Table 4 – HP StorageWorks XP Remote Web Console Software User Manual
Page 29
Continuous Access XP Journal user guide
29
primary disk array or secondary disk array changes the status of the primary and secondary data volumes
to PSUS (if the path status is normal). When a pair is split from the secondary disk array, the secondary
disk array changes the secondary data volume’s status to PSUS, and the primary disk array detects the
pair deletion (if path status is normal) and changes the primary data volume’s status to PSUS. When a pair
is deleted from the primary disk array, the primary disk array changes the status of both data volumes to
SMPL. When a pair is deleted from the secondary disk array, the secondary disk array changes the
secondary data volume’s status to SMPL, and the primary disk array detects the pair deletion (if path status
is normal) and changes the primary data volume’s status to PSUS.
When a Continuous Access XP Journal data volume pair is split or suspended, the primary disk array
generates a service information message (SIM) to notify the hosts. If SNMP is installed and operational for
Command View XP or XP Remote Web Console, this SIM results in an SNMP trap indicating the reason for
the suspension.
•
Continuous Access XP Journal pair status
The Continuous Access XP Journal Suspending and Deleting transitional states occur when a request to
change Continuous Access XP Journal pair status has been accepted, but the requested status change
(PSUS, PSUE, or SMPL) is not complete yet. These states are not reported to the host. For Suspending,
either you or the primary disk array can request the status change. For Deleting, only you can request
the status change. If you requested the status change, the final status is reported at the end of the
transition. If an error caused the status to change to PSUE, the suspended status is reported at the
beginning of the transition.
After a disk array receives a request to split or delete a pair in Flush mode, the status of the pair
remains Suspending or Deleting until the journal in the master journal group is restored in the restore
journal group and the pair is completely split or deleted. To calculate the time during which the pair
remains Suspending or Deleting, use the following equation:
C
×
(u
ч
100)
Ч
1,024
ч
V
where:
• C is the total capacity (in megabytes) of the master journal volume.
• u is the data usage rate (as a percentage) in the master journal volume.
• V is the data transfer speed between the primary and secondary disk array. The unit is MB/s
(megabytes per second).
To find the usage rate of a journal volume, use the monitoring feature (see ”
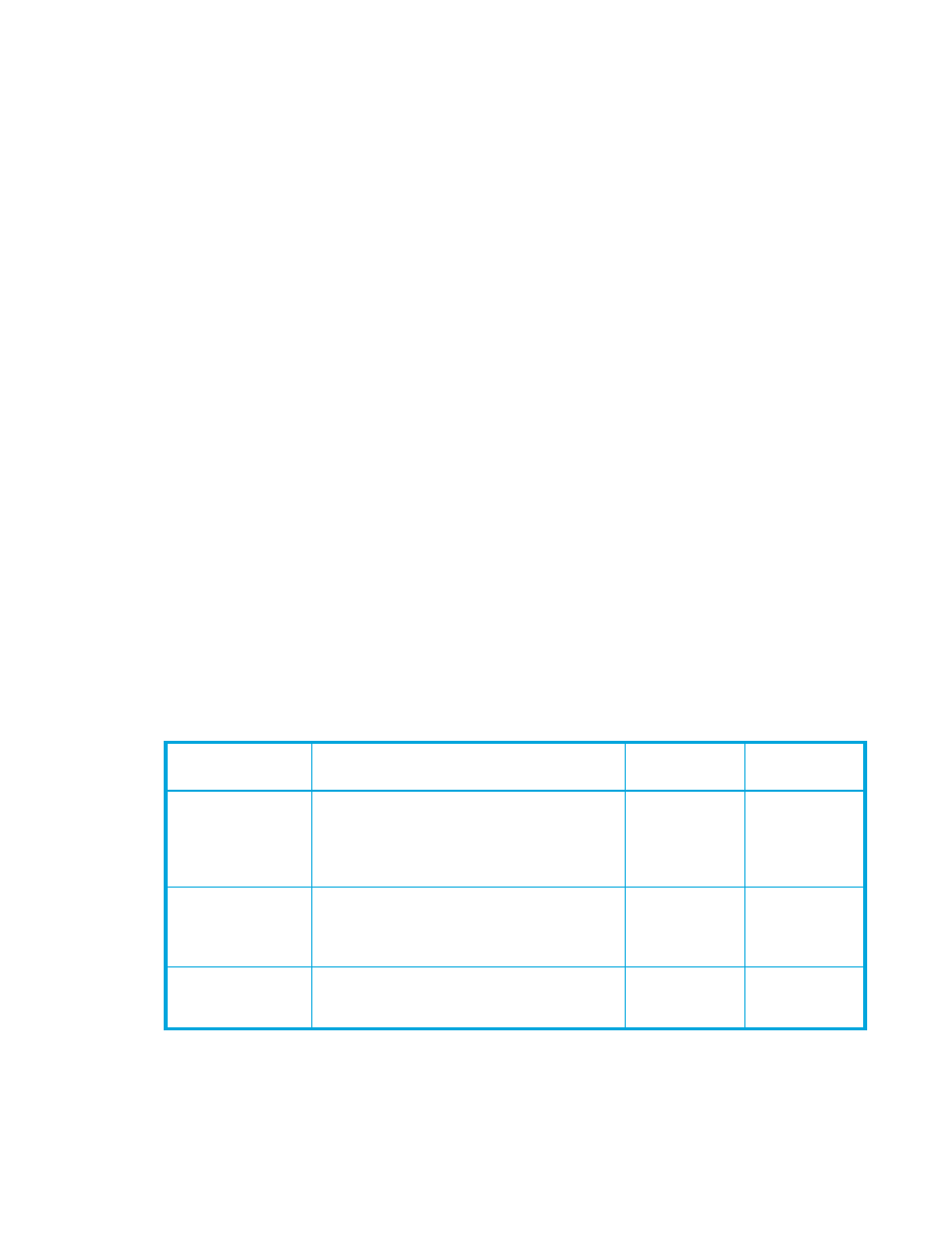
Table 4
Continuous Access XP Journal data volume pair status
Pair status
Description
Primary data
volume access
Secondary data
volume access
SMPL (simplex)
Volume is not currently assigned to a Continuous
Access XP Journal data volume pair and does not
belong in the journal group. When this volume is
added to a Continuous Access XP Journal data
volume pair, its status changes to COPY.
Read / Write
Read / Write
COPY
Initial copy operation for pair is in progress. Data
volume pair is not yet synchronized. When the
initial copy is complete, the status changes to
PAIR.
Read / Write
Read Only
PAIR
Data volume pair is synchronized. Updates to the
primary data volume are duplicated on the
secondary data volume.
Read / Write
Read Only
