Journal types, Inflow control for journal cache, Figure 6 – HP StorageWorks XP Remote Web Console Software User Manual
Page 27
Continuous Access XP Journal user guide
27
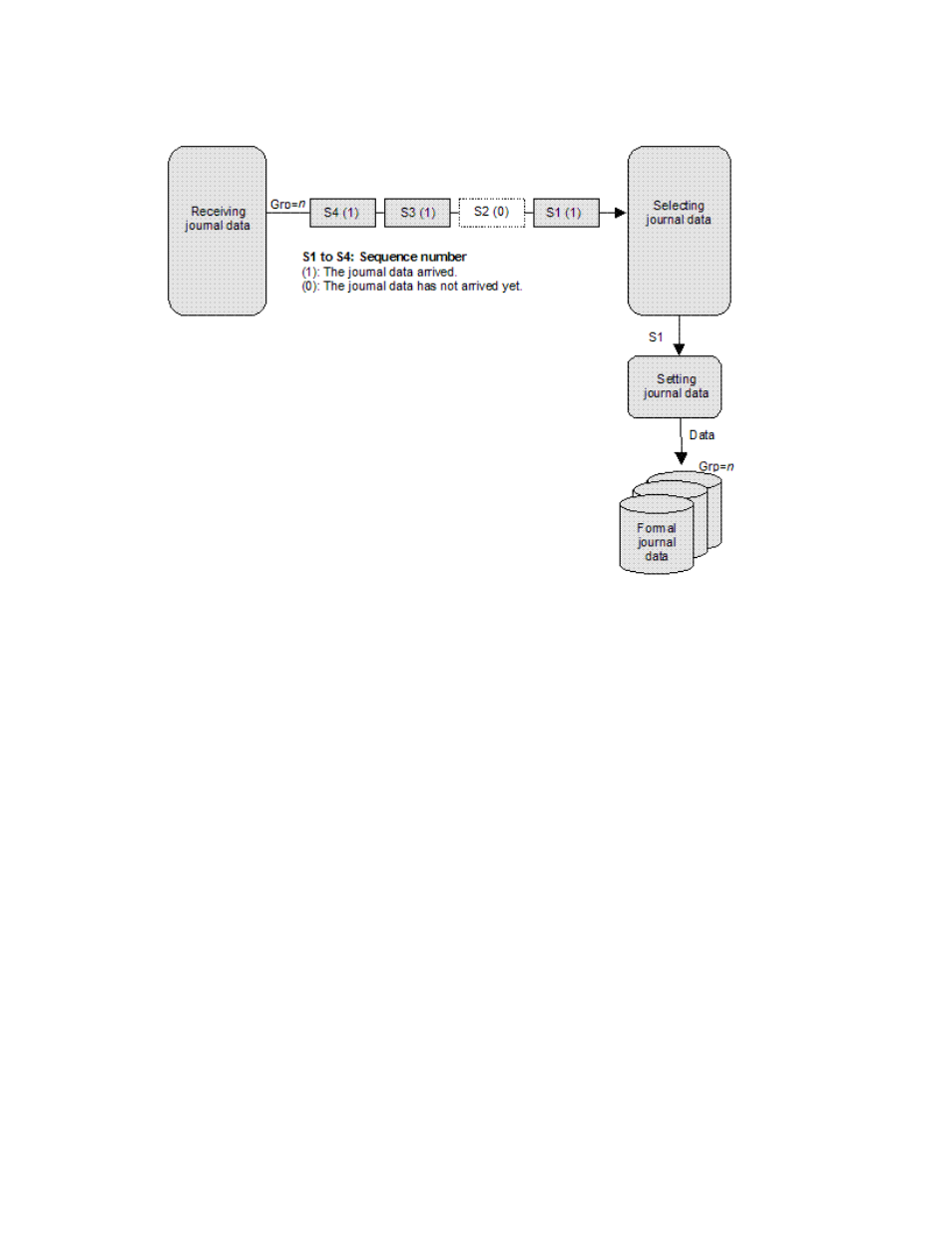
not arrived yet. The management information of journal data S2 is 0. The secondary disk array waits for
journal data S2. When journal data S2 arrives, the secondary disk array selects S2 as the next journal
data to be settled. The journal data the secondary disk array selects is marked as “host-dirty” and treated
as formal data.
Figure 6
Selecting and settling journal at secondary disk array
The secondary disk array settles and restores journal data to the secondary data volume as follows:
•
Journal data stored in cache
Journal data is copied to the corresponding cached track and promoted to format data.
•
Journal data stored in the restore journal volume
Journal data is read from the restore journal volume to cache. Journal data that is read to cache is
copied to the existing cache track and promoted to formal data. After that, the space for the restore
journal volume is released.
Journal types
In addition to journal data for updating, the primary disk array sends control information to the secondary
disk array. This control information indicates when volume pair status changes and when a primary disk
array power-off sequence is initiated, and maintains sequence numbers in periods of low host activities.
Inflow control for journal cache
You can use Continuous Access XP Journal to specify the usage rate of journal cache, which is used for
Continuous Access XP Journal processing. Journal cache stores journal data to be transferred to the
secondary disk array asynchronously with host write I/Os to primary data volumes. Usually, journal data is
stored in journal volumes before journal cache becomes full. If hosts transfer excessively increasing
amounts of data, journal cache might become full. If journal cache remains full for a specified time period,
the journal group is suspended due to a failure. You can specify the time period using the Cache Overflow
Watch option.
The disk array uses the following parameters to control data inflow into journal cache:
•
Journal cache capacity: Indicates maximum usage rate for cache that can be used for Continuous
Access XP Journal processing and is installed in the primary or secondary disk array. This parameter
can be 0 to 50 percent for primary disk arrays, and 0 to 100 percent for secondary disk arrays.
