1 process – HP OneView User Manual
Page 117
15 Quick Start: Migrating from an active/standby to an
active/active network configuration
This quick start describes the process of migrating from an existing
to an
for an enclosure.
Prerequisites
•
Minimum required privileges: Infrastructure administrator or Network administrator for adding
networks.
•
Minimum required privileges: Infrastructure administrator or Server administrator for changing
the server profile configurations.
•
Two or more fully supported Virtual Connect interconnect modules as listed in the HP OneView
Support Matrix.
•
Follow recommended naming conventions described in
“Requirements and best practices for
an active/active configuration” (page 148)
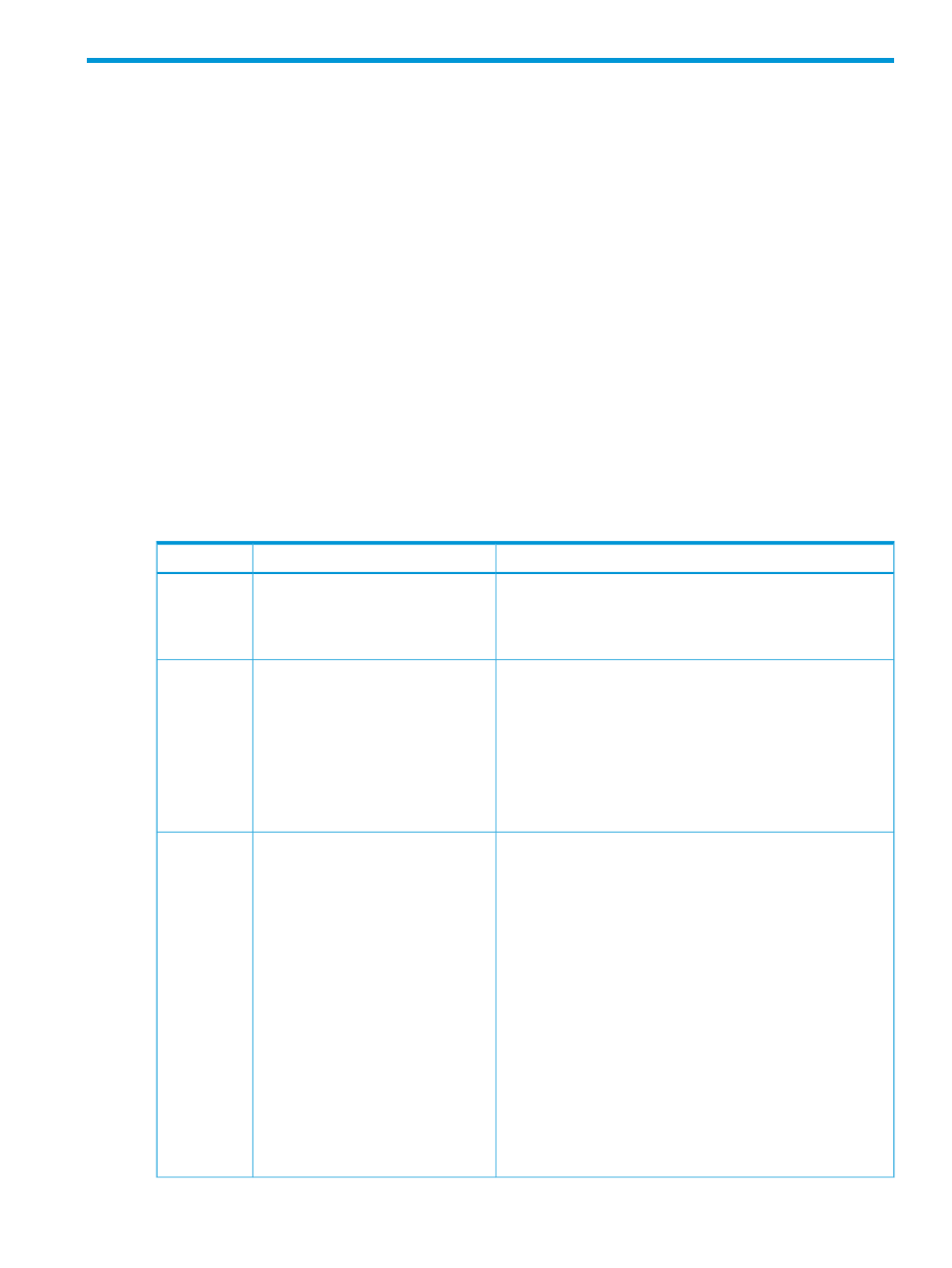
15.1 Process
When migrating from an existing active/standby configuration to an active/active configuration,
make configuration changes to the following resources:
Description
Task
Resource
For more information, see
“Managing interconnects, logical
interconnects, and logical interconnect groups” (page 141)
, the
online help for the Logical Interconnect Groups screen, or the
REST API scripting help for logical interconnect groups.
1.
Find the uplink set that you want to
convert to active/active.
2.
Record all networks within that
uplink set.
Logical
Interconnect
Groups
From the Networks screen:
•
For VLAN ID, enter the same ID as those in the original uplink
set.
•
Make sure Smart Link is selected.
•
For more information about networks, see
networks and network resources” (page 135)
, the online help
for the Networks screen, or the REST API scripting help for
networks and network sets.
3.
Create Ethernet networks with the
same external VLAN ID for each
network identified in Step 1.
4.
Ensure Smart Link is enabled on all
networks in the original uplink set.
Networks
To determine the port status (active or standby), access the
Logical Interconnects screen and review the State of each port
in the Uplink Set view.
•
HP recommends deleting the standby uplinks from the original
uplink set and then adding them to the newly created uplink
set as this method prevents connectivity loss.
If you change the name of an uplink set in Logical
Interconnect Groups and then select Actions
→Update from
group in the Logical Interconnects screen, connectivity is
briefly interrupted.
•
For more information, see
“Managing interconnects, logical
interconnects, and logical interconnect groups” (page 141)
the online help for the Logical Interconnects screen, or the
REST API scripting help for logical interconnects and the REST
API for the uplink-sets resource.
5.
Determine if all logical
interconnects have active and
standby uplink ports on the same
modules.
• If the standby uplinks are on the
same module, go to step 6.
• If the standby uplinks are on
different modules, force a
failover so that all standby
uplinks are on the same module.
Go to step 6.
6.
Edit the active/standby uplink set
and delete the standby uplinks.
7.
Create a second uplink set for the
standby uplinks removed in the
previous step.
8.
Add networks created in step 3 to
the new uplink set.
Logical
Interconnect
Groups and
Logical
Interconnects
15.1 Process
117
