1 fp (nmi) interrupt – next steps, Fp (nmi) interrupt, Next steps – Kontron S4600 SEL Troubleshooting User Manual
Page 109
System Event Log Troubleshooting Guide for EPSD
Platforms Based on Intel
®
Xeon
®
Processor E5 4600/2600/2400/1600/1400 Product Families
Chassis Subsystem
Revision 1.1
Intel order number G90620-002
99
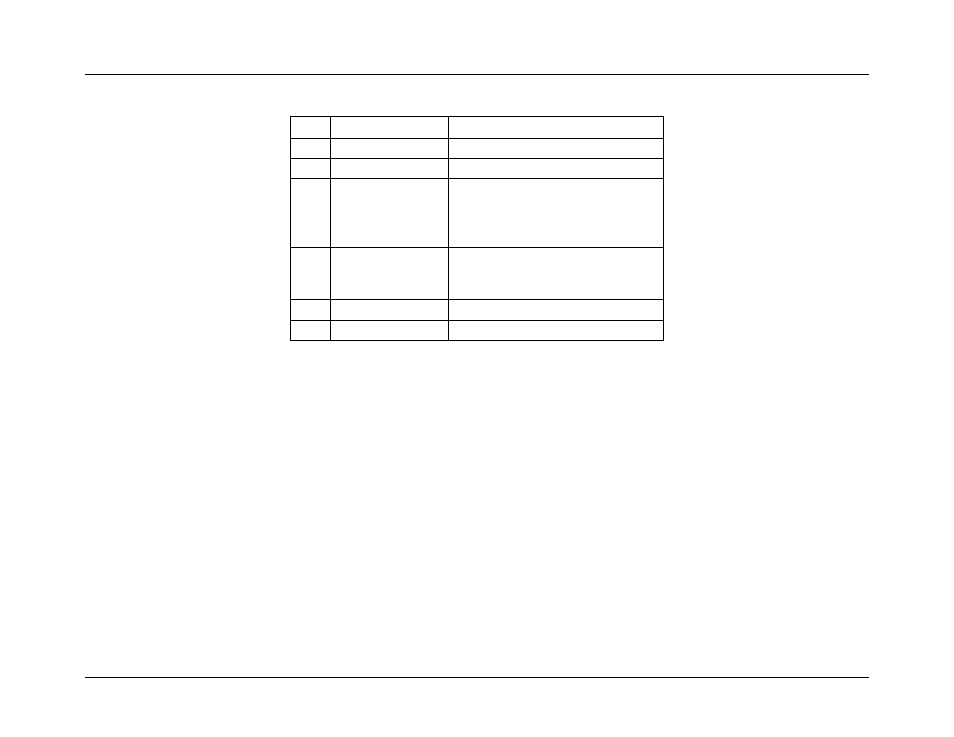
Table 75: FP (NMI) Interrupt Sensor Typical Characteristics
Byte
Field
Description
11
Sensor Type
13h = Critical Interrupt
12
Sensor Number
05h
13
Event Direction and
Event Type
[7] Event direction
0b = Assertion Event
1b = Deassertion Event
[6:0] Event Type = 6Fh (Sensor Specific)
14
Event Data 1
[7:6]
– 00b = Unspecified Event Data 2
[5:4]
– 00b = Unspecified Event Data 3
[3:0]
– Event Trigger Offset =0h
15
Event Data 2
Not used
16
Event Data 3
Not used
10.2.1
FP (NMI) Interrupt – Next Steps
The purpose of this button is for diagnosing software issues
– when a critical interrupt is generated the OS typically saves a memory
dump. This allows for exact analysis of what is going on in system memory, which can be useful for software developers, or for
troubleshooting OS, software, and driver issues.
If this button was not actually pressed, you should ensure there is no physical fault with the front panel.
This event only gets logged if a user pressed the NMI button or sent an IPMI Chassis Control command requesting this action, and
although it causes the OS to crash, is not an error.
