Characteristics of pid controllers, P component – Burkert Type 8635 User Manual
Page 146
144 - 8635
G
ENERAL
R
ULES
(A
PPENDIX
)
A PID controller has a proportional, an integral and a differential component (P, I and D components).
P component
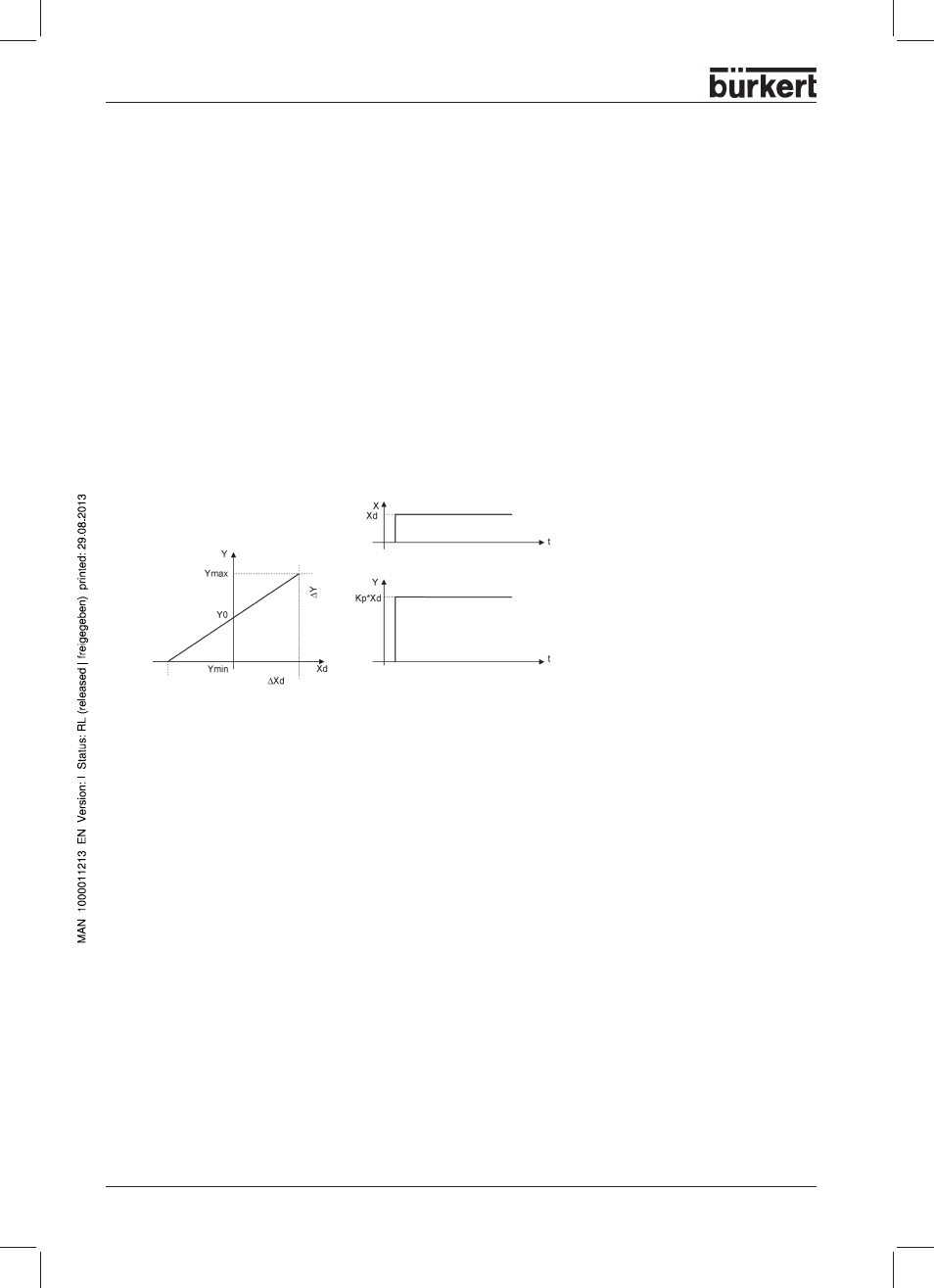
Function: Y = Kp · Xd
Where Kp is the proportional action factor (amplification factor). It is given by the ratio of the correcting
range
∆Y to the proportional range ∆Xd.
Characteristics
A pure P controller works theoretically undamped, i.e. it is fast and dynamically favourable. It has a
residual control difference, i.e. it does not completely eliminate the effects of disturbances and is thus
relatively unfavourable from a static viewpoint.
Characteristics of PID controllers
Characteristic and step response of the P component of a PID controller
Characteristic
Step response
Correcting r
ange
Proportional range
- Type 0125 (15 pages)
- Type 0121 (4 pages)
- Type 0330 (2 pages)
- Type 0331 (4 pages)
- Type 6012 (4 pages)
- Type 0127 (18 pages)
- Type 0131 (5 pages)
- Type 0141 (5 pages)
- Type 0142 (12 pages)
- Type 0145 (3 pages)
- Type 0174 (5 pages)
- Type 0211 (5 pages)
- Type 0212 (2 pages)
- Type 0212-B (18 pages)
- Type 0250 (64 pages)
- Type 0253 (2 pages)
- Type 0355 (2 pages)
- Type 0255 (15 pages)
- Type 0255 (2 pages)
- Type 8640 (55 pages)
- Type 8640 (119 pages)
- Type 8006 (34 pages)
- Type 8640 (2 pages)
- Type 0256 (15 pages)
- Type 0256 (2 pages)
- Type 0258 (72 pages)
- Type 0262 (5 pages)
- Type 0273 (6 pages)
- Type 0280 (5 pages)
- Type 0280 (2 pages)
- Type 0280 (12 pages)
- Type 0281 (2 pages)
- Type 0282 (2 pages)
- Type 0283 (2 pages)
- Type 0286 (4 pages)
- Type 0287 (15 pages)
- Type 0290 (2 pages)
- Type 0290 (14 pages)
- Type 0293 (18 pages)
- Type 0300 (6 pages)
- Type 0301 (6 pages)
- Type 0311 (2 pages)
- Type 0312 (6 pages)
- Type 6519 (4 pages)
- Type 6519 (2 pages)
