Extron Electronics VN-Matrix 250 User Guide User Manual
Page 57
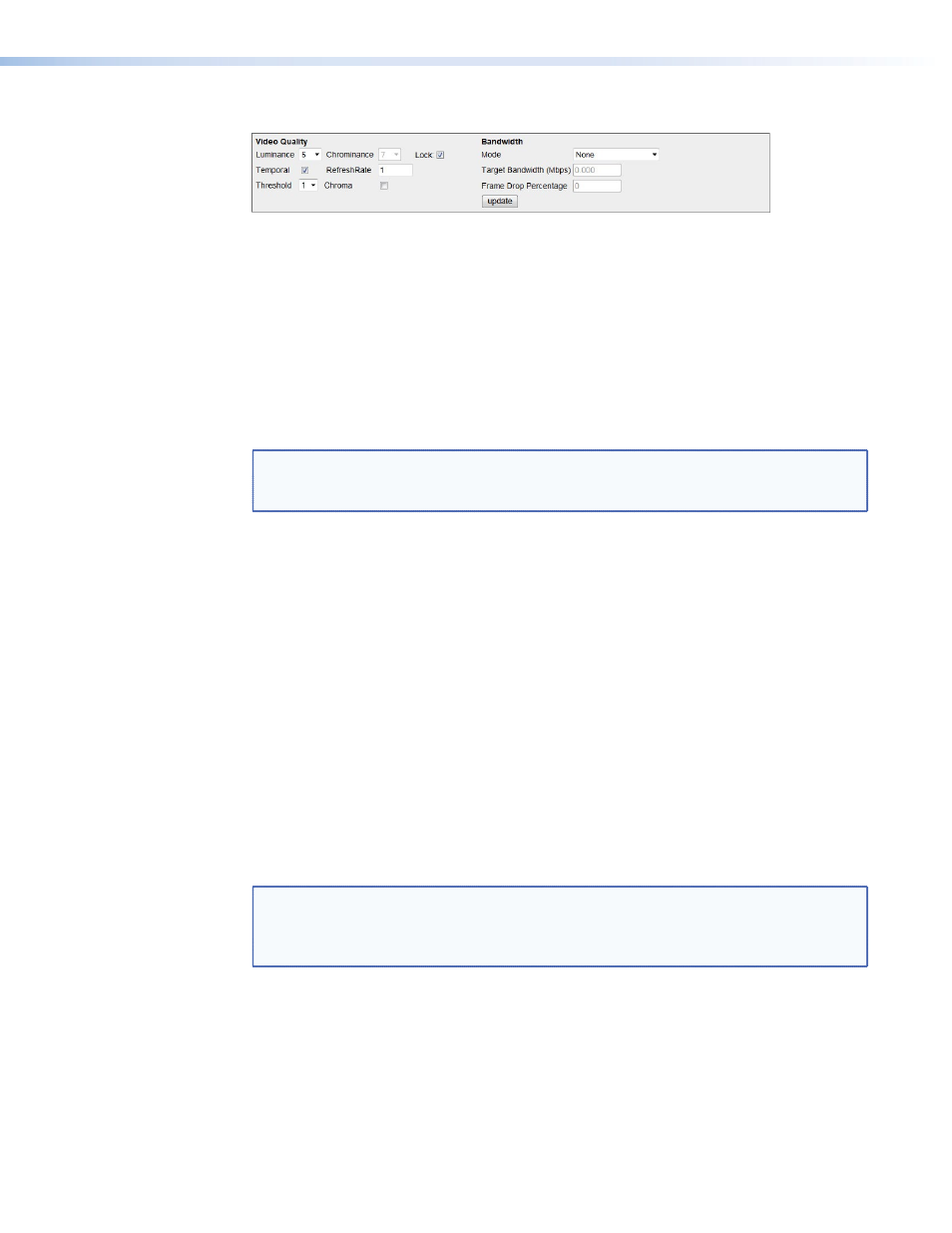
Bandwidth Panel
Figure 35.
Bandwidth Tab: Video Quality and Bandwidth Panel
The VNE 250 can apply various control modes to manage the bit rate. These control modes
are selected in the
Mode
drop‑down list.
None
— no bandwidth management policy is followed apart from the underlying
compression settings.
Manual Frame Drop
— allows the user to specify the precise fraction of frames to drop.
This doesn't manage the average bandwidth at a fixed level, but does result in a smoother
update during rapidly changing video content types. Enter the percentage of frames to
discard in the
Frame Drop Percentage
field. For example, a value of 95 (95%) discards 19
out of every 20 frames, reducing a 60 frames per second (fps) video signal to 3 fps.
NOTE: Slowing the frame rate to 1 fps may cause the decoder to behave as if the
source stream has been interrupted and it may flash up the "No Source" splash
screen.
Shared Flow rate
— limits the total network video traffic for all streams from this source
to the flow rate (in Mbps) specified in the
Target Bandwidth
field. Frames are dropped if
the instantaneous data rate is higher than the flow rate.
Peak Flow rate
— limits the network video‑traffic for a single stream from this source
to the flow rate specified in the
Target Bandwidth
field. Frames are dropped if the
instantaneous data rate is higher than the flow rate.
PBR-F
— Dynamically modifies the compression settings to limit the transmit bandwidth
to the specified rate or below. The specified compression setting is used as the minimum
compression value. The filter averages the bit rate over a period of 1 second.
PBR-F (FD)
‑ Same as
PBR-F
except frames are dropped when a larger reduction than can
be achieved with just compression settings is required.
Flow rate control modes (shared flow rate and peak flow rate modes) limit the instantaneous
traffic on the network and are useful where the network pipe between source and display
has limited bandwidth and drops traffic when this rate is exceeded. Non‑flow rate control
modes (none, manual frame drop, PBR‑F, and PBR‑F (FD) limit the average bandwidth, but
the instantaneous bandwidth can be high. Non‑flowrate control modes are best used on a
LAN where the user does not wish the VNE 250 to consume excess bandwidth.
NOTE: The actual bandwidth usage for unicast transports is multiplied by the number
of data stream destinations. For example, if the encoder has two unicast RTP
connections plus a TCP connection, it sends three data streams across the network
and requires bandwidth for each stream.
VNM 250 • VNM 250 GUI Overview
51
