HP 50g Graphing Calculator User Manual
Page 607
Page 18-40
values
⎯x
1
and
⎯x
2
, and standard deviations s
1
and s
2
. If the populations
standard deviations corresponding to the samples,
σ
1
and
σ
2
, are known, or if
n
1
> 30 and n
2
> 30 (large samples), the test statistic to be used is
If n
1
< 30 or n
2
< 30 (at least one small sample), use the following test statistic:
Two-sided hypothesis
If the alternative hypothesis is a two-sided hypothesis, i.e., H
1
:
μ
1
-
μ
2
≠ δ, The P-
value for this test is calculated as
Θ If using z,
P-value = 2
⋅UTPN(0,1, |z
o
|)
Θ If using t,
P-value = 2
⋅UTPT(ν,|t
o
|)
with the degrees of freedom for the t-distribution given by
ν = n
1
+ n
2
- 2. The
test criteria are
Θ Reject H
o
if P-value <
α
Θ Do not reject H
o
if P-value >
α.
One-sided hypothesis
If the alternative hypothesis is a two-sided hypothesis, i.e., H
1
:
μ
1
-
μ
2
<
δ, or,
H
1
:
μ
1
-
μ
2
<
δ,, the P-value for this test is calculated as:
Θ If using z,
P-value = UTPN(0,1, |z
o
|)
Θ If using t,
P-value = UTPT(
ν,|t
o
|)
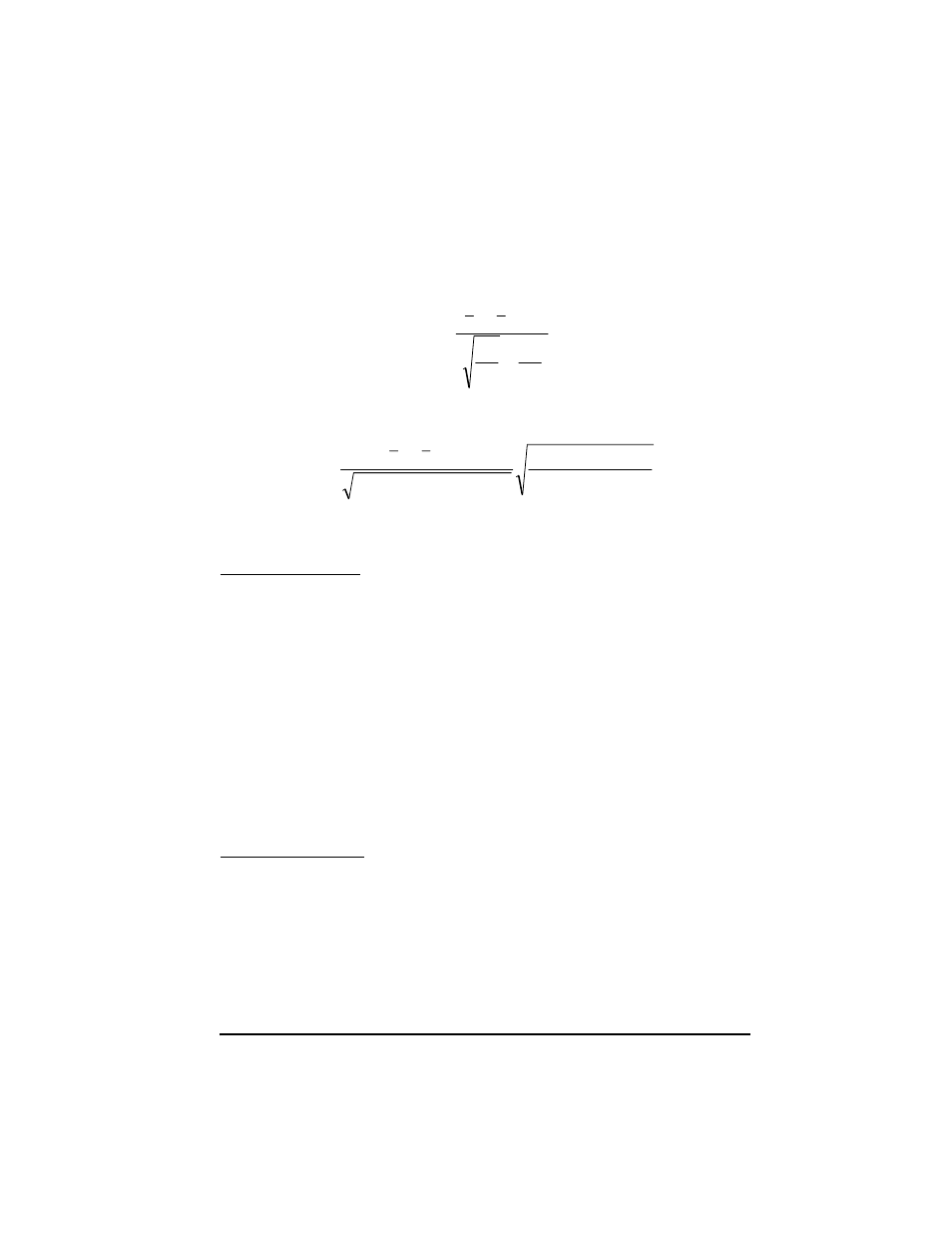
2
2
2
1
2
1
2
1
)
(
n
n
x
x
z
o
σ
σ
δ
+
−
−
=
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
2
2
2
1
1
2
1
)
2
(
)
1
(
)
1
(
)
(
n
n
n
n
n
n
s
n
s
n
x
x
t
+
−
+
−
+
−
−
−
=
δ
