Additional statistics, 267 additional statistics – Apple iWork '09 User Manual
Page 267
Chapter 10
Statistical Functions
267
Additional Statistics
This section discusses the additional statistics that can be returned by the LINEST
function.
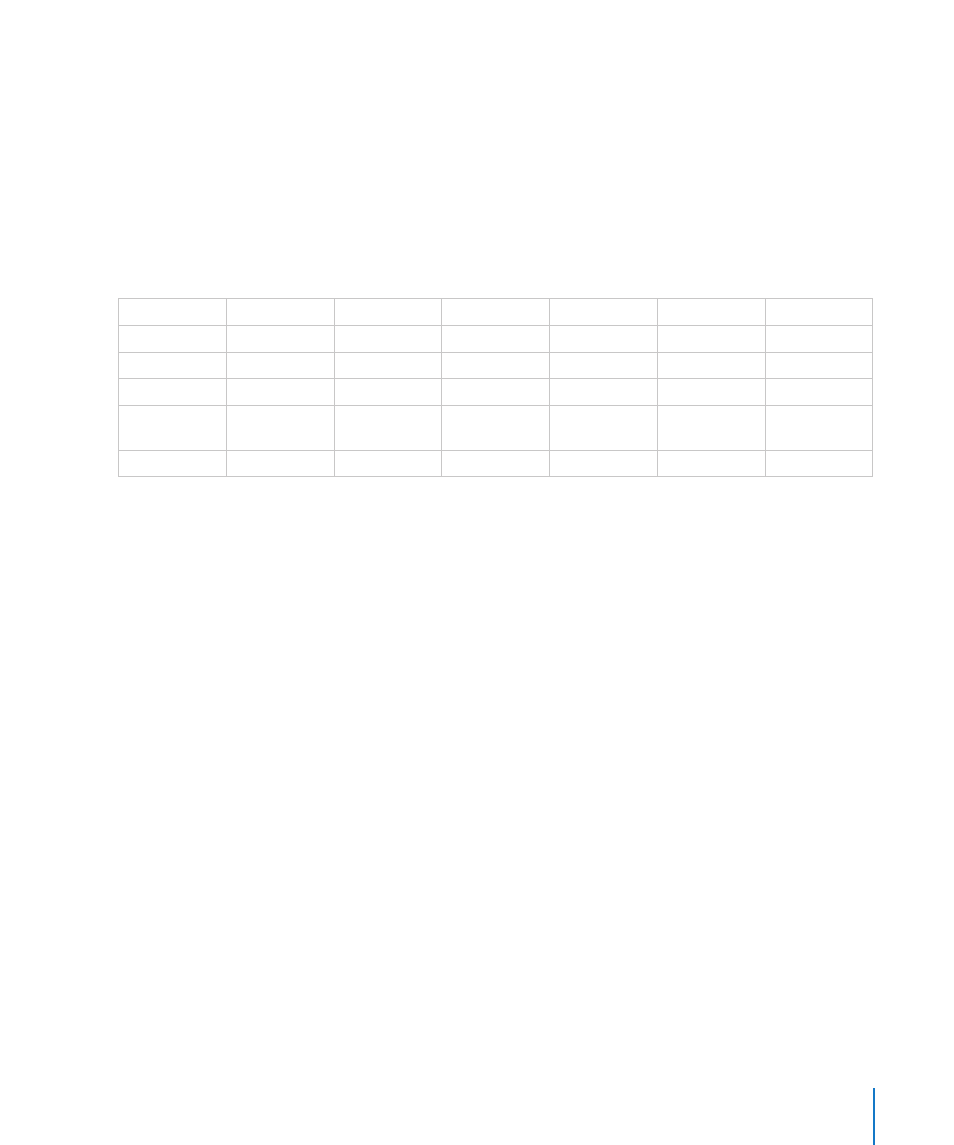
LINEST can include additional statistical information in the array returned by the
function. For purposes of the following discussion, assume that there are five sets of
known x values, in addition to the known y values. Assume further that the known
x values are in five table rows or five table columns. Based on these assumptions,
the array returned by LINEST would be as follows (where the number following an x
indicates which set of x values the item refers to):
Row/Column
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
slope x5
slope x4
slope x3
slope x2
slope x1
b (y intercept)
2
std-err x1
std-err x2
std-err x3
std-err x4
std-err x5
std-err b
3
coefficient-det
std-err y
4
F-stat
degrees-of-
freedom
5
reg-ss
reside-ss
Argument definitions
slope x: The slope of the line related to this set of known x values. The values are
returned in reverse order; that is, if there are five known x value sets, the value for the
fifth set is first in the returned array.
b: The y intercept for the known x values.
std-err x: The standard error for the coefficient associated with this set of known x
values. The values are returned in order; that is, if there are five known x value sets, the
value for the first set is returned first in the array. This is the opposite of the way the
slope values are returned.
std-err b: The standard error associated with the y-intercept value (b).
coefficient-det: The coefficient of determination. This statistic compares estimated and
actual y values. If it is 1, there is no difference between the estimated y value and the
actual y value. This is known as perfect correlation. If the coefficient of determination is
0, there is no correlation and the given regression equation is not helpful in predicting
a y value.
std-err y: The standard error associated with the y value estimate.
F-stat: The F observed value. The F observed value can be used to help determine
whether the observed relationship between the dependent and independent
variables occurs by chance.
degrees-of-freedom: The degrees of freedom. Use the degrees of freedom statistic to
help determine a confidence level.
