentage specified in the manufacturer’s data sheet, capacitors should be selected based on the minimum output
power, maximum distortion and maximum charge pump switching frequency required.
3. Additional bulk capacitance may be added to improve PSRR at low frequencies.
4. These capacitors serve as a charge reservoir for the internal switched capacitor ADC modulators and should be placed as
close as possible to the inputs. They are only needed when the PGA (Programmable Gain Amplifier ) is bypassed.
5. The value of R
L
, a current-limiting resistor used with electret condenser microphones, is dictated by the microphone
cartridge.
6. The negative terminal of the microphone inputs connects to the ground pin of the microphone cartridge. Gain is applied only
to the positive terminal.
Note 3
R
p
*
Low ESR, X7R/X5R dielectric capacitors.
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
562
562
3300 pF
R
ext
R
ext
LPF is Optional
Line Level Out
Left & Right
3300 pF
*
*
SCL\CCLK
SDA\CDIN
MICBIAS
R
L
1 µF
AIN1A
AIN1REF
1 µF
1 µF
Note 5
Note 6
Microphone 1
Microphone 2
R
L
AIN1B
Note 5
Left Analog
Input 2
AIN2A
1800 pF
1800 pF
100 k
100
AIN2B
*
*
1 µF
1 µF
100 k
100
Note 4
**
**
Analog
Input 3
AIN3B
1800 pF
100 k
100
*
1 µF
Note 4
**
Right Analog
Input 2
AD0\CS
TSTN
TSTN
1 µF
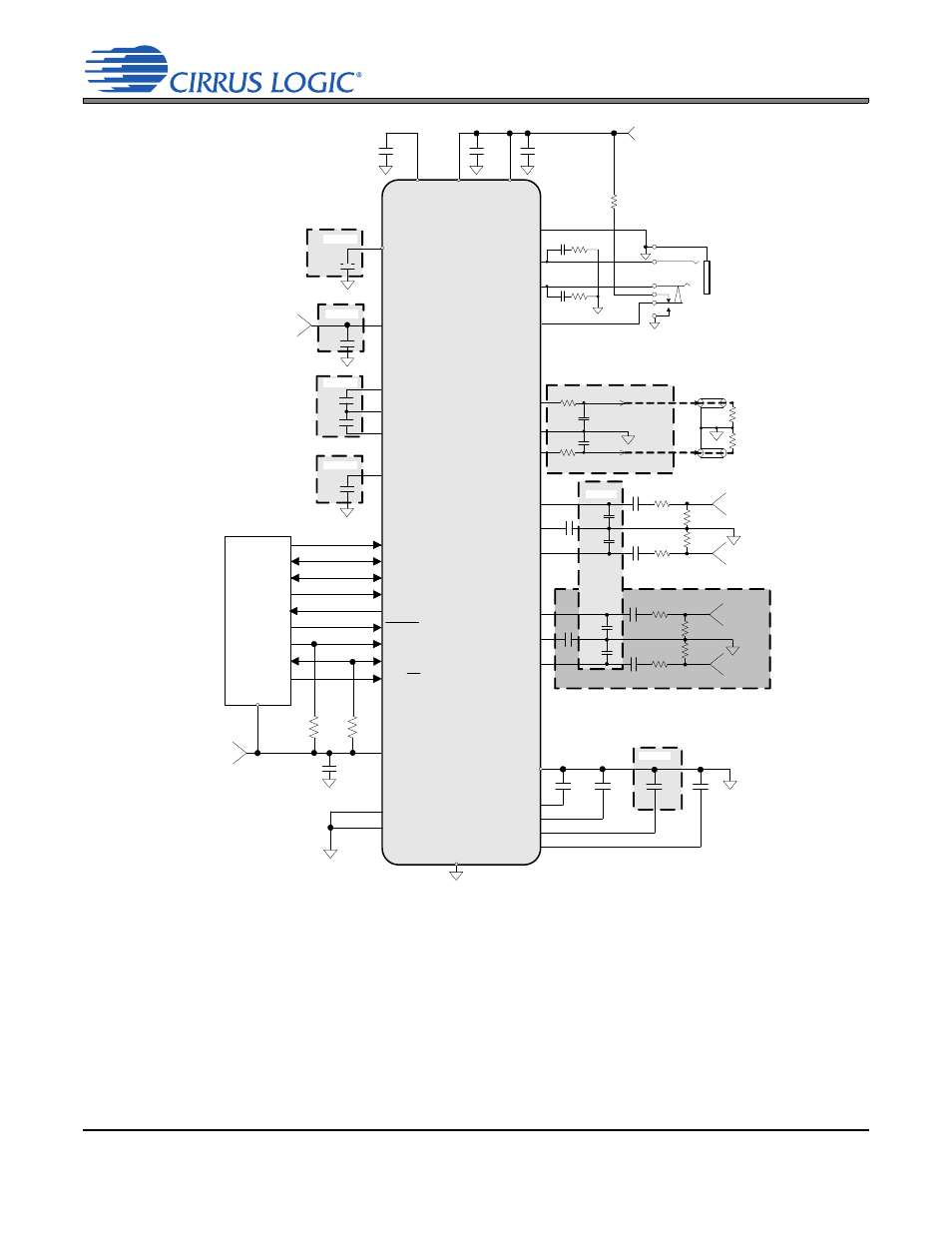
Figure 2. Typical Connection Diagram - Two Pseudo-Differential / Three Single-Ended Analog Inputs
CS42L56
Note 1
Note 2
2.2 µF
Note 1
Analog
Input 1
Analog
Input 2
1 µF
GND/Thermal Pad
VL
0.1 µF
+1.65 V to +3.63 V
RESET
R
p
LRCK
MCLK
SCLK
2.2 µF
+VHPFILT
VDFILT
LINEREF
SDIN
SDOUT
1 µF
AIN2REF
AIN1A
1800 pF
1800 pF
100 k
100
AIN1B
*
*
Digital Audio
Processor
AIN2A
1800 pF
1800 pF
AIN2B
*
*
FLYC
FLYN
-VHPFILT
2.2 µF
1 µF
1 µF
1 µF
1 µF
100 k
100
100
100
100 k
100 k
2.2 µF
**
**
VCP
AIN1REF
1 µF
LINEOUTA
LINEOUTB
0.1 µF
VA
+1.65 V to +2.75 V
0.1 µF
VLDO
2.2 µF
VQ
AGND
NPO /C0G dielectric capacitors.
1000 pF
AFILTA
AFILTB
1000 pF
2.2 µF
*
*
HPOUTB
HPOUTA
Headphone Out
Left & Right
33
0.1 µF
HPDETECT
33
0.1 µF
47 k
HPREF
FILT+
+1.65 V to +2.75 V
FLYP
2.2 µF
**
**
**
Note 1
Notes:
1. The headphone amplifier’s output power and distortion are rated using the nominal capacitance shown. Larger capacitance
reduces the ripple on the internal amplifiers’ supplies and in turn reduces the amplifier’s distortion at high output power levels.
Smaller capacitance may not sufficiently reduce ripple to achieve the rated output power and distortion. Since the actual value
of typical X7R/X 5R ceramic capacitors deviates from the nominal value by a percentage specified in the manufacturer’s data
sheet, capacitors should be selected based on the minimum output power and maximum distortion required.
2. The headphone amplifier’s output power and distortion are rated using the nominal capacitance shown and using the default
charge pump switching frequency. The required capacitance follows an inverse relationship with the charge pump’s switching
frequency. When increasing the switching frequency, the capacitance may decrease; when lowering the switching frequency,
the capacitance must increase. Since the actual value of typical X7R/X5R ceramic capacitors deviates from the nominal value
by a percentage specified in the manufacturer’s data sheet, capacitors should be selected based on the minimum output
power, maximum distortion and maximum charge pump switching frequency required.
3. Additional bulk capacitance may be added to improve PSRR at low frequencies.
4. These capacitors serve as a charge reservoir for the internal switched capacitor ADC modulators and should be placed as
close as possible to the inputs. They are only needed when the PGA (Programmable Gain Amplifier) is bypassed.
Note 4
Note 3
R
p
*
**
Low ESR, X7R/X5R dielectric capacitors.
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
562
562
3300 pF
R
ext
R
ext
LPF is Optional
Line Level Out
Left & Right
3300 pF
*
*
SCL\CCLK
SDA\CDIN
AD0\CS
TSTN
TSTN
Notes:
1. The headphone amplifier’s output power and distortion are rated using the nominal capacitance shown. Larger capacitance reduces the ripple on the internal
amplifiers’ supplies and in turn reduces the amplifier’s distortion at high output power levels. Smaller capacitance may not sufficiently reduce ripple to achieve the
rated output power and distortion. Since the actual value of typical X7R/X5R ceramic capacitors deviates from the nominal value by a percentage specified in the
manufacturer’s data sheet, capacitors should be selected based on the minimum output power and maximum distortion required.
2. The headphone amplifier’s output power and distortion are rated using the nominal capacitance shown and using the default charge pump switching frequency.
The required capacitance follows an inverse relationship with the charge pump’s switching frequency. When increasing the switching frequency, the capacitance
may decrease; when lowering the switching frequency, the capacitance must increase. Since the actual value of typical X7R/X5R ceramic capacitors deviates
from the nominal value by a percentage specified in the manufacturer’s data sheet, capacitors should be selected based on the minimum output power, maximum
distortion and maximum charge pump switching frequency required.
3. Additional bulk capacitance may be added to improve PSRR at low frequencies.
4. These capacitors serve as a charge reservoir for the internal switched capacitor ADC modulators and should be placed as close as possible to the inputs. They
are only needed when the PGA (Programmable Gain Amplifier) is bypassed.
5. The value of R
L
, a current-limiting resistor used with electret condenser microphones, is dictated by the microphone cartridge.
6. The negative terminal of the microphone inputs connects to the ground pin of the microphone cartridge. Gain is applied only to the positive terminal.
