High voltage module, M series service manual – ZOLL M Series Defibrillator Rev R User Manual
Page 132
M Series Service Manual
122
as data protection and virtual memory functions. It also has a timer, a real time clock, an interrupt controller, a serial
communication interface (SCI), and other peripheral functions necessary for the system operation. The memory
circuitry includes Flash ROM, internal flash non-volatile memory and DRAM.
The EPU acquires ECG data and runs the A/D convertor that sends data in the form of a serial stream to the CPU.
High Voltage Module
The High Voltage (HV) module includes the high voltage circuitry required for pacing and defibrillation, including the
defib charge circuitry, solid state patient relay, safety relay, defib capacitor, defib choke and front end protection
circuitry for the MFC ECG. There are two different types of HV Modules: a damped sinusoidal waveform HV module
and a Biphasic (HV) module.
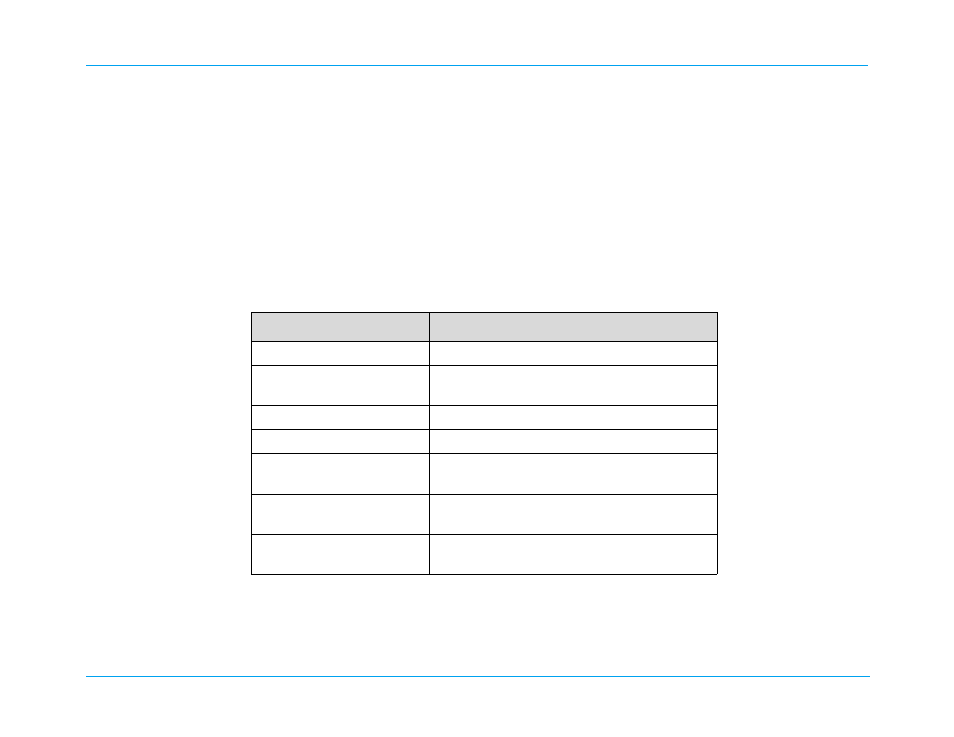
The following table describes the high voltage board components:
Component
Function
Solid State Patient Relay
Controls the delivery of therapeutic energy to patient.
Safety Relay
Discharges Defib capacitor into the internal discharge
resistor when defibrillator is not in use.
Defibrillator Capacitor
Stores energy for therapy.
Defibrillator Choke
Conditions waveform delivered to the patient.(DSW)
Front End Protection Circuitry for
the MFC ECG
Protects ECG front end against defibrillator pulses.
Monophasic HV
Provides damped sinusoidal waveform therapeutic
energy. (Monophasic units only.)
Biphasic HV
Provides biphasic waveform therapeutic energy.
(Biphasic units only.)
