I2c interface, Figure 39. block diagram of the i2c bus serial i/o, Table 50. serial control register (s2con) – ST & T UPSD3212C User Manual
Page 72: C interface
uPSD3212A, uPSD3212C, uPSD3212CV
72/163
I
2
C INTERFACE
The serial port supports the twin line I
2
C-bus, con-
sisting of a data line (SDA1), and a clock line
(SCL1) as shown in Figure
. Depending on the
configuration, the SDA1 and SCL1 lines may re-
quire pull-up resistors.
These lines also function as I/O port lines if the I
2
C
bus is not enabled.
The system is unique because data transport,
clock generation, address recognition, and bus
control arbitration are all controlled by hardware.
The I
2
C serial I/O has complete autonomy in byte
handling and operates in 4 modes.
■
Master transmitter
■
Master receiver
■
Slave transmitter
■
Slave receiver
These functions are controlled by the SFRs (see
Tables
,
, and
–
S2CON: the control of byte handling and the
operation of 4 mode.
–
S2STA: the contents of its register may also
be used as a vector to various service
routines.
–
S2DAT: data shift register.
–
S2ADR: slave address register. Slave
address recognition is performed by On-Chip
H/W.
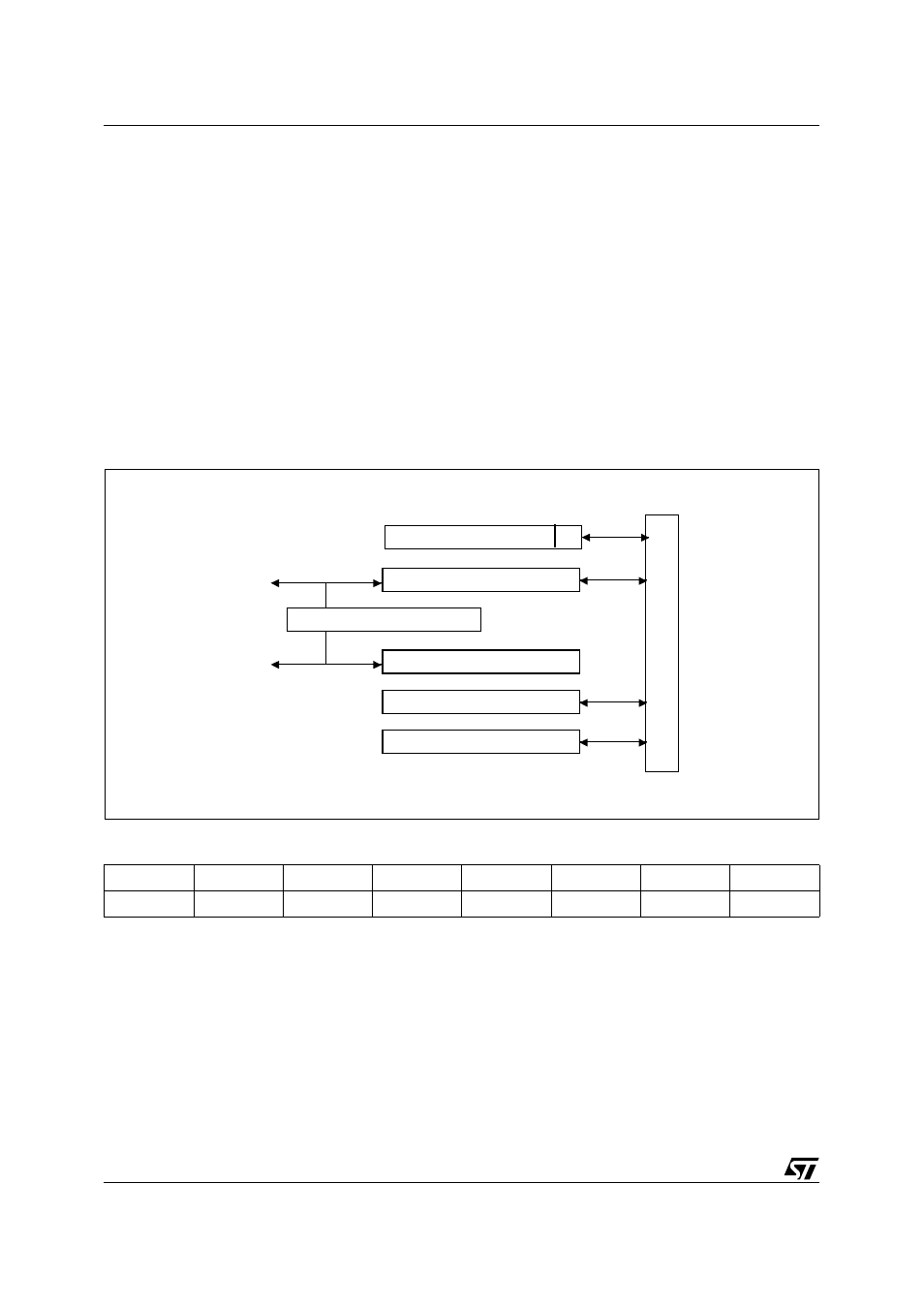
Figure 39. Block Diagram of the I
2
C Bus Serial I/O
Table 50. Serial Control Register (S2CON)
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
CR2
ENII
STA
STO
ADDR
AA
CR1
CR0
AI07430
SCL1
SDA1
Bus Clock Generator
Arbitration and Sync. Logic
Shift Register
Status Register
7
0
Slave Address
7
0
Control Register
7
0
7
0
Internal Bus
